Why do we need Application Virtualization?
Application infrastructure virtualization also makes sure that each application deployed for a big data analysis has access to the computing power required at the right time based on its relative priority.
By designing application virtualization in addition to infrastructure, the highest priority applications have top-priority access to the data and resources, this thing can be ensured.
One thing more, application infrastructure virtualization makes it easier to run applications on several devices, and previously incompatible applications can be run at the same time on the same physical machine. Creating multiple versions for different Operating Systems is not required.
Big data platforms implemented to support highly distributed, data-intensive applications will run efficiently and faster in a virtual environment.
Now, let’s have a glance at the working of Application Virtualization.
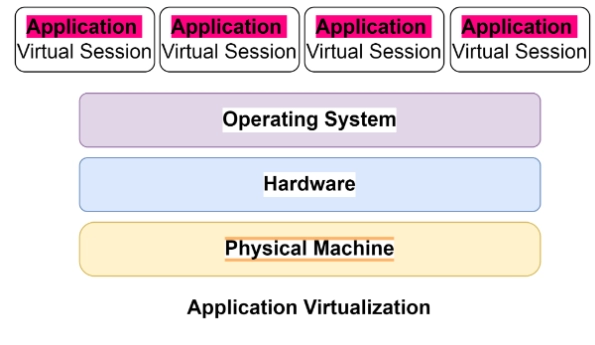
How Application Virtualization works?
The most usual technique to virtualize applications employs the server-based approach. This means an Information Technology administrator implements remote applications on a server in an organization’s data center or via a hosting service.
The administrator then uses application virtualization software to deliver the applications to a user’s device. The user is then able to access and use the application as if it were locally installed on their device, and the user’s actions are conveyed back to the server for execution.
You might wonder how Application Virtualization is of any benefit.
Advantages of Application Virtualization
-
As the data is not operated or stored on the user’s devices, no data breach occurs, should the device become compromised. The user’s device is just a display terminal. Application virtualization software provides admins central control over which users can access which applications. If a user’s app permissions within an organization change, the admin can easily remove that user’s access to a specific application. This whole mechanism increases security.
-
Application virtualization supports incident management by resolving several adverse device events by just refreshing a virtualized image and restoring the device’s environment to its last state.
-
Allows cross-platform operations. For instance, running Android apps on Windows, iOS, etc. Consequently, the organization spends less on computing hardware because employees only require basic machines to access the apps they need for work. App virtualization also enables users to use applications that normally would not work on their machines’ OS(operating system) as the app is actually running on the centralized server. This provides Scalability.
Along with these advantages, Application Virtualization comes with some disadvantages as well.
Also see, Cloud Computing
Drawbacks of Application Virtualization
-
Network outages or server problems add to the risk of system-wide failures.
-
Streaming apps for users is an interesting technology. But they have their own bandwidth requirements. They only work with specific bandwidths, if the user does not have that specific bandwidth, he/she cannot use the application.
- The Big Data environment is required to have the exact level of predictability and repeatability to ensure that the applications have access to the required data and resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the supporting solutions associated with application virtualization?
Few such supporting solutions are Citrix XenApp, Parallels Remote Application Server, VMware ThinApp, and Microsoft App-V.
Is it always a good idea to virtualize all Big Data applications?
No, it is not wise to virtualize all big data-related applications. For instance, a text analytics application may run best in a self-contained environment and virtualization would not add any benefit.
How does Application Virtualization add efficiency to the application?
It adds efficiency as it aids the easy distribution of resources according to the relative value of applications. In other words, the most important applications can receive top priority to draw from pools of available computing and storage capacity as needed.
Conclusion
This article extensively discusses Application Virtualization, its properties, advantages, drawbacks, and applications.
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding Application Virtualization, and if you would like to learn more, check out our articles on Coding Ninjas Blogs.
You can refer to our Interview Experiences, Problems, and Guided Paths to strengthen your placement preparation.
Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Coding!







