Introduction
Agile is a popular technology that allows you to build and respond to changes. It is a collection of several principles that are used in the field of project management and software development. This practice works on the continuous iteration of testing and development for the complete Agile software development life cycle of a given business project.

The whole series consists of 50+ Agile Interview Questions of various levels: Beginner, Intermediate, and Advanced.
Beginner Level Agile Interview Questions
1. What do you mean by Agile Methodology?
Agile is a project management and product development approach that prioritizes flexibility, collaboration, and customer feedback. It involves iterative cycles called sprints, frequent reassessment and adaptation, and emphasizes delivering small, functional increments of a project to respond effectively to changing requirements and customer needs.
2. What are some important parts of the Agile process?
There are several important parts of the agile process:
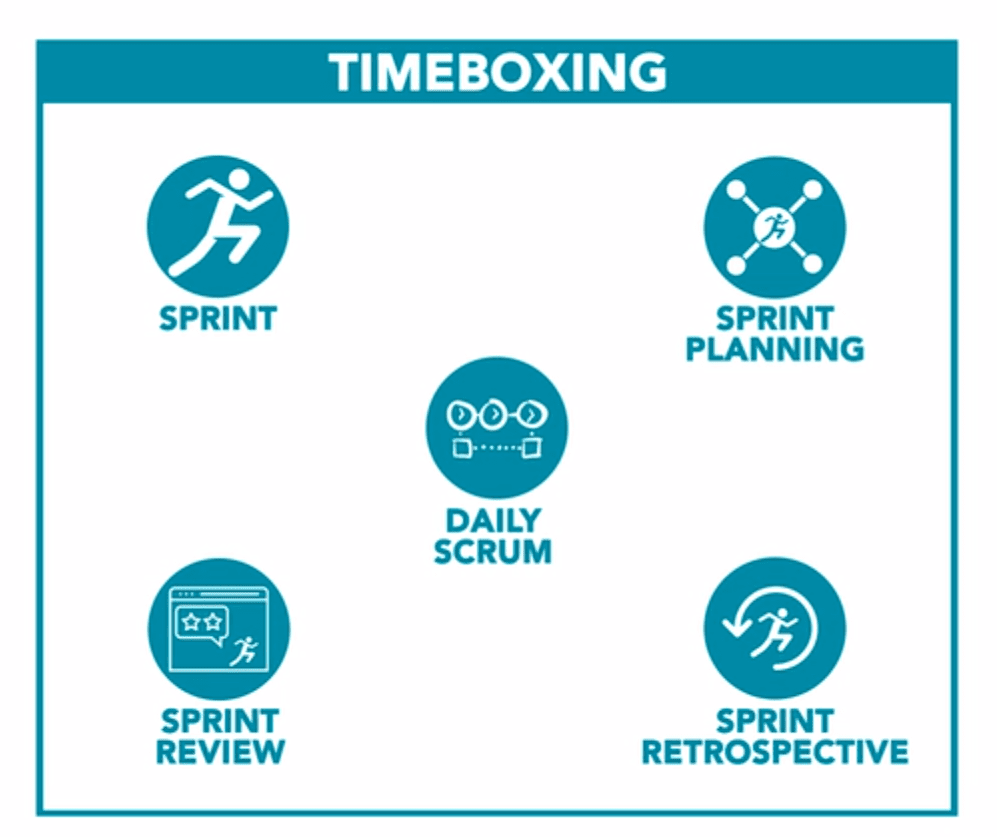
- Sprints: Short development cycles, typically 2-4 weeks.
- Backlog: Prioritized list of tasks to be completed.
- Scrum: Framework emphasizing collaboration and adaptability.
- User Stories: Descriptions of functionality from an end user's perspective.
- Daily Stand-ups: Brief team meetings for status updates.
- Retrospectives: Reflection on the team's performance for continuous improvement.
3. Name some different types of Agile methodologies.
Ans: Some of the important agile methodologies are listed below:
- Crystal Methodology
- Kanban
- Adaptive System Development (ADS)
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Lean Software Development
- Scrum
4. What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Agile Methodology?.
Ans: The advantages and disadvantages of the agile process are listed below:
Advantages
- Products are delivered quickly.
- Feedback from customers is received faster.
- Fast and continuous development.
- Agile is useful for projects when the aim isn't clear at the start but becomes clearer as the project continues.
- Code Errors are identified and eliminated quickly
Disadvantages
- Estimating resource requirements and effort is difficult.
- Very little documentation.
- When compared to other development approaches, it is more expensive.
- Large projects are difficult to scale.
- The danger of a never-ending project
5. Explain Agile Testing.
Ans: Agile testing is a software testing procedure in which software is checked for faults, mistakes, and other issues, as the name implies. It is regarded as an important aspect of the development process since it allows testers and developers to collaborate as a team, improving overall performance. It also contributes to the timely delivery of high-quality goods. Testing is frequently done so that testers can spot and fix problems early on in the development process.
6. Explain Scrum Methodology.
Ans: Scrum is a method for forming hypotheses, testing them, reflecting on the experience, and making improvements. Feedback, self-management, small teams, and work divided into sprints are all important. It works on a step-by-step basis.
7. Difference between sprint backlog and product backlog.
Ans: Sprint backlog: The development team is usually in charge of the Sprint Backlog. It only includes features and needs that are relevant to the current sprint. It's thought to be a subset of the product backlog. It is a list of everything that has to be done in order to finish a sprint. Only items that can be done during each agile sprint are included. It is solely applicable to the sprint goal in that specific sprint.
Product backlog: The project owner is usually the one who owns and maintains it. It usually includes all of the product's features as well as the product's needs. It contains a list of everything that needs to be done in order to finish the process. Everything is simply broken down into a sequence of steps. It is more focused on the product's end goal.
8. What is Scrum of Scrum mean?
Ans: Scrum of Scrums is a scalable agile technique that allows several teams to collaborate on big projects. It facilitates the development and delivery of complicated products at scale by facilitating transparency, inspection, and adaptation. It's especially effective when all members of a high-performing scrum team work toward a same goal, are perfectly aligned, and have complete trust and regard for one another.
9. Give some disadvantages of the agile model (SDLC)?
Ans: Disadvantages of agile model (SDLC)
- There's a chance that the new need will clash with the present architecture.
- There is a potential that the project will take longer than predicted if more corrections and changes are made.
- Because of the ongoing iteration, estimating the project's eventual cost may be challenging.
- Estimating resource requirements and effort is difficult.
10. What are the burn-up and burn-down charts?
Ans: The burn-up chart shows how much work has been completed on the project, and the burn-down chart shows how much work remains. As a result, the terms burn-up and burn-down are employed to describe the project's status report.
11. What do you understand by Daily Stand-Up?
Ans: The daily stand-up is a 15-minute meeting held every day (usually in the morning) in which the entire team meets to discover answers to the following three questions:
- What did you do the day before?
- What do you have planned for the day?
- Is there anything preventing you from finishing your task?
12. What are the different roles in Scrum?
Ans: Scrum Master, Product Owner, and Agile Development Team are the three different roles in Scrum
- Scrum Master: A Team leader and facilitator who assists team members in sticking to agile methodologies in order to satisfy their goals and customers' demands.
- Product owner: The person who runs the product from a business perspective and defines the requirements and prioritizes their values.
- Agile Development: The agile development team makes technical decisions and determines any dependencies.
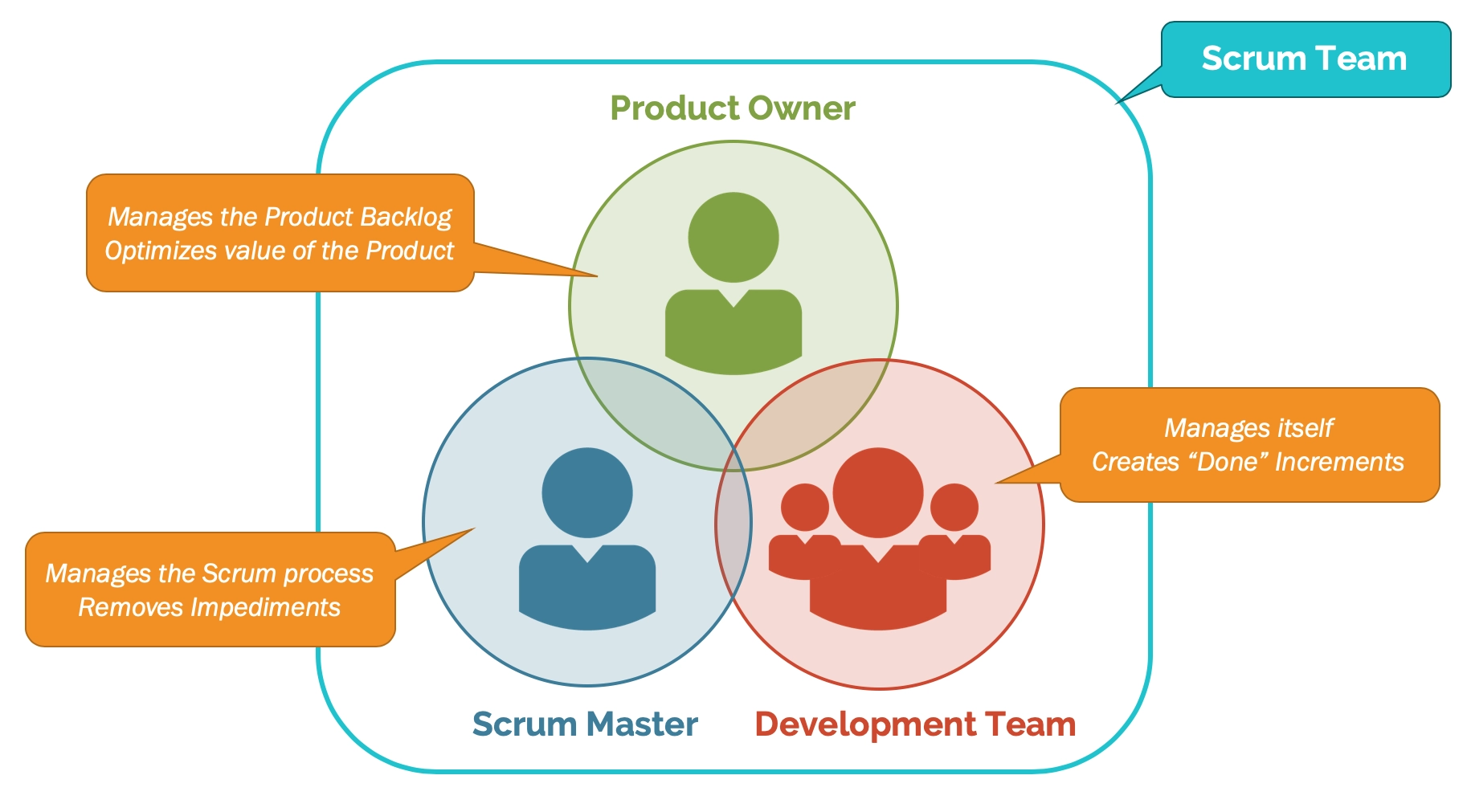
Source: Scrum.org
13. What do you know about Scrum ban?
Ans: Scrumban is a project management approach that combines key elements from two famous agile methodologies: Scrum and Kanban. Scrumban combines Scrum's structure and predictable procedures with Kanban's flexibility to improve team agility, efficiency, and productivity.
14. What are the major principles of agile testing?
Ans: Some of the major principles of agile testing are:
- Continuously provide feedback
- Keep it simple
- Enable face-to-face communication
- Practice continuous improvement
- Quickly respond to changes
15. What are the skills of a good agile tester?
Ans: The following are characteristics of a great agile tester:
- He needs to be comfortable with agile ideas and concepts.
- To communicate with the team and clients, he must have strong communication skills.
- He can prioritise tasks based on the needs of the consumer.
- He should be able to fully understand the customer's requirements.
- He should be aware of the project's risk as a result of fluctuating demand.