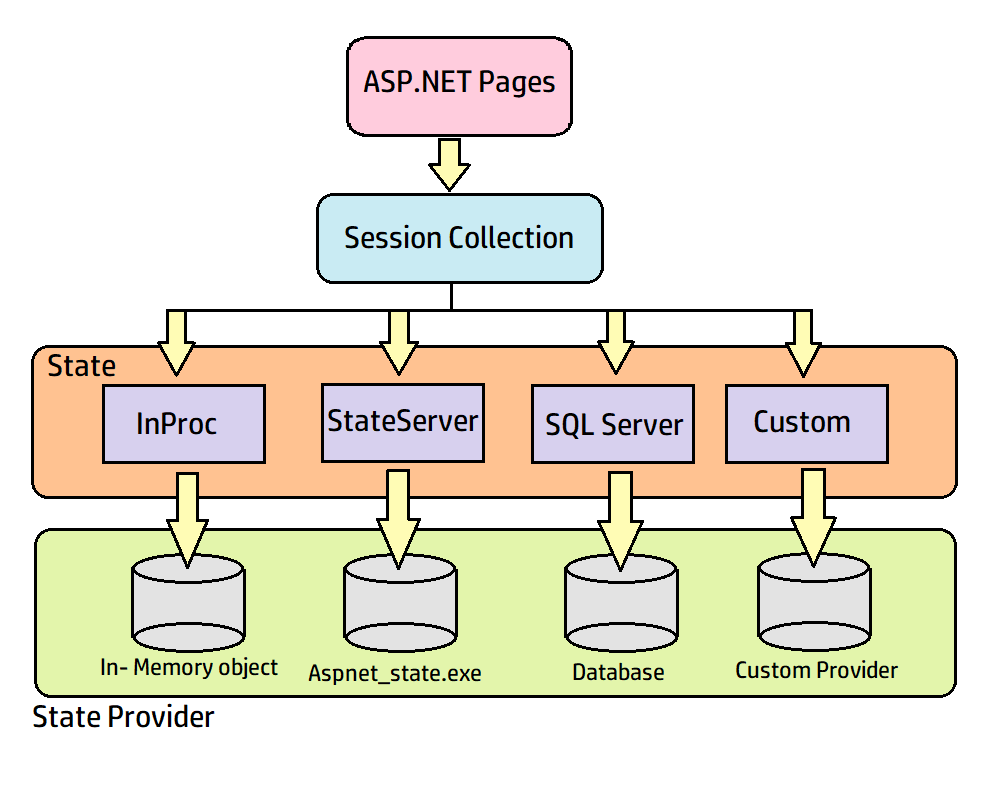
Introduction
ASP.NET session state lets you store and retrieve a user's values as the user navigates ASP.NET pages in a Web application for the particular time session. HTTP is a stateless protocol which means that a Web server treats every HTTP request for a page as an independent request. The server maintains no knowledge of variable values used during prior requests. ASP.NET session state determines requests from the same browser during a session and provides a way to store variable values for the duration of that session. By default, all the ASP.NET applications enable the ASP.NET session state.
Alternatives to ASP.NET session state contain the following:
- Application state stores variables that all users of an ASP.NET application can access.
- Profile properties persist user values in a data store without expiring them.
- Cookies.
- View state, which continues values on a page.
- The fields and query string on an HTML form is open from an HTTP request.
- ASP.NET caching stores values in memory that are available to all ASP.NET applications.
Note: Each of the ASP.NET sessions created is stored in the SessionStateItemCollection object.
Working Example
Here's an example of an input form that stores the user's email address.
// ASPnetSessionExample.aspx
<%@ Page Title="Home Page" Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="ASPnetSessionExample.aspx.cs"
Inherits="codingNinjas.ASPnetSessionExample" %>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
.table-style {
width: 100%;
}
.table-data-style {
width: 105px;
}
</style>
</head>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<p>Please fill the following details</p>
<table class="table-style">
<tr>
<td class="table-data-style">Email:</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="email" runat="server" TextMode="Email"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="table-data-style">Password:</td>
<td>
<asp:TextBox ID="password" runat="server" TextMode="Password"></asp:TextBox>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td class="table-data-style"> </td>
<td>
<asp:Button ID="login" runat="server" Text="Login" OnClick="loginBtn" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<br />
<asp:Label ID="UpperEmail" runat="server"></asp:Label>
<br />
<asp:Label ID="Email" runat="server"></asp:Label>
</form>
// ASPnetSessionExample.aspx.cs
using System;
using System.Web.UI;
namespace codingNinjas
{
public partial class ASPnetSessionExample : Page
{
protected void loginBtn(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (password.Text=="qwerty"){
// Store email into session variable
Session["email"] = email.Text;
}
if (Session["email"] != null){
// Display email
UpperEmail.Text = "The email stored to the session.";
Email.Text = Session["email"].ToString();
}
}
}
}
Output:
Idle:

On Submission: