Encryption Process
Each encryption process is divided into four sub-tasks. The first round process is as shown below:
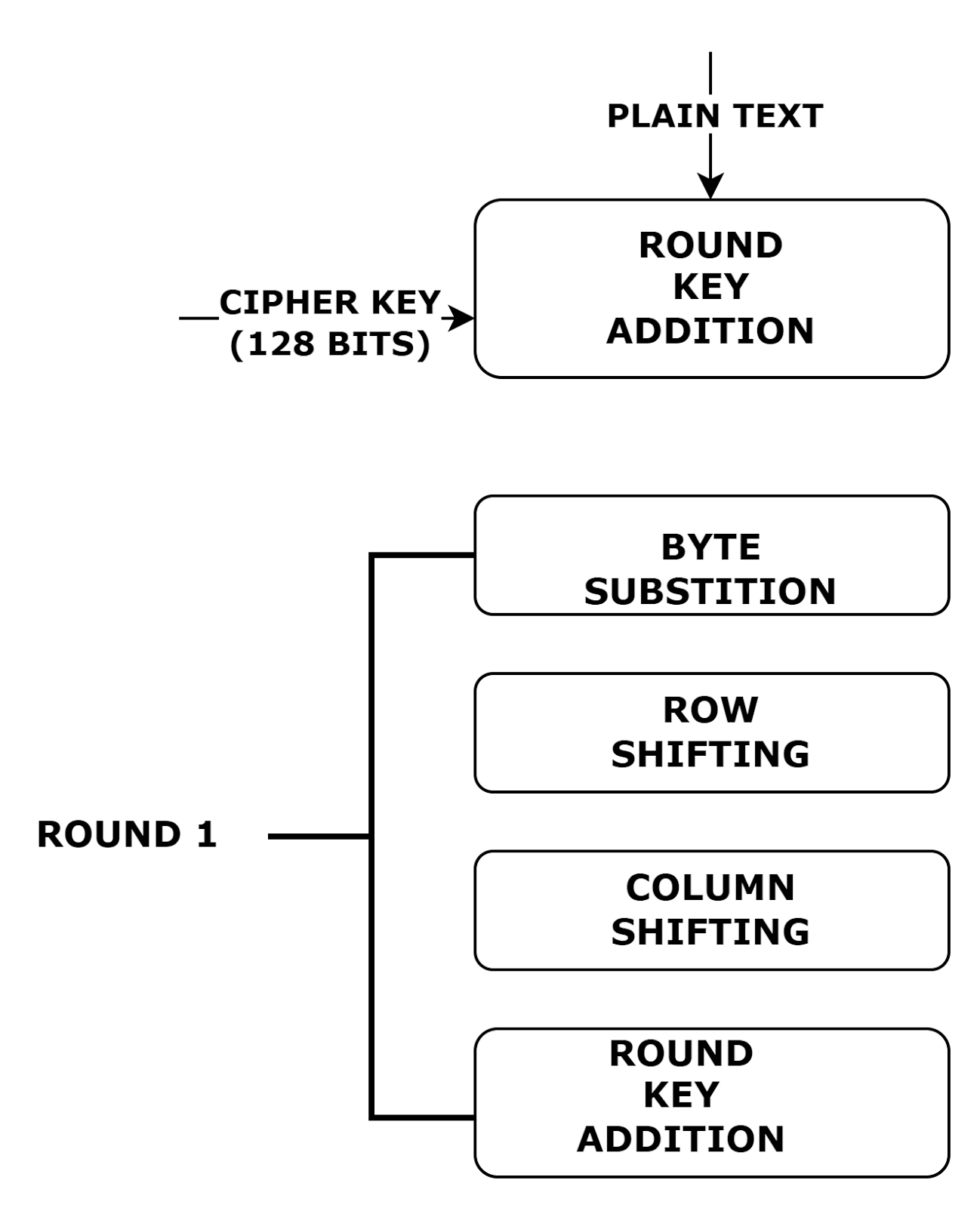
Step 1: Byte Substitution
The input bytes are shuffled using a fixed table(s-box). The result obtained is a matrix with four rows and four columns.
Step 2: Row Shifting
Each of the four rows obtained in the substitution process is made to shift one step to the left.
The shifting needs to be implemented based on the following criteria:
- The first row is kept static.
- The second row is moved one step to the left.
- The third row is moved two steps to the left.
- The fourth row is moved three steps to the left.
- The result obtained is the new matrix with the same bytes but only change in the position with respect to the other.
Step 3: Column Shuffling
A special mathematical function shuffles all the four bytes of each and every column. The new four bytes of the column as the output are replacing the original input values of the column. Hence, the resultant is another matrix consisting of new 16 bytes.
Step 4: Round Key Addition
The new matrix with 16 bytes is to be implemented over an XOR operator of 128 bytes. The result obtained is the ciphertext.
If not, then the same process is repeated again.
Decryption Process
The decryption Process for Advanced Encryption Standard is the same as the Encryption Process for Advanced Encryption Standard but is always performed in reverse order. The four different sub-processes involved are as follows:
- Round Key Addition
- Column Shuffling
- Row Shifting
- Byte Substitution
The encryption and decryption processes are carried out separately since sub-tasks are carried out in reverse order.
Applications of AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- Secure Online Transactions
AES encrypts sensitive data in online banking and e-commerce transactions, ensuring secure payment processing. It protects credit card details and login credentials from cyber threats like man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and data breaches.
- Data Encryption in Cloud Storage
Cloud service providers use AES to encrypt user data before storing it, ensuring privacy and protection against unauthorized access. Even if attackers gain access to cloud servers, AES encryption prevents them from reading the data without the correct decryption key.
- Wireless Network Security (Wi-Fi Encryption)
AES is the encryption standard in Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA2 and WPA3) protocols, securing wireless communication. It prevents hackers from intercepting data transmitted over Wi-Fi networks, reducing the risk of cyberattacks like eavesdropping and session hijacking.
Operating systems like Windows (BitLocker), macOS (FileVault), and Linux (LUKS) use AES for encrypting entire disks or specific files. This ensures that even if a device is lost or stolen, its data remains inaccessible without the decryption key.
- Messaging and Email Encryption
AES secures end-to-end encrypted messaging apps like WhatsApp and Signal, preventing third parties from intercepting private conversations. Email services also implement AES-based encryption (PGP, S/MIME) to protect sensitive emails from unauthorized access.
- Military and Government Communications
Governments and defense agencies use AES-256 encryption to secure classified information and confidential communications. The NSA has approved AES for encrypting Top Secret data, ensuring national security against cyber espionage.
AES encrypts data in IoT devices like smart home systems, healthcare monitors, and industrial sensors, preventing unauthorized access. It ensures the integrity and confidentiality of IoT communications, reducing vulnerabilities to hacking and data leaks.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the size of the block in the Advanced Encryption Standard?
The size of the block in Advanced Encryption Standard is 128-Bit.
What is the size of the key in the Advanced Encryption Standard?
The size of the key in the Advanced Encryption Standard is 128, 192 or 256 Bits.
How many iterative rounds does Advanced Encryption Standard 192 perform?
Advanced Encryption Standard 192 performs 12 rounds.
How many iterative rounds does Advanced Encryption Standard 256 perform?
Advanced Encryption Standard 192 performs 14 rounds.
What are States in AES?
The 4*4 matrices in the Advanced Encryption Standard algorithm are called States.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), a widely used symmetric encryption algorithm known for its security and efficiency. We discussed its key features, including block size, key length variations, and encryption rounds. AES provides robust protection against cryptographic attacks and is extensively used in secure communications, financial transactions, and data encryption. Understanding AES is essential for implementing strong security measures in modern applications.