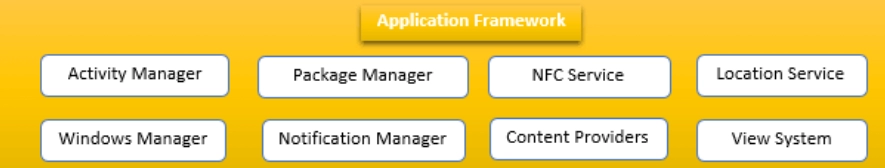
Android Application Architecture
Application architecture is a consistent blueprint that must be created before the commencement of the development process. This strategy explains how the various application components should be arranged and linked together. It gives standards that should be followed during the development process and demands some sacrifices that will help you build a well-written application that is more testable, extendable, and maintainable in the end.
According to the books, an excellent Android application should provide a solid separation of concerns and drive the UI from a model. Code that does not interact with the user interface or the operating system should not be in an Activity or Fragment. Keeping the code as clean as possible will allow you to avoid dozens of new lifecycle problems.

Source: Official Android Documentation
UI Layer
The UI layer is to displays application data on the screen. The UI should be updated to reflect the changes whenever the data changes, whether due to user activity (such as clicking a button) or external information (such as a network response).
UI elements consist of various views, and State holders contain Model Classes that hold data and bind its logic to the UI.
Data Layer
An app's business logic is stored in the app's data layer. The business logic provides your app value; it is made up of rules that govern how your app creates, saves, and modifies data.
The repository classes are in charge of Data exposure to the rest of the app and contain business logic.
The data source class should interact with a single data source, a file, a local database, or a network source. Data source classes serve as a link between the application and the system for data operations.
Domain Layer
The domain layer is a layer that sits between the UI and data layers. The domain layer is in charge of encapsulating complicated business logic and simple business logic shared by numerous ViewModels. This layer is optional because all apps will not meet these requirements. It would be best to utilize it only when necessary, such as when dealing with complexity or promoting reusability.
This layer's classes are frequently referred to as use cases or interactors. Each use case should be in charge of a particular piece of functionality.
Recommended Best Practises
Data should not be stored in-app components.
Avoid defining your app's access points as data sources, such as activities, services, and broadcast receivers. Instead, they should only work with other components to retrieve the subset of data relevant to that entry point. Each software component has a relatively short lifespan, depending on how the user interacts with their device and the system's overall health.
Reduce dependencies on Android classes.
Your app's components should only use Android framework SDK APIs like Context and Toast. Other classes in your program can be abstracted away from them, improving testability and lowering coupling inside your app.
Maintain as much relevant and current data as feasible.
Users will access your app's functionality even if their smartphone is in offline mode. Remember that not all of your users have constant, high-speed access, and even if they do, they may experience poor reception in congested areas.
Conclusion
There are some great resources that Google officially recommends. You can look at iosched, an open-source Google I/O app.
You will get an idea of how developers write their code and some common mistakes that beginner developers make.
FAQs
-
Why is Android Linux-based?
Under the hood, Android is powered by the Linux kernel. Because Linux is open-source, Google's Android developers might alter the Linux kernel to meet their requirements. To avoid having to design their kernel, Linux provides Android developers with a pre-built, already maintained operating system kernel to begin.
-
Is Android a programming software?
Android is a mobile software stack that contains an operating system, middleware, and critical apps. The Android SDK includes the tools and APIs required to start developing applications for the Android platform in Java. Android does not make use of the Java programming language.
-
Is Kotlin an Android framework?
Kotlin is a new programming language that first appeared in the Android app development industry a few years ago. The more straightforward syntax and interoperability with Java make Kotlin even more appealing for native Android app development. In the case of Kotlin, simpler syntax means less code and faster development.
Key Takeaways
Cheers if you reached here!!
The purpose of this article was to introduce you to Android Architecture, its various types, good coding practices, and understand the basic core concept of Architecture in Android Development.
Recommended Reading:
Spring Boot Architecture
If you want to learn about OS History and Versions of Android, you can jump to this article which covers them in great detail.
However, learning never stops, and there is more to learn. So head over to our Android Development Course on the Coding Ninjas Website to dive deep into Android Development and build future applications. Till then, Happy Learning!