Introduction
Assume you've created a table of records and want to change it so that only the structure within the table changes, rather than the entire table. How are you going to do it? Well, We have a great answer to that question, i.e., the ALTER TABLE COMMAND in SQL.

Source: Meme Generator
There are a plethora of use cases of the ALTER table command. It is used to add, delete, or update the data in a schema. Moreover, Alter table command can ADD or DROP various constraints on an existing table. In this article, we will discuss all the potential use cases along with the demo examples.
Recommended topics, Coalesce in SQL and Tcl Commands in SQL
ALTER command: ADD a new Column
The following syntax adds a new column in an existing table.
Syntax:
|
ALTER TABLE tableName ADD(columnName datatype); |
Consider the CUSTOMERS table having the following records:−

If we use the above command to add a new column name gender in the database without affecting the existing database, we will write the following code to make changes in the table.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CUSTOMERS ADD GENDER char(1); |
To see the changes made by the alter command, we need to specify the SELECT statement:
| SELECT * from CUSTOMERS; |
Now we can see that the table has been changed, and there is a new column named GENDER in it, while the rest of the column remains unaffected.

ALTER command: Add multiple new columns
The following syntax adds multiple columns into an existing table:
Syntax:
|
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD( column1_name datatype, column2_name datatype, ... columnN_name datatype); |
Example: Let's add two more columns, Price and Country, into our table CUSTOMERS.
Query:
|
ALTER TABLE CUSTOMERS ADD( Price float, Country Varchar); |

ALTER command: Remove a column
To drop/remove a column from an existing table, use the following syntax.
Syntax:
| ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name; |
Example: Let's say you want to delete the Column City from the table.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CUSTOMERS DROP COLUMN City; -- removes the column with name City from the table |
| SELECT * from CUSTOMERS; |

ALTER command: MODIFY THE DATATYPE
To change the data type of any column in a table, use the syntax below. We can change the data type from one already existing to another using this command.
Syntax:
| ALTER TABLE table_name MODIFY COLUMN column_name datatype; |
Example: Let's change the data type of Price from float to INT.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CUSTOMERS MODIFY COLUMN Price INT; |
Now, whenever we add the records for the Price column using the INSERT statement, it will only accept the integer values.
ALTER command: RENAME THE COLUMN NAME
The following syntax is used to rename the column name from an existing name to any desired name.
Syntax:
| ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME COLUMN column_name TO new_Column_name; |
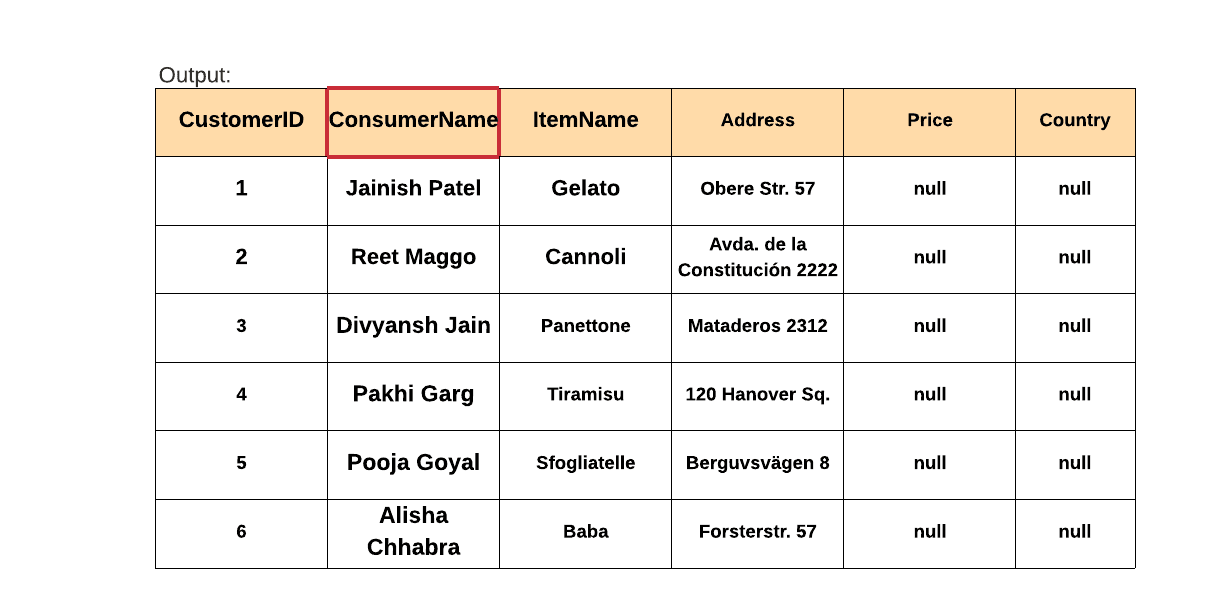
Example: Let's rename the CustomerName Column to ConsumerName:-
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CUSTOMERS RENAME COLUMN CustomerName TO ConsumerName; |
| SELECT * from CUSTOMERS; |
ALTER command: RENAME TABLE'S NAME
The following syntax is used to rename the table's name from an existing table name to any desired name.
Syntax:
| ALTER TABLE table_name RENAME TO new_table_name; |
Example: Suppose the table above has a table name CUSTOMERS, and you want to rename it to CONSUMERS, then you can do this by the following command.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CUSTOMERS RENAME TO CONSUMERS; |
Now let us see some examples for altering the Constraints. Constraints are nothing but the rules defined on the data being inserted in the columns of a table in a database.
ALTER command: ADD/DROP Constraints
There are six constraints available in SQL:
- NOT NULL
- CHECK
- UNIQUE
- PRIMARY KEY
- FOREIGN KEY
-
DEFAULT
Let us look at some of the examples through which we can add/drop constraints using the ALTER TABLE COMMAND.
ADD NOT NULL Constraint
Let's add the constraint NOT NULL to the ItemName column:
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CONSUMERS MODIFY ItemName Varchar NOT NULL; |
DROP NOT NULL Constraint
To drop the NOT NULL constraint from a column, we will change the constraint from NOT NULL to NULL.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CONSUMERS MODIFY ItemName Varchar NULL; |
ADD CHECK Constraint
Let us add the constraint for the Price column to accept the order above 1000.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CONSUMERS ADD CONSTRAINT CheckConstraint CHECK ( Price >= 1000 ); |
DROP CHECK Constraint
The following SQL query will drop the CHECK constraint from the table.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CONSUMERS DROP CONSTRAINT CheckConstraint; |
ADD UNIQUE Constraint
Let us add the constraint for the CustomerID to be UNIQUE throughout the table.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CONSUMERS ADD CONSTRAINT UniqueConstraint UNIQUE ( CustomerID ); |
Drop UNIQUE Constraint
The following SQL query will drop the UNIQUE constraint from the table.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CONSUMERS DROP CONSTRAINT UniqueConstraint; |
ADD Primary Key
Let us make the CustomerID as a Primary Key of the table CONSUMERS:
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CONSUMERS ADD PRIMARY KEY (CustomerID); |
Drop Primary Key
The following SQL query will drop the PRIMARY KEY from the table.
Query:
| ALTER TABLE CONSUMERS DROP PRIMARY KEY; |
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What exactly is the use of the ALTER TABLE command in SQL?
Ans: The SQL ALTER TABLE command allows you to modify the structure of a table in SQL. In a database, you may add, delete, or alter tables. Furthermore, you may change the constraints associated with a table, such as UNIQUE or NOT NULL.
-
After changing it to the new name, can we see the entire table with its previous name?
Ans: No, We can not see the entire table because we have changed the table name, so we will have to print the new name and delete the old name from all the alterations we have done in the commands.
-
How to add a new column with default value using ALTER TABLE command?
Ans: The ALTER command can also add a new column with a default value to an existing table. The default value is used when no value is inserted into the column. The syntax is as follows:
|
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD( column-name datatype1 DEFAULT some_value ); |




