Big Basket interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Big Basket
3 rounds | 3 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, Operating Systems, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date12 Oct 2016
Coding problem0
This was mainly an aptitude round where the questions ranged from easy to medium . More than 20 correct questions was sufficient to pass this round .
02
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date13 Oct 2016
Coding problem2
This round was purely based on Data Structures and Algorithms . One has to be fairly comfortable in solving Algorithmic problems to pass this round . Both the questions asked were quite common and luckily I had already prepared them from CodeStudio and LeetCode.
1. Tree Traversals
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of 'N'
nodes, where the nodes have integer values.
Your task is to return the ln-Order, Pre-Order, and Post-Order traversals of the given binary tree.
For example :
For the given binary tree:
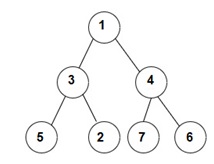
The Inorder traversal will be [5, 3, 2, 1, 7, 4, 6].
The Preorder traversal will be [1, 3, 5, 2, 4, 7, 6].
The Postorder traversal will be [5, 2, 3, 7, 6, 4, 1].
Problem approach
Iterative Inorder Traversal (Using Stack ) :
1) Create an empty stack S.
2) Initialize current node as root.
3) Push the current node to S and set root=root->left until root is NULL
4) If root is NULL and stack is not empty then
a) Pop the top item from stack.
b) Print the popped item, set root = root->right
c) Go to step 3.
5) If root is NULL and stack is empty then we are done.
Time Complexity : O(n)
Space Complexity : O(n)
Recursive Inorder Traversal :
1) Initialise a global vector "answer" which will store the final inorder traversal of our BST
2) Create a recursive function(say void Inorder(TreeNode*root)) passing the root node as its initial paramter.
3) Base Case : If we encounter a NULL node i.e. root==NULL , then simply return from the function
4)Traverse the left subtree, i.e., call Inorder(root->left)
5)Visit the root. i.e. , push root->val into ans.
6)Traverse the right subtree, i.e., call Inorder(root->right)
Time Complexity : O(n)
Space Complexity : O(n)
2. Reverse Linked List
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. You need to reverse the Linked List by changing the links between nodes.
Note :
You do not need to print anything, just return the head of the reversed linked list.
Problem approach
Iterative(Without using stack):
1) Initialize three pointers prev as NULL, curr as head and next as NULL.
2) Iterate through the linked list. In loop, do following.
// Before changing next of current,
// store next node
next = curr->next
// Now change next of current
// This is where actual reversing happens
curr->next = prev
// Move prev and curr one step forward
prev = curr
curr = next
3)Finally the prev pointer contains our head , i,e. ,head=prev .
TC : O(n)
SC: O(1)
Recursive:
1) Divide the list in two parts - first node and rest of the linked list.
2) Call reverse for the rest of the linked list.
3) Link rest to first.
4) Fix head pointer
TC:O(n)
SC:O(n)
Iterative(Using Stack):
1) Store the nodes(values and address) in the stack until all the values are entered.
2) Once all entries are done, Update the Head pointer to the last location(i.e the last value).
3) Start popping the nodes(value and address) and store them in the same order until the stack is empty.
4) Update the next pointer of last Node in the stack by NULL.
TC: O(n)
SC:O(n)
03
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration45 Minutes
Interview date14 Oct 2016
Coding problem1
This round basically tested some concepts from Data Structures and File Manipulation .
1. Intersection Of Two Arrays
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given two arrays 'A' and 'B' of size 'N' and 'M' respectively. Both these arrays are sorted in non-decreasing order. You have to find the intersection of these two arrays.
Intersection of two arrays is an array that consists of all the common elements occurring in both arrays.
Note :
1. The length of each array is greater than zero.
2. Both the arrays are sorted in non-decreasing order.
3. The output should be in the order of elements that occur in the original arrays.
4. If there is no intersection present then return an empty array.
Problem approach
Union :
1) Initialize an empty hash set or hash map mp;
2) Iterate through the first array and put every element of the first array in the set mp.
3) Repeat the process for the second array.
4) Print the set mp.
Intersection:
1) Initialize an empty set mp.
2) Iterate through the first array and put every element of the first array in the set mp.
3) For every element x of the second array, do the following :
Search x in the set mp. If x is present, then print it.
Time complexity : O(m+n) under the assumption that hash table search and insert operations take O(1) time.
Space complexity : O(m+n) in case of Union and O(min(m,n)) in case of Intersection

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Big Basket
0 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6544 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes









