Introduction
Ruby is one of the most used programming languages around the world because of the functionality it provides. Ruby is an interpreted, dynamic and purely object oriented language which was developed in 1995 by Yukihiro Matsumoto. The main idea behind the creation of ruby was to have language that can be typed in simple syntax to handle data and logic to solve problems.

Applications of Ruby
- Desktop applications
- Static websites
- Data processing tools
- Automation tools
Now after the brief introduction about ruby let's get to know about how we can implement arrays in ruby. We will learn about the syntax of arrays in ruby and operations we can apply on it.

Arrays in ruby
Ruby arrays are collections of any object that are ordered and integer-indexed. An index is assigned to each element in an array and is used to refer to it. String, Integer, Fixnum, Hash, Symbol, and even other Array objects can be stored in Ruby arrays. Arrays in Ruby aren't as rigid as those in other languages. While adding elements to a Ruby array, it grows automatically.
Arrays in Ruby can be created with more than one method and we will learn about them.
Syntax
Method1
Calling a .new() class method to create the array in Ruby with zero, one or more than one arguments.
#This syntax will intialize an array with the name of arraysname.
arraysname = Array.new()
#We can declare size with the new class method
arraysname = Array.new(10)
#We check the size of array with size and length method like
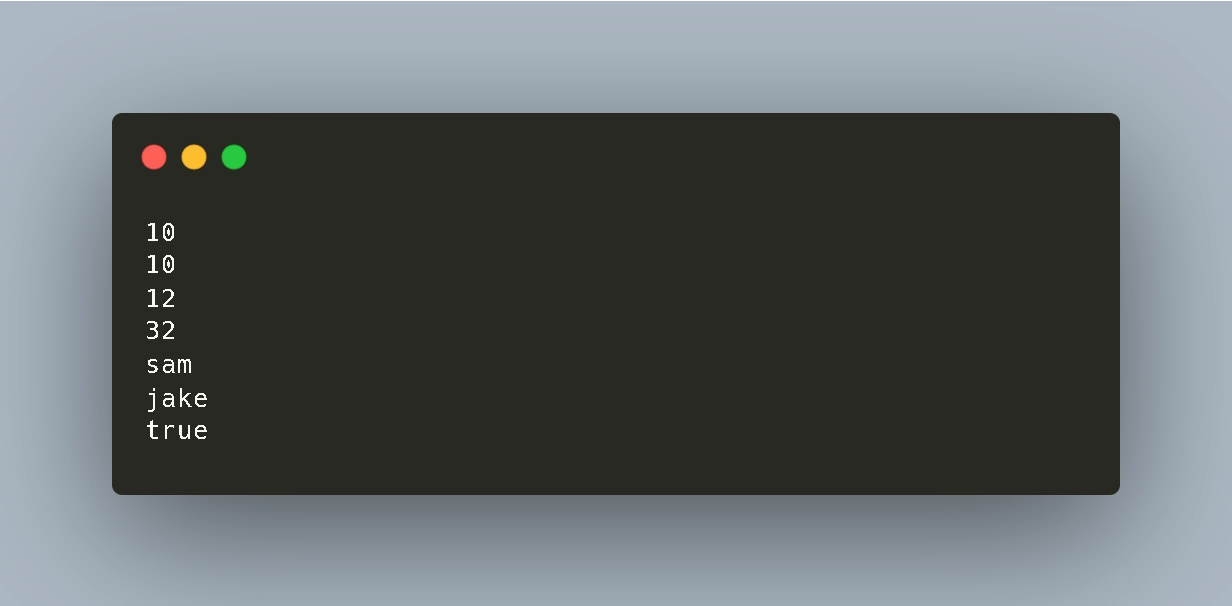
puts arraysname.size
puts arraysname.length
#declaring the elements in array
arraysname = [12,32,"sam","jake",true]
#printing the array
puts arraysnameOutput of the above code:
Method2
Using .literal constructor or square brackets [ ].
By using literal constructor there are more than one ways to intialize an array.
Let’s see them:
#method1
Arrayname1 = [1,2,3,4,5,'first array' ]
#method2
Arrayname2= Array.[](1,2,3,'second array')
#method3
Arrayname3 = Array[ 1,2,3,4,5,6,'third array']
# by using "#{ }" we can display the array elements in a block
puts "#{Arrayname1}"
puts "#{Arrayname2}"
puts "#{Arrayname3}"Output of the above program:

Accessing elements

We can access the elements with indexing like arrayName[2] will return us the element at the position 2. We can also use negative indexing to access the elements like [-1] will return the element present at last in the array.

Time for an Example:
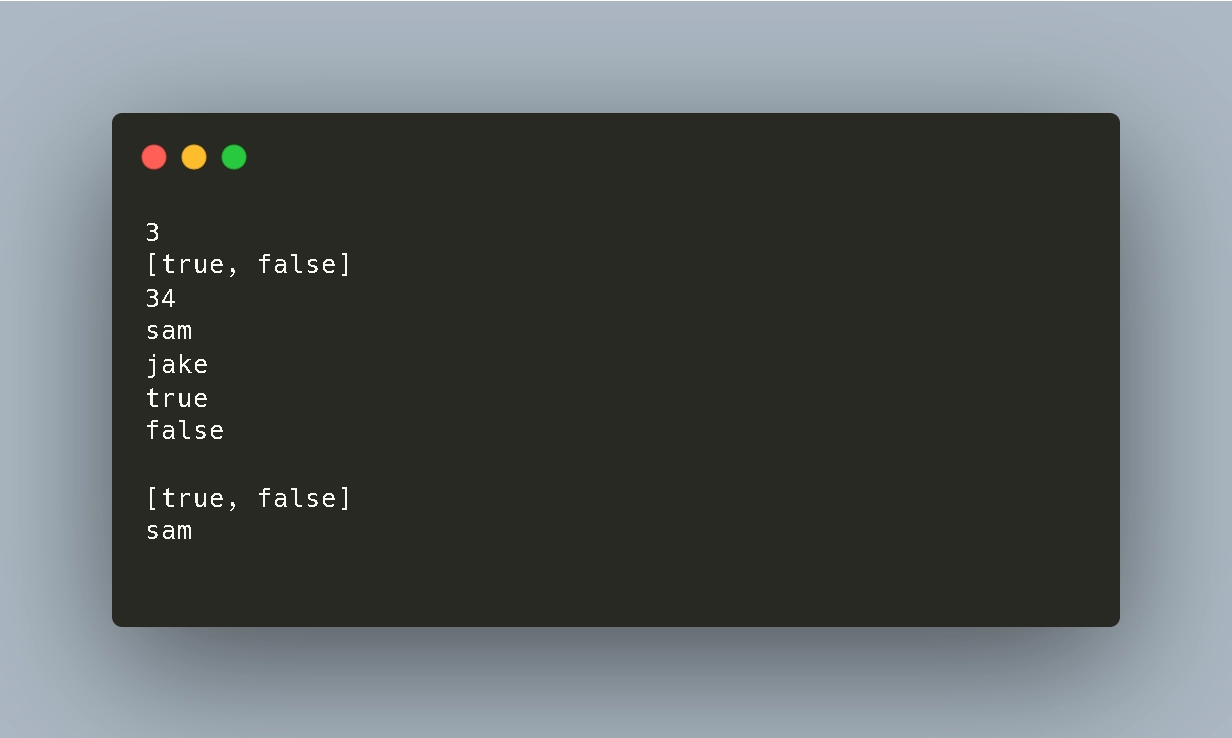
arrayname = [12,3,34,"sam","jake",[true,false]]
puts arrayname[1]
puts "#{arrayname[5]}"
puts arrayname[2,4]
#accessing the element more than size of array
puts arrayname[10]
#can access the elemets with negative indexing
# by using "#{ }" we can display the array elements in a block
puts "#{arrayname[-1]}"
puts arrayname[-3]Output:
Built in array methods
We are going to introduce a few built-in methods that are essential to know when you are working with ruby in order to make our work easier.
For all the methods we are going to use array:
example = [12,3,34,4,5,6]
.length
.length method will return us the total length of the array by counting the elements.
puts example.lengthOutput => 5
.first and .last
.first will return us the first element present in the array and .last will return us the last element in the array.
puts example.first
puts example.lastOutput => 12
6
.take
.take method will return us the first n elements in the array. n is the number will be given in the parameter in .take.
puts example.take(3)This will return us the first three elements from the array.
Output => [12,3,34]
.drop
.drop method will return us the elements in the array after the index n. n is the number will be given in the parameter in .take.
puts example.drop(3)Output => [4,5,6]
.pop
.pop method removes the last element from the array.
puts example.popOutput => 6
6 is the deleted element from the array
.shift
.shift method removes the first element from the array.
puts example.shiftOutput => 12
12 is the deleted element from the array
.push
.push method adds an element to the end of the array.
puts example.push(9)Output => [12,3,34,4,5,6,9]
.unshift
.unshift method adds an element at the beginning of the array.
puts example.unshift(0)Output => [0,12,3,34,4,5,6]
.delete
.delete method removes a specific element from the array.
puts example.delete(34)Output => 34
34 is the deleted element from the array.
.reverse
.reverse method reverses the array elements but does not mutate it. So we have to declare another array to store the reversed array.
reversed = example.reverse
puts reversedOutput => [6,5,4,34,3,12]
There are more built in methods available to us that we can apply in ruby like .each , .select, .include? and many more. You can explore them and use them and practice these above built in methods so that you can use them more efficiently in your code.
Check out this problem - First And Last Occurrences Of X






