Android OS Versions
Google announced in August 2019 that the confectionary scheme would be discontinued and that future Android versions would utilize numerical ordering.
Android 10 was the first Android version to be released in numerical order.
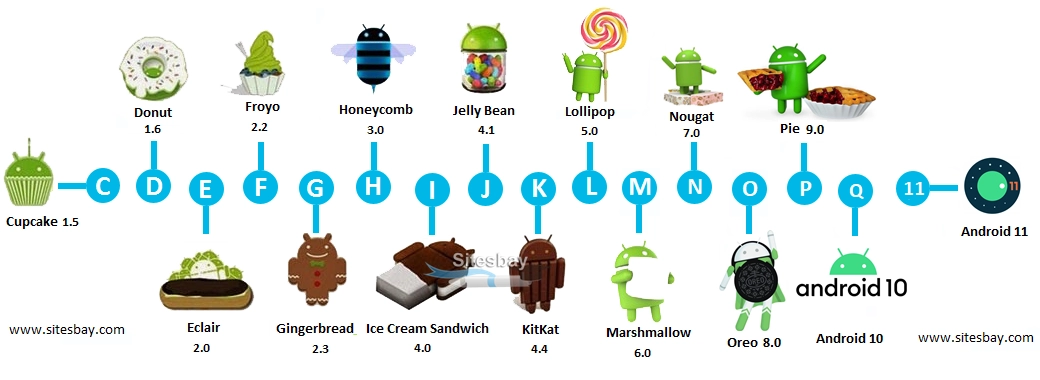
Source: Sitesbay
Android 1.0 to 1.1: No codename
In September 2008, Android officially released Android version 1.0. It is the very first version of the Android operating system. It includes a web browser that can display HTML and XHTML web pages, a camera, and a connection to an online email server (POP3, IMAP4, and SMTP).
Google Calendar, Google Sync, Google Maps, Google Search, Google Talk, Instant messaging, Media player, Notifications display in the status bar, background, YouTube video player, Alarm Clock, Calculator, Dialer, Pictures (Gallery), Wi-Fi and Bluetooth support are all included in this version.
Android 1.5: Cupcake
On April 27, 2009, Android 1.5 was released with the codename dessert item (Cupcake). It runs the Linux kernel 2.6.27. It includes a third-party virtual keyboard, MPEG-4 video recording, playback, a copy, and paste tool, animated screen translations, an auto-rotation option, the ability to post a movie to YouTube, photographs to Picasa, and the ability to view phone usage history.
Android 1.6: Donut
Android 1.6, codenamed Donut, was released on September 15, 2009. It has various new features such as voice and text entry search, bookmark history, contacts, web, say a string of text, faster camera access, the ability to choose multiple photographs for deletion, text-to-speech engine support, and WVGA screen resolutions.
Android 2.0 to 2.1: Eclair
Android 2.0, codenamed Eclair, was released on October 26, 2009. It was built with the Linux kernel 2.6.29. It includes several new features such as expansive account sync, Microsoft Exchange email support, Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to tap a Contact photo and select to call, SMS, the ability to search all saved SMS, MMS messages, the ability to delete the earliest message automatically when the described limit is reached, Minor API, and minor bug fixed.
Android 2.2 to 2.2.3: Froyo
Android 2.2 (Froyo) was released on May 20, 2010, on the Linux kernel 2.6.32. It has several features such as speed, memory, and performance optimization. JIT compilation, JavaScript engine into the Browser application, integration of Chrome's V8, support for Android Cloud to Device Messaging service, security upgrades, Adobe Flash support, and speed improvements are all included.
Android 2.3 to 2.3.7: Gingerbread
Android 2.3 (Gingerbread) was released on December 6, 2010, on the Linux kernel 2.6.35. It now supports extra-large screen sizes, has a revised user interface design with better simplicity and efficiency, enhanced copy/paste capability, chooses a word by press-holding, supports Near Field Communication (NFC), headphone virtualization, and a new Download Manager.
It has improved Nexus S bug fixes, audio or video chat with Google Talk, network performance for Nexus S 4G, Gmail app, battery efficiency, addressed a voice search bug and added Google Wallet compatibility for Nexus S 4G.
Android 3.0 to 3.2.6: Honeycomb
Android 3.0 (Honeycomb) was released on February 22, 2011, for the first Android tablet based on the Linux kernel 2.6.36.
It includes features such as a holographic user interface for tablets, added system Bar, simplified multitasking by tapping Recent Application in the System Bar, a redesign of the keyboard for faster typing, hardware acceleration, quick access to camera exposure, support for multi-core processors, UI refinements, connectivity for USB accessories, support for joysticks and gamepads, a high-performance Wi-Fi lock, improved hardware support, Google Books, and a fix for data connectivity issues with Bluetooth.
Android 4.0 to 4.0.4: Ice Cream Sandwich
Android 4.0.1 (Ice Cream Sandwich) was released on October 19, 2011, and was based on the Linux kernel 3.0.1. It was the last version of the Adobe System Flash player that was officially supported.
It introduces a slew of new features, including refinements to the Holo interface, a new Roboto font family, the separation of widgets in a new tab, integrated screenshot capture, improved error correction on the keyboard, improved copy and pastes functionality, a built-in photo editor, minor bug fixes, graphics improvements, spell-checking, and improved camera performance.
Android 4.1 to 4.3.1: Jelly Bean
Google launched Android 4.1 (Jelly Bean) during the Google I/O conference on June 27, 2012. It is built on the Linux kernel 3.0.31.
It includes the following updates: a smoother user interface, improved accessibility, expandable notifications, a bug fix for the Nexus 7, one-finger gestures to expand/collapse notifications, lock screen improvements, multiple user accounts (tablets only), a new clock app, Bluetooth low energy support, volume for incoming calls, 4K resolution support, native emoji support, and bug fixes for the Nexus 7 LTE.
Android 4.4 to 4.4.4: KitKat
Google released Android 4.4 on September 3, 2013. (KitKat). Its code name was initially "Key Lime Pie." On October 31, 2013, Google began on Google's Nexus 5. The amount of RAM that Android should have is at least 340 MB.
Other devices which have less than 512 MB of RAM must be reported as low RAM devices. It includes new features such as a clock that no longer displays bold hours, wireless printing capability, WebViews based on the Chromium engine, sensor batching, a built-in screen recording feature, improved application compatibility, and a camera application that loads Google+ Photo rather than Gallery.
Android 5.0 to 5.1.1: Lollipop
On June 25, 2014, Android L was renamed Lollipop. On November 12, 2014, it was formally unveiled. Lollipop includes a redesigned user interface, support for 64-bit CPUs, print previews, material design, Project Volta for improved device battery life, multiple user accounts, audio input and output via USB devices, join Wi-Fi networks, support for multiple SIM cards, high-definition voice calls, device protection, and native Wi-Fi calling support.
Android 6.0 - 6.0.1: Marshmallow
On May 28, 2015, the Android 6.0 Marshmallow was released under the codename Android M for the Nexus 5 and 6 phones and the Nexus 9 tablet.
Android Marshmallow was released on October 5, 2015, for all Android smartphones. It includes new features like App Standby, Dozes mode to save battery life, native fingerprint reader support, runtime permission requests, USB-C connectivity, and Unicode 7.0 & 8.0 emoji support.
Android 7.0 to 7.1.2: Nougat
The Android operating system's major release was Nougat. The initial codename for it was Android N. On March 9, 2016, it was released as a developer preview and factory images for the Nexus device.
The final preview build was released on August 22, 2016, with the following features: file-based encryption, screen zoom, multi-window support, new Data Saver mode, JIT compiler makes app installation 75 percent faster, picture-in-picture support, support manager APIs, circular app icon support, send GIFs directly from the default keyboard, battery usage alerts.
Android 8.0 to 8.1: Oreo
Android 8.0 Oreo was the Android operating system's eighth major version. On March 21, 2017, it was initially made available for developer preview. On July 24, 2017, the final developer preview was made public.
On August 21, 2017, its stable version was released, which included several features such as picture-in-picture support, support for Unicode 10.0 emoji (5.0), restructured settings, adaptive icons, notification channels, notification dots, two times faster boot time, Google Play Protect, Integrated printing support, Neural network API, shared memory API, Android Oreo Go Edition, autofill framework, automatic light, and dark themes, and more.
Android 9.0: Pie
Android 9.0 Pie was the Android operating system's ninth major version. Google first announced it and released a preview version on March 7, 2018. On August 6, 2018, it was officially released. The clock has been shifted to the left of the notification bar, a screenshot button has been added, and the battery % is always displayed.
Android 10
Android 10 is the tenth version of the Android operating system. Android 10 is being developed under the codename Android Q. Google first announced it on March 13, 2019, and its first beta version was released on the same day, followed by its second beta on April 3, 2019.
On September 3, 2019, Android 10's stable version was launched. It has new rights to access location in the background, a floating settings panel, support for an AV1 video codec, fingerprint authentication support, and WPA3 Wi-Fi security.
Android 11
Android 11 is the eleventh big release of the Android operating system. It is the 18th version of the Android mobile operating system, released on September 8, 2020. Since Android 10, the alphabetic naming system based on deserts has been discontinued. As a result, this operating system has been labeled Android 11.
It includes features like Conversation, Accessibility where you can navigate through voice commands. Device controls for maintaining all devices in one place and privacy give more security to using a smartphone in today's generation.
Android 12
Android 12 is the twelfth big release and the nineteenth version of Android, the mobile operating system created by the Open Handset Alliance, led by Google. On May 18, 2021, the first beta was released. Android 12 was made available to the public on October 4, 2021, via the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and was made available to supported Google Pixel devices on October 19, 2021.
It includes features like User Interface, including larger buttons, more animation, and a new look for home screen widgets. System services such as the WindowManager, system server, PackageManager, and interrupts have all seen performance boosts.
Apps requesting location data can now be limited to approximate rather than exact location data. The fast settings toggle now include controls to block apps from using the camera and microphone system-wide. If they are active, an indicator will appear on the screen.
Android 13
Tiramisu, the codename for Android 13, is a planned major update of the Android smartphone operating system. On February 10, 2022, the first preview version was released.
First, the split-screen has a somewhat different UI, with rounded corners on the two apps. Although no apps use it, a new photo picker is launched. The Quick Settings pulldown animation has been modified, tiny modifications have been made to popup windows and the media player, and vibration can now be turned off completely.
The user's function has been enhanced, with the ability to choose which specific user can access apps. To safeguard privacy, none of the apps will include any sensitive information. This version allows third-party apps to use themed (monochrome) icons.
Check this out : usb debugging
FAQs
-
Why is Android better than iOS?
With native apps, both iOS and Android can make video calls. The disadvantage of iOS is that it has less flexibility and customizability than Android. In comparison, Android is more free-form, which translates to a lot greater phone selection in the first place and more OS customization choices after you're up and running.
-
How can I determine which Android operating system I have?
Open the Settings app on your phone—Tap System near the bottom, then System Update. Check your Android version and Android security update for further information.
-
Is Apple older than Android?
People have pointed out that Android began in 2003 and was purchased by Google in 2005. That was two years before Apple's first iPhone, which debuted in 2007. They worked on it for years before it was included in the first iPhone.
Key Takeaways
Cheers if you reached here!!
This article aimed to introduce you to Android History and its version and features of Android OS.
Recommended Reading:
Difference Between Analog and Digital Computer
If you want to learn about Android Studio, you can jump to this article which covers them in great detail.
However, learning never stops, and there is more to learn. So head over to our Android Development Course on the Coding Ninjas Website to dive deep into Android Development and build future applications. Till then, Happy Learning!







