Classification of Movie Reviews with Tensorflow
We’ll build a simple model using Tensorflow to classify the movie reviews as positive or negative.
We’ll use the IMDB Movies dataset for this task. The dataset is available in the Tensorflow library. It has 50,000 polar reviews, binary classified as either positive or negative. Out of 50K, 25K are for training, and 25K are for testing purposes.
Importing Necessary Libraries
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Loading the dataset and splitting it into Training and Testing
train_data, test_data = tfds.load(name="imdb_reviews", split=["train", "test"], batch_size=-1, as_supervised=True)
train_examples, train_labels = tfds.as_numpy(train_data)
test_examples, test_labels = tfds.as_numpy(test_data)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
The testing and training set both contain 25,000 reviews.
Example Review
train_examples[:1]

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output: This was an absolutely terrible movie. Don't be lured in by Christopher Walken or Michael Ironside. Both are great actors, but this must simply be their worst role in history. Even their great acting could not redeem this movie's ridiculous storyline. This movie is an early nineties US propaganda piece. The most pathetic scenes were those when the Columbian rebels were making their cases for revolutions. Maria Conchita Alonso appeared phony, and her pseudo-love affair with Walken was nothing but a pathetic emotional plug in a movie that was devoid of any real meaning. I am disappointed that there are movies like this, ruining actor's like Christopher Walken's good name. I could barely sit through it.
train_labels[:1]

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output: array([0])
This review is negative because corresponding to the 1st index, we have 0 stored in the labels array.
Building the Model
We’ll convert the text into embeddings vectors to represent the text data. We’ll be using pre-trained text embedding as the first layer so that we don’t have to do all the hefty text-preprocessing.
We’re using this model for text embedding and transfer learning.
There will be 16 neurons in the first and the only hidden layer in our model and one in the output layer. The last neuron will predict 1 or 0 depending on the positive or negative review.
model = "https://tfhub.dev/google/nnlm-en-dim50/2"
hub_layer = hub.KerasLayer(model, input_shape=[], dtype=tf.string, trainable=True)
model = tf.keras.Sequential()
model.add(hub_layer)
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'))
model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(1))
model.summary()

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output
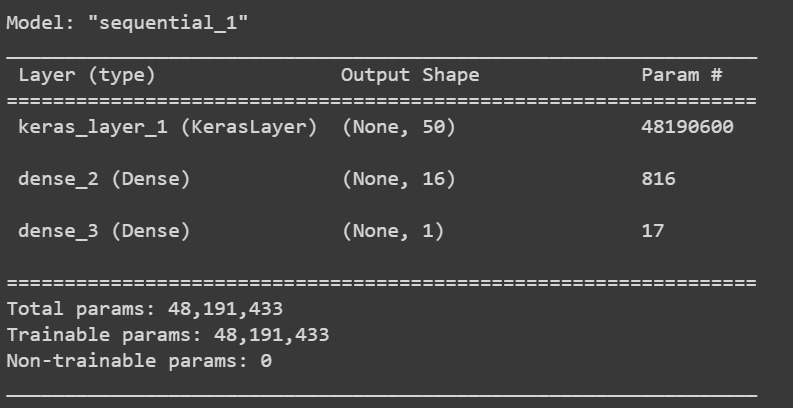
Configuring the Model
Since our task is binary classification, we’ll use the Binary Crossentropy to calculate the loss and Binary accuracy metrics to evaluate the model.
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[tf.metrics.BinaryAccuracy(threshold=0.0, name='accuracy')])

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Training the model with the Training Dataset
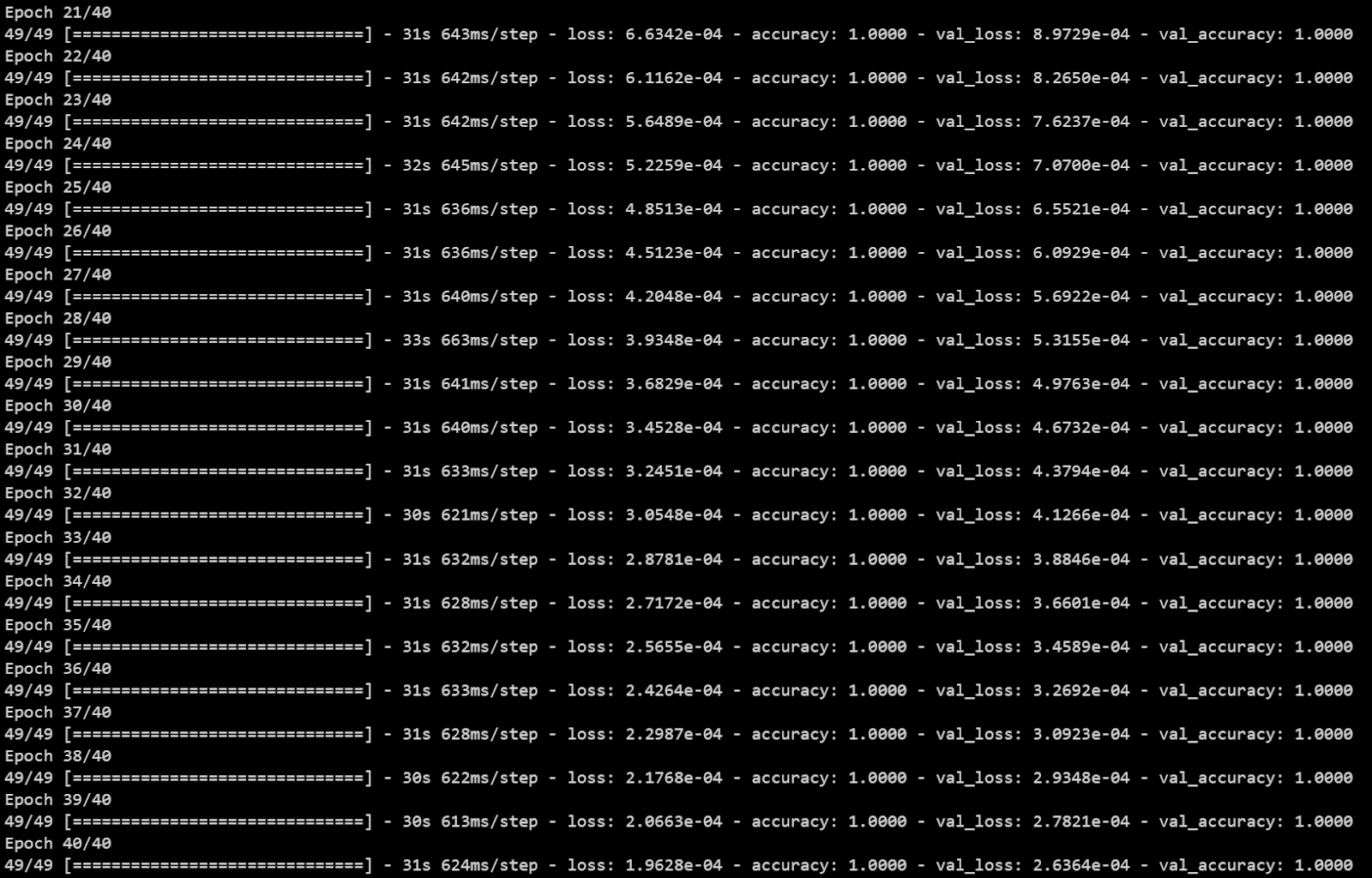
history = model.fit(train_examples, train_labels,
epochs=40,
batch_size=512,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
verbose=1)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output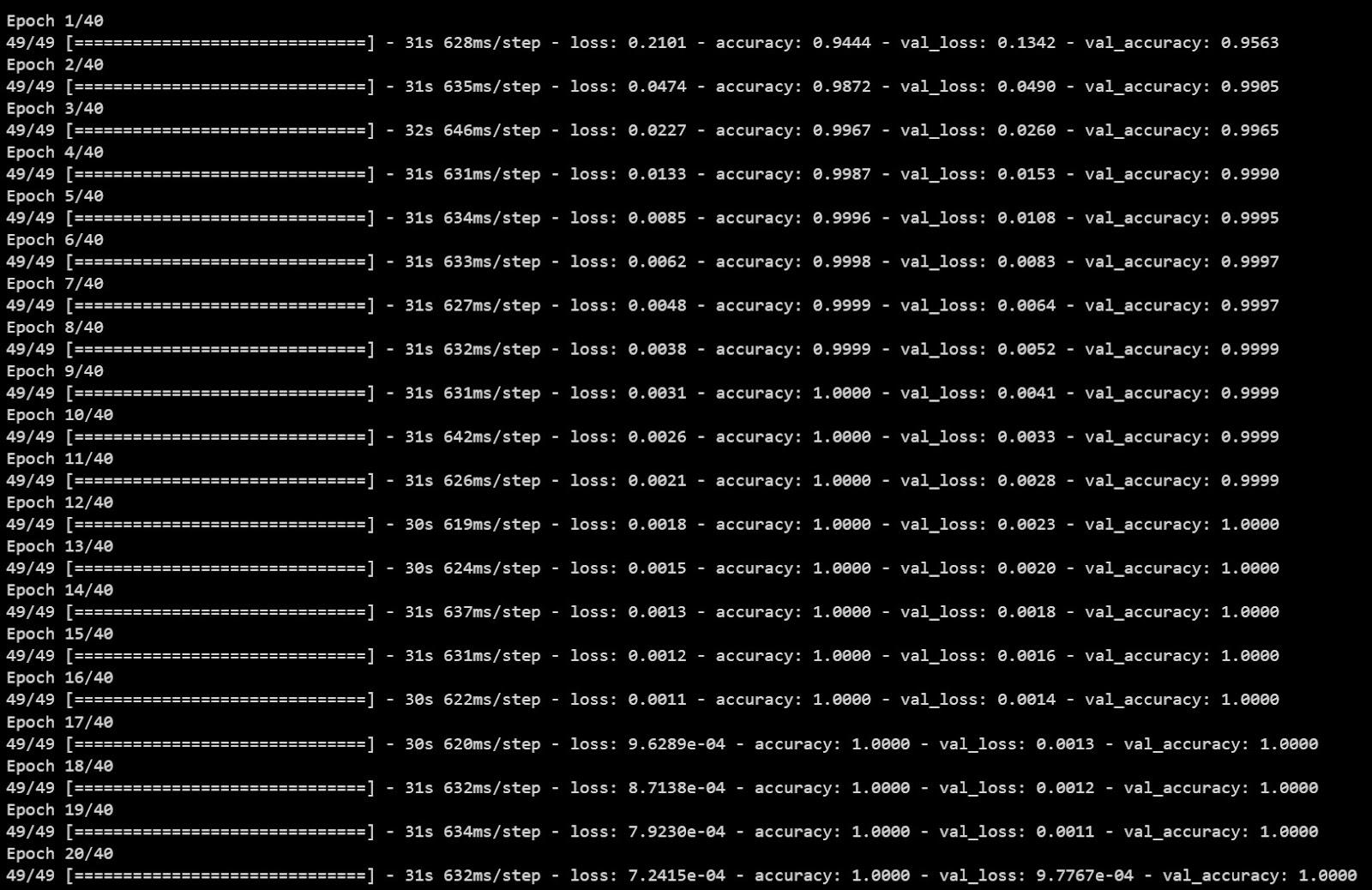
Evaluating the model’s performance with the Testing Dataset
results = model.evaluate(test_examples, test_labels)
print(results)

You can also try this code with Online Python Compiler
Output

Result
Our model gives an accuracy close to 84% with the unseen dataset. The loss is around 83%. Considering our model is elementary, the result is pretty good. We can increase the accuracy by changing hyperparameters or changing the number of hidden layers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the different types of datasets available in the TensorFlow library?
Ans. There are many types of datasets that are available in TensorFlow, such as:
- Audio Datasets
- Graphs type
- Image Datasets
- Image Classification
- Object Detection
- Text
Q2. What is ImageDataGenerator?
Ans. ImageDataGenerator is one of the features of tensorflow.keras API. We use it to perform data augmentation, such that we can train our model with different new combinations of data. With ImageDataGenerator, we do not generate new images directly, but the dataset images are transformed dynamically.
Q3. What are the basic steps in building an ML model using TensorFlow?
Ans. We can build a model with Tensorflow by following these easy steps:
- Installing and importing Tensorflow
- Loading the dataset
- Splitting the dataset in training and testing
- Initializing the model
- Configuring the model
- Training the model on the available dataset
- Evaluating the model on the unseen dataset
Q4. Who developed Tensorflow and why?
Ans. Google’s Brain Team developed Tensorflow with the sole intention of making Machine Learning and Deep Learning tasks easier for every individual. Tensorflow has many users ranging from novice to expert.
Key Takeaways
Check out this link if you are a Machine Learning enthusiast or want to brush up your knowledge with ML blogs.
If you are preparing for the upcoming Campus Placements, don't worry. Coding Ninjas has your back. Visit this link for a carefully crafted and designed course on-campus placements and interview preparation.










