Grofers interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
Data Analyst
Grofers
4 rounds | 8 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
I developed skills in data manipulation, visualization, and statistical analysis. Starting with smaller projects, I gained practical experience and gradually took on more challenging assignments. I've worked in diverse industries, honing my domain expertise. I stay updated with the latest trends and continuously learn to stay at the forefront of the field. Effective communication and collaboration have been crucial in contributing to data-driven decision-making. I'm excited to take on more complex projects and make a positive impact through data analysis.
Application story
The company arrived at my college and contacted the placement cell. Subsequently, the placement cell conducted all the application procedures, including detailed verifications and eligibility checks.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
Technical Skills: Strong proficiency in data analysis tools, programming languages like SQL and Python, data visualization platforms, and statistical analysis techniques.
Relevant Experience: Previous work experience and data analysis projects align well with the requirements of the Data Analyst position.
Communication Skills: Ability to effectively communicate complex data findings to non-technical stakeholders.
Preparation
Duration: 5 months
Topics: Data Manipulation and SQL, Data Visualization, Statistical Analysis, Python, Data Cleaning and Preprocessing, Database Management
Tip
Tip 1: Practice Problem-Solving - Data Analysts are problem solvers. Practice working on analytical puzzles and case studies to improve your problem-solving abilities.
Tip 2: Gain Domain Knowledge - If you're aiming for a specific industry or domain, familiarize yourself with the key metrics, challenges, and trends relevant to that field. Domain knowledge enhances the value of your analysis.
Tip 3: Learn Data Visualization - Practice creating clear and insightful data visualizations using tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Python libraries like Matplotlib and seaborn. Visualizations are essential for effectively conveying findings to stakeholders.
Tip 4: Master Data Analysis Tools - Become proficient in data analysis tools such as SQL for data manipulation and retrieval, Excel for data cleaning and basic analysis, and a programming language like Python or R for advanced data analysis and visualization.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: 7.5 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1: Data Projects: Include relevant personal or academic data analysis projects.
Tip 2: Relevant Skills: Highlight data analysis tools and languages you're proficient in.
Tip 3: Keywords and ATS: Optimize your resume with relevant keywords for applicant tracking systems.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration60 minutes
Interview date17 Jun 2021
Coding problem2
1. Stock Buy and Sell Problem
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given an array/list 'prices' where the elements of the array represent the prices of the stock as they were yesterday and indices of the array represent minutes. Your task is to find and return the maximum profit you can make by buying and selling the stock. You can buy and sell the stock only once.
Note:
You can’t sell without buying first.
For Example:
For the given array [ 2, 100, 150, 120],
The maximum profit can be achieved by buying the stock at minute 0 when its price is Rs. 2 and selling it at minute 2 when its price is Rs. 150.
So, the output will be 148.
Problem approach
Step 1: Initialize minPrice to a high value and maxProfit to 0.
Step 2: Iterate through stock prices.
Step 3: Update minPrice to the minimum of the current price and minPrice.
Step 4: Update maxProfit to the maximum of the current profit and the difference between the current price and minPrice.
Step 5: Return maxProfit after the iteration.
2. Reverse bits of an Integer
Moderate
0/80
Asked in companies



There is a song concert going to happen in the city. The price of each ticket is equal to the number obtained after reversing the bits of a given 32 bits unsigned integer ‘n’.
Problem approach
Step 1: Initialize the result and num_bits to 0 and the number of bits in the integer (e.g., 32 for a 32-bit integer).
Step 2: Iterate from 0 to num_bits - 1.
Step 3: Extract each bit from the input integer using right-shift and bitwise AND.
Step 4: Shift and set the bits in the result.
Step 5: After the loop, the result will hold the integer with its bits reversed.
02
Round
Easy
Online Coding Interview
Duration45 minutes
Interview date20 Jun 2021
Coding problem3
1. Single Element in a Sorted Array
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a sorted array ‘arr’ of ‘n’ numbers such that every number occurred twice in the array except one, which appears only once.
Return the number that appears once.
Example:
Input: 'arr' = [1,1,2,2,4,5,5]
Output: 4
Explanation:
Number 4 only appears once the array.
Note :
Exactly one number in the array 'arr' appears once.
Problem approach
Step 1: Use binary search with two pointers, left and right.
Step 2: While the left is less than or equal to the right, perform a binary search and adjust the pointers based on the middle element and its adjacent elements.
Step 3: After the loop, return the element at index left (or right) as the single unique element.
2. Trapping Rain Water
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a long type array/list 'arr’ of size 'n’.
It represents an elevation map wherein 'arr[i]’ denotes the elevation of the 'ith' bar.
Print the total amount of rainwater that can be trapped in these elevations.
Note :
The width of each bar is the same and is equal to 1.
Example:
Input: ‘n’ = 6, ‘arr’ = [3, 0, 0, 2, 0, 4].
Output: 10
Explanation: Refer to the image for better comprehension:

Note :
You don't need to print anything. It has already been taken care of. Just implement the given function.
Problem approach
Step 1: Initialize left_max, right_max, and total_water variables.
Step 2: Traverse the input height array to fill the left_max array with the maximum height on the left of each element.
Step 3: Traverse the input height array in reverse to fill the right_max array with the maximum height on the right of each element.
Step 4: Traverse the input height array again to calculate trapped water for each element and add it to total_water.
Step 5: Return total_water as the result.
3. Burn Binary Tree
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given a binary tree of 'N' nodes.
Your task is to find the path from the leaf node to the root node which has the maximum path sum among all the root to leaf paths.
For Example:
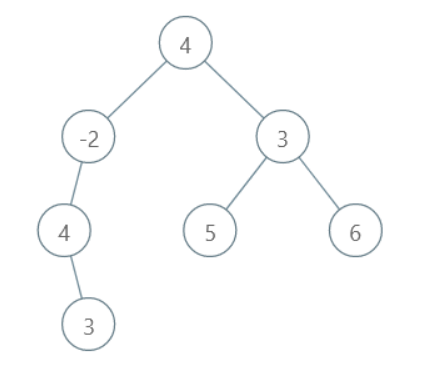
All the possible root to leaf paths are:
3, 4, -2, 4 with sum 9
5, 3, 4 with sum 12
6, 3, 4 with sum 13
Here, the maximum sum is 13. Thus, the output path will be 6, 3, 4.
Note:
There will be only 1 path with max sum.
Problem approach
Step 1: Implement a Depth-First Search (DFS) function to calculate the time for fire to reach each node from the starting node.
Step 2: Start DFS traversal from the given starting node, setting the initial time to 0.
Step 3: During traversal, pass the time to child nodes recursively, updating it with the burning time of the current node.
Step 4: Return the maximum time among all nodes after the DFS traversal, representing the time taken to burn the entire binary tree.
03
Round
Hard
Video Call
Duration40 minutes
Interview date24 Jun 2021
Coding problem2
1. Parallel Courses
Hard
30m average time
65% success
0/120
Asked in companies


You are given an integer N which denotes the number of courses numbered from 1 to N and a matrix ‘prerequisites’, in which each row contains exactly two integers ‘A’ and ‘B’ which represents the course ‘A’ has to be studied in some semester before studying course ‘B’.
You are supposed to find the minimum number of semesters required to study all the courses.
If it is impossible to study all the courses, then return -1.
Note :
There is no limitation on taking the number of courses in a particular semester as long as all the prerequisites for taking the course are satisfied.
Problem approach
Step 1: Create a graph representation of courses and their prerequisites.
Step 2: Initialize a queue with courses that have no prerequisites.
Step 3: Use BFS to process courses in the queue, decrementing the in-degree of prerequisites.
Step 4: Add courses with in-degree 0 to the queue for the next semester.
Step 5: Repeat steps 3-4 until all courses are processed, tracking the semesters taken.
Step 6: Return the semesters or -1 if there's a cycle in the graph.
2. Puzzle
Pay an employee using a gold rod of 7 units
An employee works for an employer for 7 days. The employer has a gold rod of 7 units. How does the employer pay the employee, so that the number of employee’s rod units increases by one at the end of each day? The employer can make at most 2 cuts in the rod.
(Hint- after the end of the day employees can’t spend any part of the rod)
04
Round
Medium
HR Round
Duration40 minutes
Interview date28 Jun 2021
Coding problem1
1. Basic HR Questions
Tell me about yourself.
Why did you choose a career as a Data Analyst?
How do you handle tight deadlines and pressure while working on?
What motivates you to excel in your work?

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Grofers
1425 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Grofers
1260 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Grofers
1416 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes




