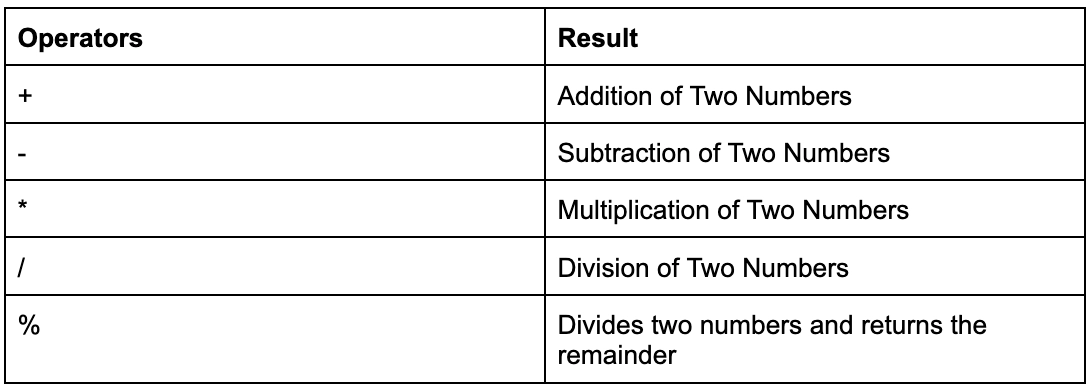
Arithmetic Operators in Java
These operators are mathematical operators that may be used to execute simple or complicated arithmetic operations on the operands, which are primitive data types. These operators are a collection of unary and binary operators that may be used on one or two operands. Let's have a look at the different arithmetic operators that Java has to offer.
Addition(+)
This is a binary operator that adds two operands.
Syntax:
num1 + num2
Example:
import java.io.*;
public class Addition {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num1 = 100, num2 = 200, sum = 0;
// Displaying the two numbers
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// adding the two numbers
sum = num1 + num2;
System.out.println("The sum = " + sum);
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output :
num1 = 100
num2 = 200
The sum = 300
Subtraction(-)
This is a binary operator that subtracts two operands.
Syntax:
num1 - num2
Example:
import java.io.*;
public class Subtraction{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num1 = 200, num2 = 100, diff = 0;
// Displaying the two numbers
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// subtracting the two numbers
diff = num1 - num2;
System.out.println("The Difference = " + diff);
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output :
num1 = 200
num2 = 100
The Difference = 100
You can also read about Java Destructor and Swap Function in Java
Multiplication(*)
This is a binary operator that Multiplies two operands.
Syntax:
num1 * num2
Example:
import java.io.*;
public class Multiplication {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num1 = 60, num2 = 40, res = 0;
// Displaying the two numbers
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// multiplying the two numbers
res= num1 * num2;
System.out.println("The Multuplication = " + res);
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output :
num1 = 60
num2 = 40
The Multiplication = 2400
Division(/)
This is a binary operator that divides the first operand (dividend) by the second operand (divisor), resulting in the quotient.
Syntax:
num1 / num2
Example:
import java.io.*;
public class Division {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num1 = 200, num2 = 100, div = 0;
// Displaying the two numbers
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// dividing the two numbers
div= num1 / num2;
System.out.println("The Division = " + div);
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output :
num1 = 200
num2 = 100
The Division = 2
Modulus(%)
This is a binary operator that returns the remainder after dividing the first operand (dividend) by the second operand (divisor).
Syntax:
num1 % num2
Example:
import java.io.*;
public class Modulus{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num1 = 3, num2 = 2, mod = 0;
// Displaying the two numbers
System.out.println("num1 = " + num1);
System.out.println("num2 = " + num2);
// remaindering the two numbers
mod = num1 % num2;
System.out.println("The Remainder = " + mod);
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output :
num1 = 3
num2 = 2
The Remainder = 1
Compile it on online java editor.
Also check out Addition of Two Numbers in Java here.
Real-Life Use Cases of Arithmetic Operators in Java
Arithmetic operators are more than just basic math tools — they power everyday features in real-world Java applications. From billing systems to utility calculators, developers use these operators to build logic that users rely on daily. Let’s explore two practical use case types that beginners can easily relate to.
1. Calculating Discounts, Averages, Totals
In e-commerce platforms and billing systems, arithmetic operators help calculate prices, apply discounts, and average values like grades or ratings.
Example 1: Calculating Discount
double price = 500;
double discount = 10; // in percent
double finalPrice = price - (price * discount / 100);
System.out.println("Final Price: " + finalPrice); // Output: 450.0

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Example 2: Calculating Average Marks
int m1 = 85, m2 = 90, m3 = 88;
double average = (m1 + m2 + m3) / 3.0;
System.out.println("Average Marks: " + average);

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Example 3: Total Price for Multiple Items
int itemPrice = 200, quantity = 4;
int total = itemPrice * quantity;
System.out.println("Total Bill: " + total);

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
2. Basic Math Utilities in Java Programs
Developers often build utility functions using arithmetic operators for tasks like temperature or currency conversion, making apps more useful and interactive.
Example 1: Celsius to Fahrenheit
double celsius = 25;
double fahrenheit = (celsius * 9/5) + 32;
System.out.println("Fahrenheit: " + fahrenheit);

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Example 2: Currency Conversion
double usd = 100;
double inrRate = 83.2;
double inr = usd * inrRate;
System.out.println("INR: " + inr);

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Example 3: Area of a Rectangle
int length = 5, width = 4;
int area = length * width;
System.out.println("Area: " + area);

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 operators in Java?
Java arithmetic operators are used to accomplish operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
What is the function of operators?
An operator is a tool that is used to change individual data elements and deliver a result. These things are referred to as operands or arguments. Special characters or keywords are used to represent operators.
What is an example of an operator?
An operator is defined as someone who controls a machine or the management or owner of a firm. A telephone switchboard operator is one example of an operator. An operator is someone who controls a crane at a loading dock, for example.
Conclusion
In this article we have extensively discussed arithmatic operators topics and their implementation in Java.With the help of examples of each, we saw addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and modulus operators in detail.
Check out the java interview questions to get hands-on experience with frequently asked interview questions and land your dream job.
To learn more about Micro Operations, refer to Arithmetic Micro Operations.
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding Aithmetic Operators in Java and if you would like to learn more, check out our articles on core java programming .






