Josh Technology Group interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Josh Technology Group
5 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Journey
Right from my first year, we were told to do coding to bag internships. Therefore, I started with basic coding in C++ when I was in first year. Then I took a DSA course from Coding Ninjas and practised well from it. I was able to solve most of the difficult questions by then. I also did Interview Bit 2 months before applying for interviews.
Application story
I applied in on-campus placement process. The company visited our campus for internships and placements. I was shortlisted on the basis of resume and coding test.
Why selected/rejected for the role?
I was rejected because I was not able to give optimised approach for one of the coding problems. I felt there was a lack of practise from my end.
Preparation
Duration: 3 months
Topics: DSA, CS FUNDAMENTALS, WEB CONCEPTS, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Take your time before directly jumping onto the solution even if you have done the code already, it might be possible that interviewer would add any constraints of his own choice.
Tip 2 : Speak out loud, that's very important. If you are stuck onto something in between the interview, don't just sit idle or give up. Talk to your interviewer, let him/her know what's going in your mind, what approach are you trying to implement. The interviewer is your only friend in that room.
Tip 3 : Don't worry if you haven't been into Competitive Programming before, you can still crack a lot of companies with decent DSA skills, projects are add on.
Tip 4 : For preparation, go through coding ninja's course thoroughly. It's very likely to encounter same questions that are already in the course itself. Common problems like, stock span, balanced parentheses, edit distance-DP, etc.
Tip 5 : Don't panic on seeing a question that you haven't done before. Try to break the given problem into small problems first just like we do in DP, it will surely help you out in building logic if not solution.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7.5 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Take a nice template for resume, you can even refer sites like novoresume.com. It has got good templates, just pick any with no fancy fonts and colors. Keep it simple.
Tip 2 : Be very specific. Write out important stuff only if you applying for a tech job. No one's going to see your dance/acting skills while interviewing you.
Tip 3 : If you have mentioned your projects, make sure you add your source code's link/github repo link as hyperlink to it. That's very important, it helps interviewer know that you have done this project and you're not faking it.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration45 minutes
Interview date14 Feb 2020
Coding problem0
There were around 50 mcq's on C/C++ concepts.
There was no negative marking though.
02
Round
Medium
Online Coding Interview
Duration45 minutes
Interview date14 Feb 2020
Coding problem1
Online coding round.
We could only write pseudo code and couldn't test against test cases.
1. Level order traversal of a Binary Tree.
Easy
15m average time
85% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree of integers. You are supposed to return the level order traversal of the given tree.
For example:
For the given binary tree
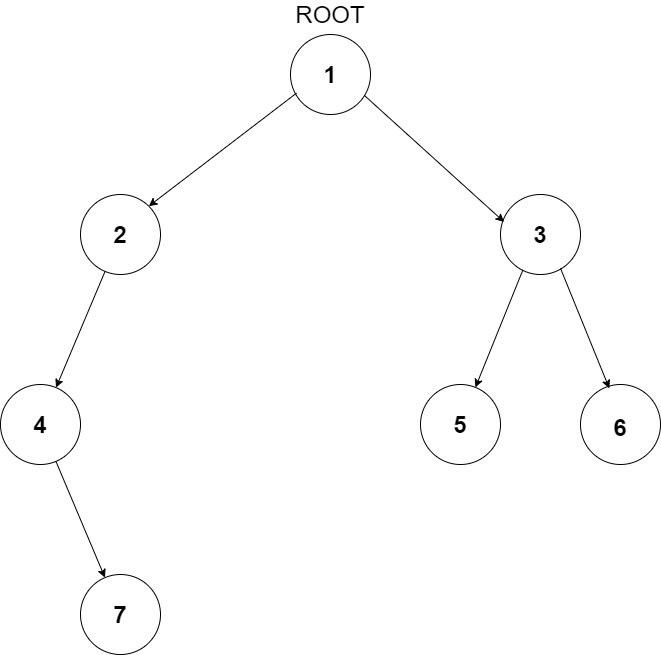
The level order traversal will be {1,2,3,4,5,6,7}.
Problem approach
Again i had already done this question in the course itself so it was a cake walk for me.
Solution:
Step 1: Create an empty queue which accepts BinaryTreeNode.
Step 2: Put root of the binary tree in the queue.
Step 3: Loop while queue is not empty
3a. store the current size of the queue which will help us know how many nodes are there which needs to be printed at one level.
3b. Dequeue the first node from the queue.
3c. Print it's data.
3d. If the dequeued node has left or right child, enqueue it to the queue.
3e. Print a line as we move to next level.
03
Round
Easy
Face to Face
Duration50 minutes
Interview date17 Feb 2020
Coding problem2
It was onsite face to face technical round where i was asked 2 coding questions.
It lasted for 40-50 minutes.
1. Kth ancestor of a node in binary tree
Hard
50m average time
35% success
0/120
Asked in companies



You are given an arbitrary binary tree consisting of N nodes numbered from 1 to N, an integer 'K', and a node 'TARGET_NODE_VAL' from the tree. You need to find the Kth ancestor of the node 'TARGET_NODE_VAL'. If there is no such ancestor, then print -1.
The Kth ancestor of a node in a binary tree is the Kth node in the path going up from the given node to the root of the tree. Refer to sample test cases for further explanation.
Note:
1. The given node 'TARGET_NODE_VAL' is always present in the tree.
2. The value of each node in the tree is unique.
3. Notice that the Kth ancestor node if present will always be unique.
Problem approach
I solved this question recursively.
Step 1: Find the given node in the tree.
Step 2: If node not found then simply return null, else check if K is greater than 0, if yes that means we haven't found the Kth ancestor, so we decrement the value of K.
Also we check if K value is 0 then we have found Kth ancestor, and we print it and return null and with base case if root == null, we return.
2. Equilibrium indices of a sequence
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given an array/list 'SEQUENCE' denoting the sequence of 'N' integers. Your task is to find the equilibrium indices of the sequence in 'SEQUENCE'.
The equilibrium index of a sequence of integers is defined as the index such that the sum of all the elements at lower indices is equal to the sum of elements at higher indices.
Note:
1. 'SEQUENCE' may contain more than one equilibrium indices.
2. If there are no equilibrium indices, return an empty sequence.
3. Consider the sum of elements lower than the first index and higher than the last index to be 0 (zero).
04
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration50 minutes
Interview date17 Feb 2020
Coding problem1
Only 7 students were shortlisted after the first face to face round out of 40 students.
The interviewer seemed cool and was trying to calm down me as i was getting nervous.
Again there were 2 coding questions.
1. Reverse linked list
Moderate
15m average time
85% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a singly linked list of integers. Your task is to return the head of the reversed linked list.
For example:
The given linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4-> NULL. Then the reverse linked list is 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> NULL and the head of the reversed linked list will be 4.
Follow Up :
Can you solve this problem in O(N) time and O(1) space complexity?
05
Round
Medium
Face to Face
Duration90 minutes
Interview date17 Feb 2020
Coding problem2
This was the last technical round and there were only 5 students left at the end of day.
The interview started at around 6:30 in the evening.
1. Replace with Sum of greater nodes
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given a binary tree with 'N' number of nodes, convert it to a Greater Tree such that data of every node of the original BST is changed to the original node’s data plus the sum of all node’s data greater than or equal to the original data of the node in the BST.
A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree data structure that has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with data less than the node’s data.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with data greater than the node’s data.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example:
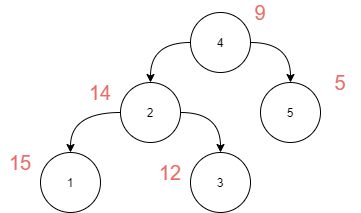
Answer:
Because only 5 is greater than 4 in the above BST, node 4 will be updated to 9 (4 + 5 = 9).
Nodes 3, 4, and 5 are greater than 2, hence node 2 will be modified to 14 (2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 14).
Node with data 5 will remain the same because there is no node in the BST with data greater than 5.
Nodes 2,3, 4, and 5 are greater than 1, hence node 1 will be modified to 15 (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15).
Nodes 4 and 5 are greater than 3, hence node 3 will be modified to 12 (3 + 4 + 5 = 12).
Problem approach
Step 1: I made a helper function where i passed the root node and 0 which worked as the sum in it.
Step 2: Made a base case, if root is null, return.
Step 3: Went to the rightmost node of the tree as the rightmost node is the only node which will have highest value in whole BST.
Step 4: Added the root's data to the sum variable which was passed in the helper function.
Step 5: After adding the root's sum with the sum variable, update the current root data with that sum.
Step 6: Call recursively on left side of the tree by sending root.left as root node and updated sum in helper function.
2. Nuts and bolts
Easy
15m average time
80% success
0/40
Asked in company

Given a set of ‘N’ nuts of different sizes and ‘N’ bolts of different sizes. There is a one-one mapping between nuts and bolts. Your task is to find the correct match of nuts and bolts from the given set and assign a nut to a bolt when it is matched.
Note:
1. A comparison of a nut to another nut or a bolt to another bolt is not allowed. It means nut can only be compared with bolt and bolt can only be compared with a nut to see which one is bigger/smaller.
2. The set of Nuts/Bolts will consist of numeric strings that represent their sizes. The size of each nut/bolt will be equal to its numerical value. For example, the size of ‘10’ will be equal to 10.
3. For every bolt, there will exist a nut of the same size.
4. Don’t return or print anything. Modify the original sequence of nuts and bolts such that each nut of a particular size matches its bolt of the same size.
5. Store the matched pair of nuts and bolts in any order.
Problem approach
Solution 1: I tried solving this problem with brute force way first, starting with the first bolt and compare it with each nut until we find a match. In the worst case we require n comparisons. Doing this for all bolts gives O(n^2) complexity. hence i was asked to optimize it further,
Solution 2:I tried using the hashmap and came up to the solution as well.
Step 1: Traverse the nuts array and create a hashmap
Step 2: Traverse the bolts array and search for it in hashmap.
Step 3: If it is found in the hashmap of nuts than this means bolts exist for that nut.
Time complexity for this solution was O(n) but interviewer wanted me to solve it using quick sort and that's where i couldn't recollect my thoughts and even after thinking so much, couldn't come up with quick sort method as it was 3rd round for the day as well and was too tired.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
6 rounds | 14 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
5570 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
5 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
3256 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
1130 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
7 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Josh Technology Group
1122 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
3713 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Arcesium
2667 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by BNY Mellon
2336 views
0 comments
0 upvotes






