Introduction
Ansible is a simple, open-source IT engine that automates application deployment, intra-service orchestration, cloud rendering, and many other IT tools. Ansible is easy because it does not use any agents or custom security infrastructure. Ansible uses a playbook to describe change functions. The playbook uses a very simple language, i.e., YAML (a human-readable language measurement language), which is very easy for people to understand, read, and write.
If you are preparing for an Ansible interview in the future and are looking for a quick guide before your interview, then you have come to the right place.
This blog consists of the Top 90 Ansible Interview Questions and Answers. Let's have a look at them.

Most Recommended Topic: Html interview questions
Beginner Level Ansible Interview Questions For Freshers
1. What is Ansible?
Ansible is a configuration management system. Used for setting up and managing infrastructure and applications. Allows users to use and update applications using SSH without installing an agent on the remote system.
2. Explain Configuration management.
Configuration management in Ansible is the practice of defining and maintaining an IT infrastructure using scripts known as Playbooks. Ansible allows you to specify how systems should be configured, including software installations, configuration files, and system updates. Configuration management helps you organize your operations and enhance the security.
3. What is the use of Ansible?
Ansible manages IT infrastructure and delivers software applications to remote nodes. Ansible lets you use the app in multiple nodes with a single command. However, there is a need for some programming knowledge to understand Ansible texts.
4. What are the features of Ansible?
Ansible has the following features:
- Agentless: Unlike Puppet or Chef, no software or agent controls the nodes
- Python: Built on Python, which is very easy to read and write and is one of the most vital programming languages.
- SSH: Ensuring the anonymous network makes it secure and easy to set up
- Push architecture: The main idea is to push multiple codes to prepare and execute actions on client nodes.
- Set: This is very easy to set up with a shallow learning curve. It is open-source; hence, anyone can access it.
- Manage inventory: Machine addresses are stored in a simple text format, and we can add different sources of information to pull the list using plug-ins like OpenStack, Rackspace, etc.
5. What are the benefits of Ansible?
Ansible has many capabilities, including:
- It only requires the SSH service running on the targeted machines.
- Python is the only dependency needed, and, fortunately, many programs come pre-installed.
- It requires minimal resources; therefore, there is a low overhead.
- It becomes easy to read and understand as these activities can be written in YAML.
- Unlike other tools, most of which are process-oriented, Ansible is declarative, describes the desired condition, and fulfills the requirements necessary to achieve it.
6. What is the Ansible Galaxy?
Ansible can communicate with clients suspended in the command line using the Ansible command. It also allows you to make automatic stops using the Ansible-playbook command. To create a primary index structure, you can use the Ansible-integrated tool, the ansible-galaxy.
7. What are the requirements of the Ansible server?
If you are a Windows user, you need to have a virtual machine where Linux can be installed.
8. Describe the different parts of Ansible.
The following are some parts:
- Inventory
- Playbooks
- It plays
- Jobs
- Modules
- Roles
- Holders
- Facts
- Templates
- Variable
9. What is Ansible Inventory and its types?
An Ansible inventory is a file or collection of files that specifies the hosts on which Ansible should operate. The inventory files list the IP addresses of the target systems and organize them into groups, which allows you to execute and manage tasks on multiple hosts. There are two main types of Ansible inventory:
- Static Inventory: This is the traditional form of Ansible inventory. It consists of static and manually maintained files where you define your hosts and groups. It is simple to set up and suitable for smaller environments.
- Dynamic Inventory: Dynamic inventories are generated dynamically using scripts. These scripts query the cloud providers or other data sources to discover and define hosts and groups. Dynamic inventories are especially useful in large and rapidly changing environments.
10. Is Ansible an open-source tool?
Yes, Ansible is an open-source tool because we can rewrite modules. The automated open-source engine provides the source for automated applications as needed.
11. Name the language in which Ansible is written?
Ansible is written in Python and PowerShell.
12. Distinguish between Ansible Playbooks and Roles.
The following are the differences between Roles and Playbooks:
| Roles | Playbooks |
|---|---|
| A set of tasks and additional files to configure the hosts | A mapping between roles and hosts |
Roles are considered group activities in a single container. We can use the MySQL setup role and postfix setup. Examples: Web Servers etc. | The playbook points out what is going on there. Sometimes a playbook contains one play, but we can get the number as needed. Example: site.yml, web servers.yml, etc. |
13. What are the changes to Ansible?
The variables are the same as the variables in another programming language. These are given the amount used to determine playbooks. We can also apply the conditions using variables:
- hosts: your host
vars:
port_Tomcat: 2050Here, a portable Tomcat port is defined, and the value given to the port number is 2020.
14. Differentiate between a variable name and an environment variable?
The following are the differences between Variable Name and Environmental Variable:
| Variable Name | Environment Variable |
|---|---|
| We need to add a string to create dynamic names. | Existing variables are required to achieve environmental variables. |
| We can define more variable names by adding character units. | We should use the Ansible playbook to create variables. |
| Ipv4 address is used for dynamic variable names. | Use [{ansible_env.SOME_VARIABLE_A}} to get remote environmental variables |
15. What are CDs and CIs, and what is Ansible's relationship with them?
The CD represents continuous delivery, and the CI represents continuous integration; both ways to develop software.
On CD, engineers are developing software that can be downloaded to production at any time. The CI, on the other hand, contains each engineer that loads a standard set combination (usually daily), which results in multiple daily combinations. Ansible is an ideal CI / CD process tool, which provides stable infrastructure for providing a targeted location and sending a request to it.
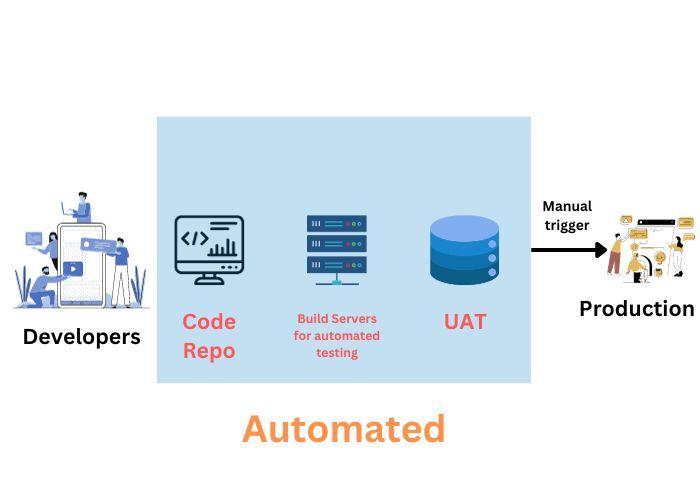
16. Explain what a “playbook” is.
The playbook contains a series of YAML-based files that send commands to remote computers via text. Engineers can optimize all complex areas by transferring text to required systems instead of using individual commands to remotely configure computers from the command line. Playbooks are one of Ansible's strongest retailers and are often referred to as the building blocks of the tool.
17. What is the Ansible Tower?
It is a business-based web-based solution that enhances Ansible access to other IT teams by installing an easy-to-use UI (user interface). Its main function is to serve as the basis for all the organization's default activities, allowing users to monitor the configuration and make quick submissions.
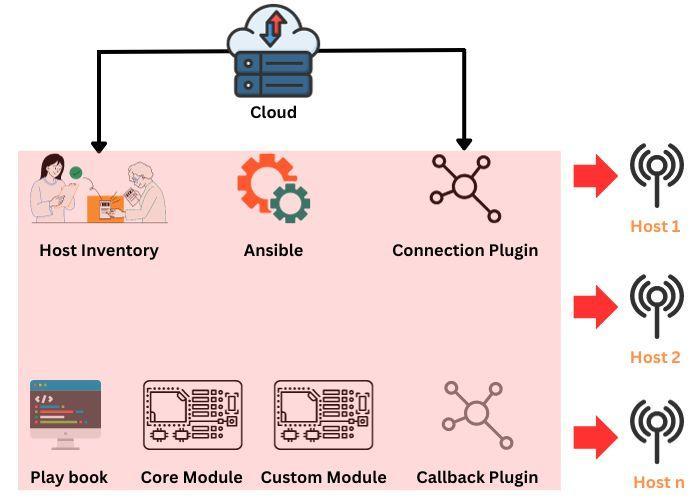
18. Explain how Ansible works.
Ansible is divided into two types of servers: control machines and nodes. Ansible is installed on a control computer, and the control machines manage the nodes via SSH.
The control machine contains a configuration file that replaces the node system. Ansible uses the playbook on the controller to extract modules from node systems. Since Ansible is useless, there is no need for an external company tool to connect nodes.
19. What is the Code difference between JSON and YAML?
JSON:
{
"object": {
"key": "value",
"array": [
{
"null_value": null
},
{
"boolean": true
},
{
"integer": 1
},
{
"alias": "aliases are like variables"
}
]
}
}
YAML:
---
object:
key: value
array:
- null_value:
- boolean: true
- integer: 1
- alias: aliases are like variables20. Describe ad hoc commands with an example.
Ad hoc commands are simple, single-line commands used to perform a specific task. You can think of ad hoc instructions as another way to write playbooks. An ad hoc command example is
Command: ansible host -m netscaler -a "nsc_host=nsc.example.com user=apiuser password=apipass"21. Differentiate between ansible and chef?
The following are the differences between Ansible and Chef:
| Ansible | Chef |
|---|---|
| It is easy to set up | It is not easy to set up |
| It is easy to manage | It is not easy to manage |
| Python is used(YAML) | Ruby is used(DSL) |
| The self support package is about $5000 per year | standard plans start at $72 anually per code |
22. What is a YAML file, and how do we use it in Ansible?
YAML files are like any other formatted text file with a few rules similar to those of JSON or XML. Ansible uses this syntax in playbooks as it is more readable than other formats.
23. How can YAML files be effectively utilized in prominent programming languages like JAVA, Python, and more?
In prominent programming languages like Java and Python, YAML files are commonly used for configuration and data serialization. In Python, libraries like PyYAML allow you to parse and generate YAML files easily. On the other hand, Java has libraries like SnakeYAML for similar purposes. For other programming languages, YAML files can be parsed using external libraries or built-in methods.
24. Where are tags used?
Tags are attributes that set the physical structure, games, functions, and roles. If a comprehensive playbook is needed, it is beneficial to use part of it instead of everything. This is where tags are used.
25. What protocol does Ansible use to communicate with Linux and Windows?
For Linux, the protocol used is SSH.
In Windows, the protocol used is WinRM.
26. Explain Ansible tasks.
A task is a unit of Ansible action. It helps by breaking the policy of setting up small files or code blocks. These blocks can be used to perform the process automatically. For example, installing software or a software update:
Command: Enter <package_name>
Command: update <software_name>27. Explain Idempotency.
Idempotency is an Ansible feature that ensures that only the necessary changes are possible. One or more tasks can be performed multiple times, but it will not replace anything already fixed or working properly. It can be used in Ansible using the created attribute. For example, if the task is to create a directory on the server, then the directory will only be created if it does not already exist. Idempotency ensures quality assurance for both users and software teams.
28. What are the different strategies used to evaluate Ansible projects?
There are three strategies for evaluating Ansible projects:
- Manual Run: Ensures that the system is in custom mode. Although it is an easy way to test Ansible projects, it increases the risk because the results in the test site may not be the same as in the production area.
- Check mode: Check mode lets you know what modules would have changed if the playbook had been used without testing mode. It lets you check whether the project is behaving the way you want it to. Test mode is similar to simulation and is a less commonly used method in Ansible.
- Asserts: It repeats how the test works in programming languages like Python. It ensures that the system has reached the real state, not as an analogy, which you get in test mode. The vaccine shows that the worker did what he was expected to do.
29. How can you upgrade the Ansible reboot module to more than 600 seconds?
The Ansible reboot module can be upgraded for over 600 seconds using the syntax below:
- name: Restart the Linux system
restart:
restart_the closing time: 100030. How to use Docker modules in Ansible?
Docker modules require a Python Docker SDK installed on the host using Ansible.
With Python 2.7 or Python 3, it can be installed using the following:
$ pip insert docker.
With Python 2.6, a version before 2.0 will be required. It can be installed using the following:
$ pip install 'docker-py> = 1.7.0'31. How to install Ansible on the CentOS system?
It can be done easily in two simple steps:
1: Set up the EPEL Repository
EPEL (Extra Enterprise Linux Packages) is an open-source and free community-based repository project from the Fedora team that provides high-quality Linux distribution software packages, which include RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux), CentOS, and Scientific Linux.
The Ansible package is not available in the default repositories, so we will enable the EPEL repository via the command below:
sudo rpm -ivh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
It will download all the required packages that will be required to install Ansible.
2: Install Ansible
Now your EPEL repository has been added, all you have to do is install Ansible using the command below:
yum insert ansible -y
That's all! It is a two-step process that takes just a minute!
If you wish to check out the Ansible version installed on your system, use the command below:
ansible -version32. Explain a few basic words or concepts in Ansible.
Here are some of the keywords used when responding to Ansible:
- Control Machine: The Control Machine is responsible for providing managed servers. The machine on which Ansible is installed.
- Inventory: An inventory is a launch file that contains information about the various servers you own.
- Playbook: A code file written in YAML format. The playbook contains tasks that need to be done or spontaneously.
- Task: Each task represents one process that needs to be done, e.g., enter the library.
- Module: A module is a set of tasks that can be performed. Ansible has 100 built-in modules, but you can also customize them.
- Role: A Proper role is a predefined way of organizing playbooks and other files to facilitate sharing and reusing supply components.
- Play: The work done from beginning to end, or the making of a playbook, is called a game.
- Fact: Fact is a global variable that stores information about a system, such as virtual network connections or operating systems.
- Handlers: Used to activate a service condition, such as restarting or stopping a service.
33. Define the concept of infrastructure as a Code (IaC).
Infrastructure such as Code (IaC) is the process of managing and using data servers, storage systems, system configuration, and network infrastructure.
In traditional configuration management systems, minute-by-minute configuration modifications are required in the hands of system administrators and the IT support team. But with IAC, all configuration information is managed and stored in a standard file system, where the system automatically controls infrastructure changes and deals with system configuration.
Therefore, we do not need much effort as everything is managed and automated following the IAC method. Tools like Ansible can be used to use the IAC method.
Must Read Powershell Interview Questions




