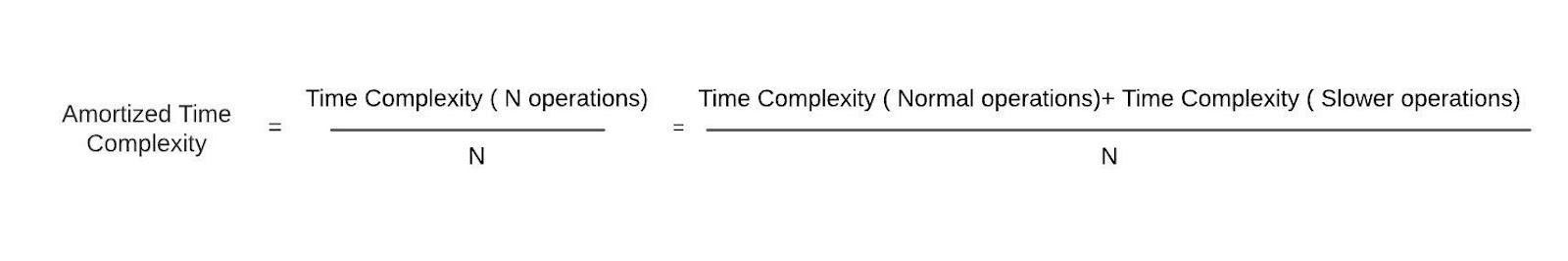Introduction
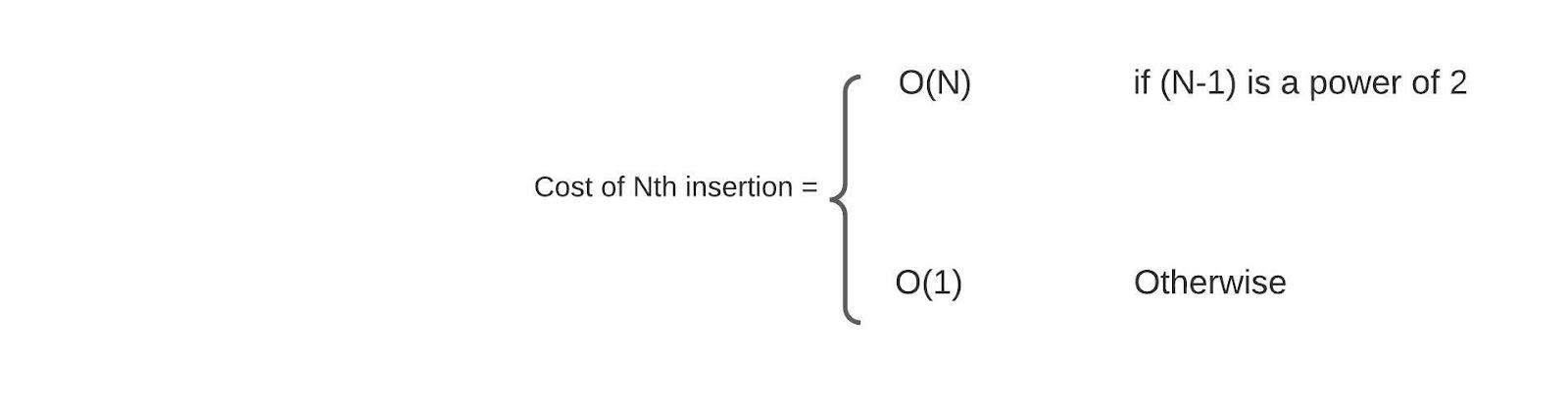
Amortized analysis is a method for analyzing a sequence of operations in an algorithm and gives the average time or space taken by the algorithm over the complete sequence. It is useful when a few operations in the sequence are very slow, and others are faster to execute. Amortized time complexity in data structures analysis will give the average time taken per operation, which will be better than worst-case time complexity. The Data Structures for which we need to study ‘amortized time complexity in data structures’ include Dynamic array, Disjoint sets, Hash Tables, etc.

Recommended topic, kth largest element in an array , hash function in data structure
Aggregate Method
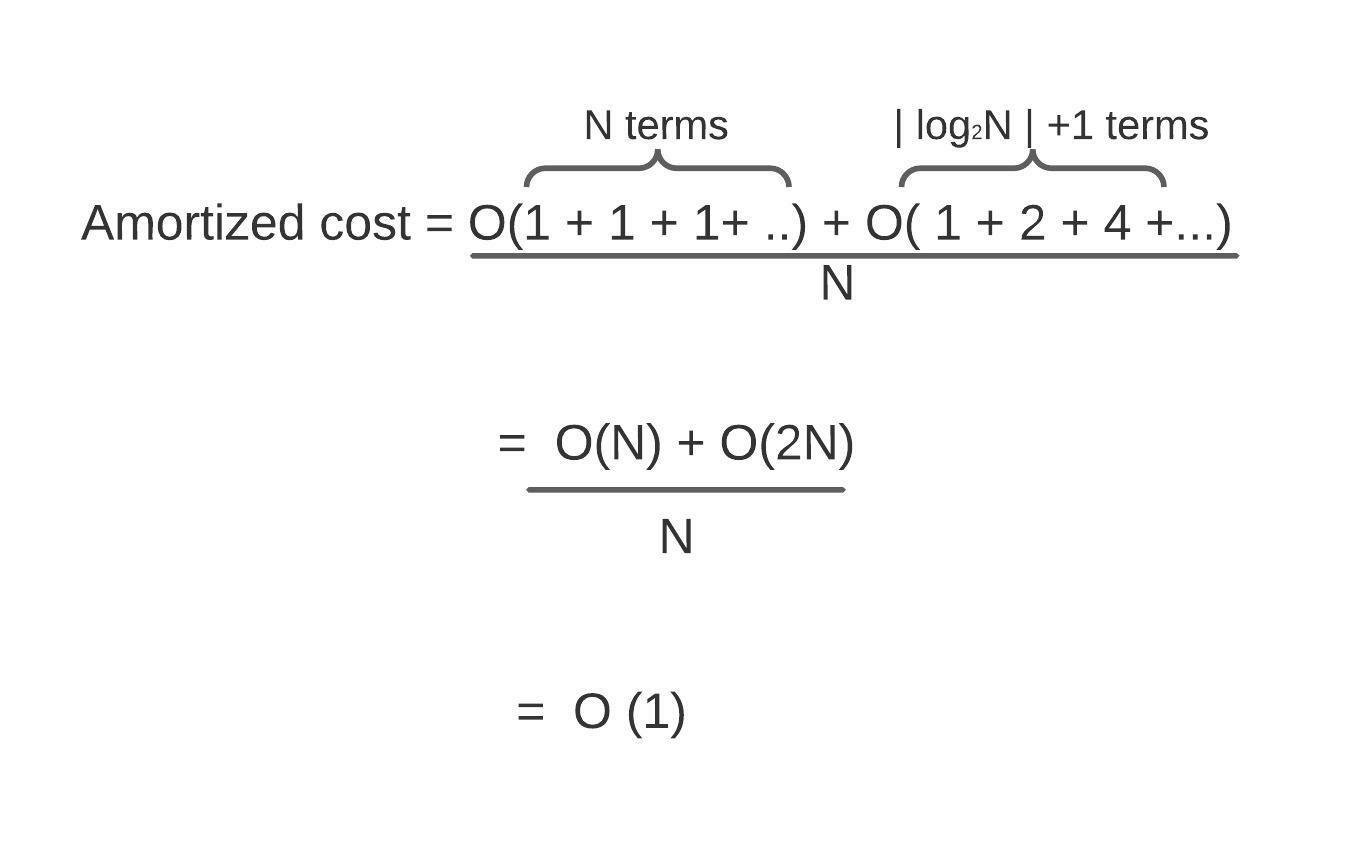
This section will discuss the method used for calculating amortized time complexity in data structures. The aggregate method calculates the average time complexity of operations in the amortized analysis by using the following mathematical formula: