Sanchhaya Education Private Limited interview experience Real time questions & tips from candidates to crack your interview
SDE - Intern
Sanchhaya Education Private Limited
3 rounds | 6 Coding
problems
Interview preparation journey
Preparation
Duration: 2.5 months
Topics: Data Structures, Recursion, Dynamic Programming, OOPS, Pointers
Tip
Tip 1 : Be very clear with the basics of each topic.
Tip 2 : Be thorough with the projects mentioned in the resume.
Application process
Where: Campus
Eligibility: above 70%
Resume tip
Tip 1 : Don't lie on your resume.
Tip 2 : The number of projects on the resume does not matter, what matters is that you must be thorough with your projects.
Tip 3 : Do not write too much, it should be simple and decent
Interview rounds
01
Round
Easy
Online Coding Test
Duration160 minutes
Interview date6 Oct 2020
Coding problem2
The online assessment consisted of four components, a code debugging section (20 minutes), a coding test (70 minutes), a workstyles assessment (20 minutes) and a reasoning ability section (35 minutes). Code debugging questions were pretty simple and straightforward. The coding test consisted of 2 questions, first was similar to two Sum problem. Second question was similar to find the critical edges in a graph. The workstyles assessment section contained certain behavioural questions.
Reasoning ability section consisted of aptitude questions. This round was basically to check the problem solving skills of the candidate.
1. Two Sum
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies



You are given an array of integers 'ARR' of length 'N' and an integer Target. Your task is to return all pairs of elements such that they add up to Target.
Note:
We cannot use the element at a given index twice.
Follow Up:
Try to do this problem in O(N) time complexity.
2. Bridges In A Graph
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Given an undirected graph of V vertices and E edges. Your task is to find all the bridges in the given undirected graph. A bridge in any graph is defined as an edge which, when removed, makes the graph disconnected (or more precisely, increases the number of connected components in the graph).
For Example :
If the given graph is :
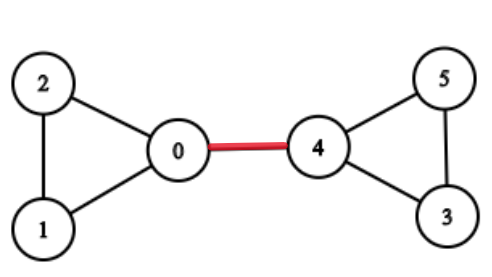
Then the edge between 0 and 4 is the bridge because if the edge between 0 and 4 is removed, then there will be no path left to reach from 0 to 4.and makes the graph disconnected, and increases the number of connected components.
Note :
There are no self-loops(an edge connecting the vertex to itself) in the given graph.
There are no parallel edges i.e no two vertices are directly connected by more than 1 edge.
02
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration50 minutes
Interview date9 Oct 2020
Coding problem2
I was asked two coding questions. First question was related to binary tree and second question was to implement LRU cache.
I had to code both questions. The interviewer asked me the time and space complexity for both the questions.
1. Binary Tree Pruning
Moderate
20m average time
80% success
0/80
Asked in companies



You have been given a Binary Tree where the value of each node is either 0 or 1. Your task is to return the same Binary Tree but all of its subtrees that don't contain a 1 have been removed.
Note :
A subtree of a node X is X, plus every node that is a descendant of X.
For Example :
Look at the below example to see a Binary Tree pruning.
Input: [1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
Output: [1, 1, 1, -1, 1, -1, 1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
For example, the input for the tree depicted in the below image would be :
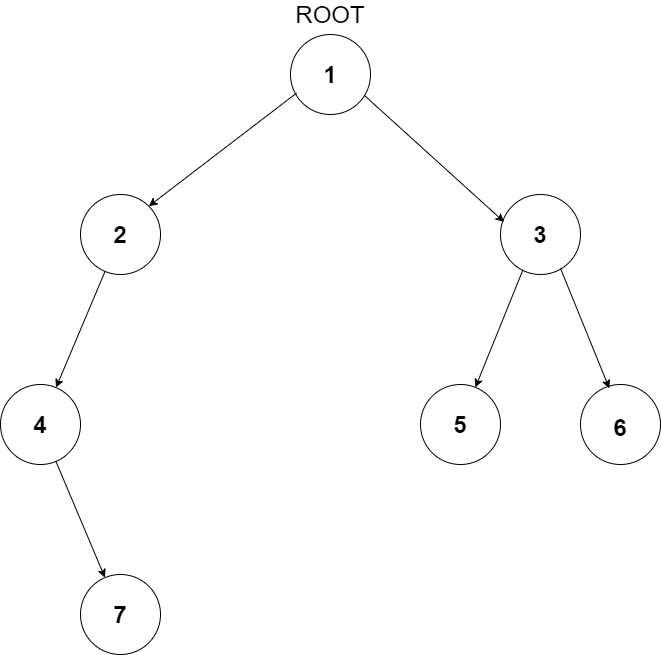
1
2 3
4 -1 5 6
-1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1
-1 -1
Explanation :
Level 1 :
The root node of the tree is 1
Level 2 :
Left child of 1 = 2
Right child of 1 = 3
Level 3 :
Left child of 2 = 4
Right child of 2 = null (-1)
Left child of 3 = 5
Right child of 3 = 6
Level 4 :
Left child of 4 = null (-1)
Right child of 4 = 7
Left child of 5 = null (-1)
Right child of 5 = null (-1)
Left child of 6 = null (-1)
Right child of 6 = null (-1)
Level 5 :
Left child of 7 = null (-1)
Right child of 7 = null (-1)
The first not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent of the first two nodes of the current level. The second not-null node (of the previous level) is treated as the parent node for the next two nodes of the current level and so on.
The input ends when all nodes at the last level are null (-1).
Note :
The above format was just to provide clarity on how the input is formed for a given tree.
The sequence will be put together in a single line separated by a single space. Hence, for the above-depicted tree, the input will be given as:
1 2 3 4 -1 5 6 -1 7 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
2. LRU Cache Implementation
Moderate
25m average time
65% success
0/80
Asked in companies



Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache to support the following operations:
1. get(key) - Return the value of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.
2. put(key, value), Insert the value in the cache if the key is not already present or update the value of the given key if the key is already present. When the cache reaches its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting the new item.
You will be given ‘Q’ queries. Each query will belong to one of these two types:
Type 0: for get(key) operation.
Type 1: for put(key, value) operation.
Note :
1. The cache is initialized with a capacity (the maximum number of unique keys it can hold at a time).
2. Access to an item or key is defined as a get or a put operation on the key. The least recently used key is the one with the oldest access time.
03
Round
Easy
Video Call
Duration30 minutes
Interview date2 Nov 2020
Coding problem2
I was asked two coding questions and some conceptual questions about priority heap data structure. I was able to code the optimized approach for the first question. But second question was a little tricky for me as I had never heard it before.
1. Langford Pairing
Easy
10m average time
90% success
0/40
Asked in companies


You are given a positive integer N. Return a list of integers of size 2N containing all the integers from 1 to N (both inclusive) twice arranged according to Langford pairing. If no such pairing exists return -1 is the only list element.
Note:
There may be more than one Langford pair possible, you need to return anyone permutation.
For example:
For N = 4, one possible Langford pairing will be:-
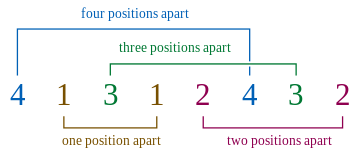
2. Ninja theater
Hard
45m average time
55% success
0/120
Asked in companies


You have been appointed as the technical lead in the very famous ninja theater. Due to the recent pandemic, all the people inside the theater must follow social distancing. There are ‘N’ seats in a single row in the ninja theater, numbered from 0 to ‘N’ - 1 inclusive. As a technical lead, your task is to find a seating arrangement for ninja theater such that when a person enters the theater, he/she must sit in the seat that maximizes the distance from the closest person.
Note :
1) If the theater is empty, i.e., if no one is in the theater, they sit in the first seat(seat number 0).
2) If there are multiple seats that maximize the distance from the closest person, they sit in the seat with the lowest number.

Here's your problem of the day
Solving this problem will increase your chance to get selected in this company
Skill covered: Programming
What is the purpose of the return keyword?
Choose another skill to practice
Similar interview experiences
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by OYO
4782 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 3 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
1012 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
2 rounds | 5 problems
Interviewed by Meesho
6544 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - 1
3 rounds | 9 problems
Interviewed by Salesforce
3567 views
0 comments
0 upvotes
Companies with similar interview experiences
SDE - Intern
3 rounds | 6 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
15557 views
4 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
4 rounds | 7 problems
Interviewed by Microsoft
15418 views
1 comments
0 upvotes
SDE - Intern
2 rounds | 4 problems
Interviewed by Amazon
10180 views
2 comments
0 upvotes






