
Introduction
ALOHA is a network access management system that coordinates and arbitrates access to a shared communication channel. It was developed by Norman Abramson and his colleagues in the 1970s at the University of Hawaii. ALOHA stands for Additive Links On-Line Hawaii Area. ALOHA is a network access management system that coordinates and arbitrates access to a shared communication channel.
ALOHA
ALOHA is a network access management system that coordinates and arbitrates access to a shared communication channel.
Some of the properties of aloha are:
- Aloha is a random access protocol.
- Aloha is LAN-based.
- Each station transmits without detecting whether the transmission channel is idle or not.
- A collision occurs when two frames transmit on the same channel simultaneously. Due to this, the frames get destroyed.
Types of ALOHA
There are two types of ALOHA:
- Pure ALOHA
- Slotted ALOHA
Pure ALOHA
- The stations transmit frames anytime they have data to send in pure ALOHA.
- When two or more stations transmit simultaneously, there is a collision, and the frames are destroyed.
- Pure ALOHA is a Random Access Protocol. It is LAN Based. There is no propagation time in Pure ALOHA.
- When a station transmits a frame in pure ALOHA, it expects the receiver to acknowledge it. If the acknowledgment is not received from the receiver within a specified time, the station assumes that the receiver is destroyed. The station then sends a frame again after a random time so that the new transmitted frame does not collide with the same frame.
- When two or more stations transmit simultaneously on the same channel, then a collision occurs. So when our message is transmitting, no other message should start transmitting at the same channel to prevent a collision. Similarly, there should be no message transmitting at that time when our message started transmitting. Thus no message should have started transmitting Tt time before our message started transmitting. Therefore vulnerable time = 2 x Transmission time.
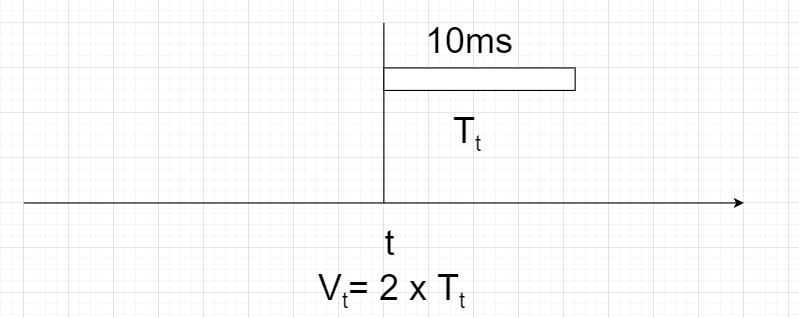
Vulnerability time = 2 x Transmission time
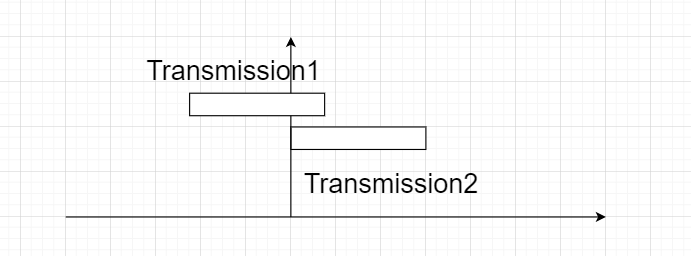
In the above figure, we can see that while the first transmission1 has not ended, another transmission started, and thus, they collide.
- Efficiency is given by n= G x e-2G, where G is the number of stations that want to transmit the data.
Differentiating the efficiency of transmission with respect to G and equating it to 0 we get e-2G(2xG-1) =0. Thus G=½. Thus, if one station transmits from every two stations, the efficiency will be maximum.
Thus the rate of successful transmission is G x e-2G at G=½ i.e. 1 x e-2 = 18.39%.
Slotted ALOHA
- The pure ALOHA has a high chance of collision. So the slotted ALOHA was made to improve the efficiency of the pure ALOHA.
- Collisions occur in slotted aloha, but they are half compared to pure aloha.
- Here the channel is divided into slots having fixed time intervals.
- Efficiency is given by n= G x e-G, where G is the number of stations that transmit the data.
Differentiating the efficiency of transmission with respect to G and equating with 0, we get e-G(G-1) =0. Thus G=1.
Thus the rate of successful transmission is G x e-G at G=1 i.e. 1 x e-1 = 36.79%. Here we can see that the successful transmission rate is double that of Pure ALOHA
- Slotted aloha is also a random access protocol.
- Here, Vulnerability time = Transmission time.
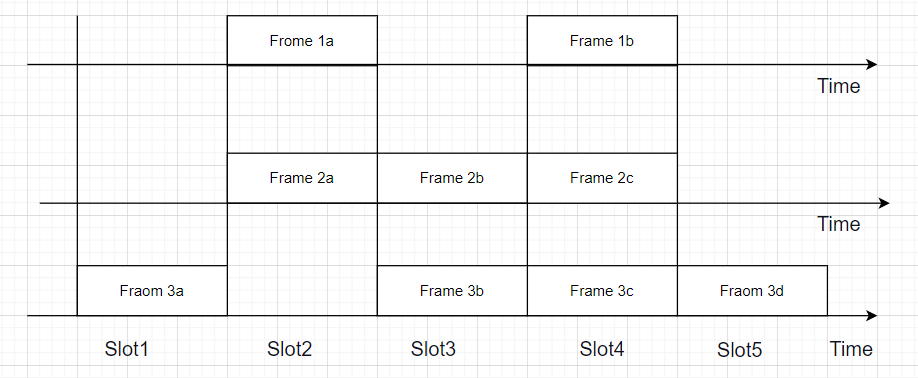
Figure showing Slotted ALOHA
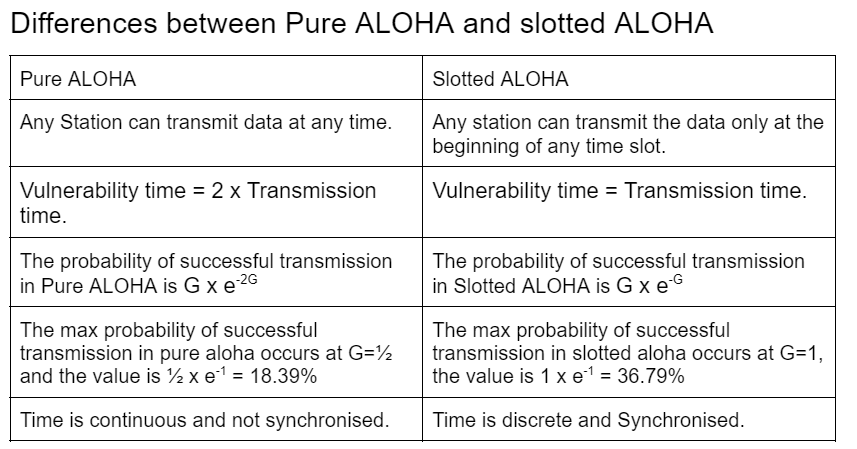
Figure showing difference between Pure ALOHA and Slotted ALOHA
Conclusion
From the above discussion, we can say that the slotted aloha is better than pure aloha because pure aloha has a successful transmission rate of 18.39%. In comparison, slotted aloha has a successful transmission rate of 36.79%.





