Salesforce interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - 1
Salesforce
4 rounds | 9 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 4 Months
Topics: Data Structures, Algorithms, System Design, Aptitude, OOPS
Tip
Tip 1 : Must do Previously asked Interview as well as Online Test Questions.
Tip 2 : Go through all the previous interview experiences from Codestudio and Leetcode.
Tip 3 : Do at-least 2 good projects and you must know every bit of them.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: Above 7 CGPA
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Have at-least 2 good projects explained in short with all important points covered.
Tip 2 : Every skill must be mentioned.
Tip 3 : Focus on skills, projects and experiences more.
Interview rounds
01
Round
Medium
Online Coding Test
Duration75 Minutes
Interview date18 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
This was an online coding round where we had 2 questions to solve under 75 minutes. The questions were of Medium to Hard level of difficulty and I found the problem statements to be a bit tricky.
1. Balanced parentheses
Moderate
10m average time
90% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an integer ‘N’ representing the number of pairs of parentheses, Find all the possible combinations of balanced parentheses with the given number of pairs of parentheses.
Note :
Conditions for valid parentheses:
1. All open brackets must be closed by the closing brackets.
2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
For Example :
()()()() is a valid parentheses.
)()()( is not a valid parentheses.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) First make a recursive function, say ‘solve’ taking the number of opening brackets ‘opening’, number of closing brackets ‘closing’ output string ‘output’, and an array of strings ‘ans’ as arguments.
2) Make the base condition as if ‘opening’ = 0 and ‘closing’ = 0 then push the output string in the ‘ans’ and return.
3) If ‘opening’ is not equal to zero then call the ‘solve’ function recursively by decrementing ‘opening’ by 1 and inserting ‘(‘ into the ‘output’.
4) If ‘closing’ > ‘opening’ then call the ‘solve’ function recursively by decrementing ‘closing’ by 1 and inserting ‘)’ into the ‘output’.
TC : O(2 ^ N), where N is the given integer.
SC : O(N)
2. Longest Happy String
Moderate
25m average time
75% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Ninja likes to play with strings, and he calls a string ‘S’ Happy if it only contains letters ‘a’, ‘b’, and ‘c’, and no three consecutive letters in the string are the same. For example, ‘aa’, ‘aab’, ‘aabbcc’ are the happy strings, but ‘aaa’, ‘aaza’, ‘aaabbb’ are not happy strings.
You are given three non-negative integers ‘X’, ‘Y’, ‘Z’. You need to find the longest happy string such that it contains ‘a’ at most ‘X’ times, ‘b’ at most ‘Y’ times, and ‘c’ almost ‘Z’ times.
Note:
There can be more than one possible string with maximum size. In that case, you can return any of them.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Let the 'X', 'Y', 'Z' be the maximum availability ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’ respectively.
2) Declare an empty string say ‘S’ to store the answer string.
3) Run a loop till (x + y + z)
3.1) If ( 'X' >= 'Y' and 'X' >= 'Z' and the last two letters in ‘S’ is not “aa” ) or ( the last two letters in ‘S’ are “bb” or “cc” and 'X' is nonzero).
Add ‘a’ to ‘S’, and update 'X' to ‘x - 1’.
3.2) If ( 'Y' >= 'X' and 'Y' >= 'Z' and the last two letters in ‘S’ is not “bb” ) or ( the last two letters in ‘S’ are “aa” or “cc” and 'Y' is nonzero).
Add ‘b’ to ‘S’, and update 'Y' to ‘y - 1’.
3.3) If ( 'Z' >= 'Y' and 'Z' >= 'X' and the last two letters in ‘S’ is not “cc” ) or ( the last two letters in ‘S’ are “bb” or “aa” and 'Z' is nonzero).
Add ‘c’ to ‘S’, and update 'Z' to ‘z - 1’.
4) Return S.
TC : O(X+Y+Z), where X, Y, Z are the given maximum number a, b, and c respectively that the output string can have.
SC : O(X+Y+Z)
02
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date18 Aug 2021
Coding problem2
This round had 2 preety decent questions of DSA . The interviewer was also quite freindly and helpful. I was able to solve both the questions under the given time frame and also discussed their respective time and space complexites.
1. Print All Paths
Moderate
45m average time
55% success
0/80
Asked in companies


You are given a graph with ‘N’ nodes and ‘M’ unidirectional edges. Also you are given two integers ‘S’ and ‘D’ denoting the source and destination. Your task is to find all the paths from ‘S’ to ‘D’.
Note: An ordered set of nodes { S, u1, u2...un, D} is a valid path between ‘S’ and ‘D’, if all nodes along the path are unique.
For example:
For given N = 4, M = 4, S = 0 and D =3.
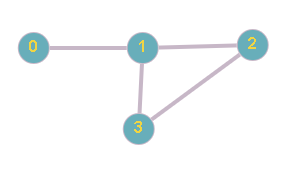
In the above example, the path 0 -> 1 - > 3 is a valid path as all nodes along the path are unique and the path 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3 is not a valid path because node 1 is visited twice.
Problem approach
Approach (Using Backtracking) :
Let ‘allAllPaths(n, m, edges, src, des)’ be the function that returns a 2D array that contains all the possible paths.
1) Take the following variables: 2D array ‘Graph’, to store graphs and ‘Visited’ array to mark each node whether it is visited or not.
2) Clear graph, initialize the visited array to false.
3) Run a loop from 0 to 'm' :
3.1) Add the undirected edge between edges[i] [0] and edges[i][1].
4) Take an 2D array 'allPaths' to store the answer.
5) Take an array 'currPath' to store the current path.
6) Push ‘src’ in ‘currPath’ and mark visited[src] equal to true.
7) Make a dfs(n, allPaths, currPath, src, des, graph, visited) and call the dfs function.
8) Return ‘allPaths’.
TC : O(N ^ N), where N is the number of vertices.
SC : O(N ^ N)
2. Cycle Detection in a Singly Linked List
Moderate
15m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



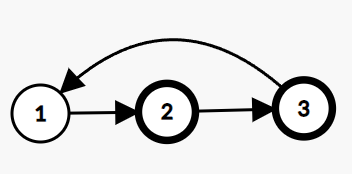
You are given a Singly Linked List of integers. Return true if it has a cycle, else return false.
A cycle occurs when a node's next points back to a previous node in the list.
Example:
In the given linked list, there is a cycle, hence we return true.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Initialize slow and fast at the beginning.
2) Start moving slow to every next node and moving fast 2 jumps, while making sure that fast and its next is not null.
3) If after adjusting slow and fast, if they are referring to the same node, there is a cycle otherwise repeat the process
4) If fast reaches the end or null then the execution stops and we can conclude that no cycle exists.
TC : O(N), where N = total number of nodes
SC : O(1)
03
Round
Medium
Video Call
Duration60 Minutes
Interview date18 Aug 2021
Coding problem4
This round had 1 question related to BST followed by some standard questions from OOPS and Operating Systems.
1. Pair with Given Sum in a Balanced BST
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You are given the ‘root’ of a Balanced Binary Search Tree and an integer ‘target,’ you have to tell if there exists any pair of nodes such that the sum of their value is equal to the target.
More formally check if there exist any two distinct nodes, whose sum is equal to ‘target.’
Note:
A binary search tree, also called an ordered or sorted binary tree, is a rooted binary tree whose internal nodes each store a key greater than all the keys in the node's left subtree and less than those in its right subtree.
A balanced binary search tree is a tree in which each node has either 0 or 2 children.
Example:
For Example, the root node is given as follows :
‘ROOT’ = 5 2 6 -1 -1 -1 -1 and ‘target’ = 8, The answer will be true since the sum of both leaf nodes is equal to 8.
Problem approach
Approach :
1) Maintain a hash-map ‘mp,’ which keeps track of the nodes we have visited.
2) We will use a helper function, ‘helper’.
3) ‘helper’ takes ‘root,’ ‘target,’ and ‘mp’ as input parameters, where ‘root’ is the root of the binary tree, ‘target’ is the value which should be equal to sum of 2 nodes and ‘mp’ is the hash-map we use to keep track of nodes visited.
3.1) For a given root ‘toFind’ value is the other half that we need to find to make a pair whose sum is equal to ‘target’, for the given ‘root’s data value.
3.2) If for the current node we have visited a node whose value is ‘toFind’ and they are not the same nodes, we return true.
3.3) Else we recur for the left and right nodes of the current node.
3.4) If we find the pair, we return true. Else we return false as the final answer.
TC : O(N), where N = number of nodes in the binary tree.
SC : O(N)
2. OOPS Question
What is Early Binding and Late Binding in C++ ?
Problem approach
OOP is used commonly for software development. One major pillar of OOP is polymorphism. Early Binding and Late
Binding are related to that. Early Binding occurs at compile time while Late Binding occurs at runtime. In method
overloading, the bonding happens using the early binding. In method overriding, the bonding happens using the late
binding. The difference between Early and Late Binding is that Early Binding uses the class information to resolve
method calling while Late Binding uses the object to resolve method calling.
Early Binding : In Early Binding, the class information is used to resolve method calling. Early Binding occurs at
compile time. It is also known as the static binding. In this process, the binding occurs before the program actually
runs. Overloading methods are bonded using early binding.
Late Binding : In Late Binding, the object is used to resolve method calling. Late Binding occurs at runtime. It is also
known as dynamic binding. In this process, the binding occurs at program execution. Overridden methods are
bonded using late binding.
3. OS Question
What is deadlock? How to prevent deadlock?
Problem approach
Deadlock : Deadlock is a scenario where a set of processes is blocked because each process has acquired a lock on
a particular resource and is waiting for another resource locked by some other process.
A deadlock can occur in almost any situation where processes share resources. It can happen in any computing
environment, but it is widespread in distributed systems, where multiple processes operate on different resources.
Steps to prevent Deadlock :
1) No Mutual Exclusion :
It means more than one process can have access to a single resource at the same time. It’s impossible because if
multiple processes access the same resource simultaneously, there will be chaos. Additionally, no process will be
completed. So this is not feasible. Hence, the OS can’t avoid mutual exclusion.
2) No Hold and Wait :
To avoid the hold and wait, there are many ways to acquire all the required resources before starting the execution.
But this is also not feasible because a process will use a single resource at a time.
Another way is if a process is holding a resource and wants to have additional resources, then it must free the
acquired resources. This way, we can avoid the hold and wait condition, but it can result in starvation.
3) Removal of No Preemption :
One of the reasons that cause the deadlock is the no preemption. It means the CPU can’t take acquired resources
from any process forcefully even though that process is in a waiting state. If we can remove the no preemption and
forcefully take resources from a waiting process, we can avoid the deadlock.
4) Removal of Circular Wait :
In the circular wait, two processes are stuck in the waiting state for the resources which have been held by each
other. To avoid the circular wait, we assign a numerical integer value to all resources, and a process has to access
the resource in increasing or decreasing order.
4. OS Question
What is meant by Multitasking and Multithreading in OS?
Problem approach
Multitasking : It refers to the process in which a CPU happens to execute multiple tasks at any given time. CPU
switching occurs very often when multitasking between various tasks. This way, the users get to collaborate with
every program together at the same time. Since it involves rapid CPU switching, it requires some time. It is because
switching from one user to another might need some resources. The processes in multi-tasking, unlike multi-
threading, share separate resources and memories.
Multithreading : It is a system that creates many threads out of a single process to increase the overall power and
working capacity of a computer. In the process of multi-threading, we use a CPU for executing many threads out of a
single process at any given time. Also, the process of creation depends entirely on the cost. The process of
multithreading, unlike multitasking, makes use of the very same resources and memory for processing the execution.
04
Round
Easy
HR Round
Duration30 Minutes
Interview date18 Aug 2021
Coding problem1
This was my last round and I hoped it to go good just like the other rounds. The interviewer was very straight to point
and professional. The interview lasted for 30 minutes.
1. Basic HR Question
Tell me something not there in your resume.
Problem approach
If you get this question, it's an opportunity to choose the most compelling information to share that is not obvious from
your resume.
Example :
Strength -> I believe that my greatest strength is the ability to solve problems quickly and efficiently, which makes me
unique from others.
Ability to Handle Pressure -> I enjoy working under pressure because I believe it helps me grow and become more
efficient .
Tip : Emphasize why you were inspired to apply for the job. You can also explain that you are willing to invest a great
deal of energy if hired.
These are generally very open ended questions and are asked to test how quick wit a candidate is. So there is
nothing to worry about if you have a good cammand over your communication skills and you are able to propagate
your thoughts well to the interviewer.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3359 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
1532 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
1137 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
5 rounds | 12 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
114869 views
24 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
4 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
58031 views
5 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
35057 views
7 comments
0 upvotes






