Assignment in Ruby
Nonoverridable = operator does Assignment in Ruby. It helps us to assign value to a particular variable. For example, look into the below value assignment in ruby. Value 1 is assigned to variable x
X = 1

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
We can combine value assignment in ruby with other operators such as '+' and '-' :
X += 1 # This help's us in the increment of x.Please note Ruby does not have any ++ like C++ and Java.
Y -= 1 # This helps us in the Decrement of y. Please note Ruby does not have any -- like C++ and Java.

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
Ruby does support parallel assignments. By parallel assignment, we mean it allows more than one value and more than one variable in the assignment expressions:
x, y = 1, 2 # This Expression is similar to saying x = 1; y = 2
a, b = b, a # This line of code swap the value of two variables
x,y,z = [1,2,3] # Array elements automatically assigned to variables

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
Returning more than one value is allowed for methods in ruby, and parallel assignment helps in conjunction with such methods.
For example:
CODE
# Convert_to_polar method helps to convert Cartesian (x,y) coordinates to Polar
def convert_to_polar(x,y)
# Angle Computation
angle = Math.atan2(y,x) \
# Computing Distance
distance = Math.hypot(x,y)
# Return Distance and Angle
[distance, angle] # The last expression is the return value
end
# Using Parallel Assignment to collect
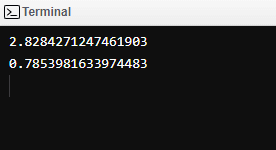
distance, angle = convert_to_polar(2,2)
puts distance
puts angle

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
OUTPUT
All Methods ending with an equals sign (=) are special because Ruby allows them to be invoked using assignment syntax. If an object o has a method named x=, then the following two lines of code do the very same thing:
o.x=(1) # Normal method invocation syntax
o.x = 1 # Method invocation through assignment

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
This is just a straightforward method of assigning values to a variable. But ruby does support multiple types of assignments. Let's understand all the different types of assignments ruby supports
Abbreviated Assignment in Ruby
Ruby supports abbreviated assignments. We can mix several operators with the assignment. E.g. Adding one to an object, we can write.
CODE
# Abbreviated Assignment for var
var = 1
var += 2
puts var
# Above Code is similar to the following below code
var = 1
var = var + 2
puts var

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
OUTPUT

CODE OUTPUT
We can use multiple operators in the same way. Operators like +, -, *, /, %, **, &, |, ^, <<, >> could be added in together with assignment operator. There are also ||= and &&=. The former would make an assignment if the value were nil or false, while the &&= completes an assignment if the value stood not nil or false.
Implicit Array Assignment in Ruby
Ruby allows us to implicitly create an array by listing multiple values during the assignment. Below program implicitly creates an Array during the assignment. We can also see how using * or the “splat” operator or unpack an Array while assigning somewhat resembles the multiple assignments we looked at above.
CODE
a = "This", "Is", "Implicit", "Array", "Assignment"
print a
a = *[10, 20, 30]
puts
print a # prints [10, 20, 30]
a = 10, *[20, 30]
puts
print a # prints [10, 20, 30]

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
OUTPUT

CODE OUTPUT
Array Decomposition during an Assignment
Ruby allows Array decomposition in method arguments. Ruby allows us to decompose an Array during an assignment by using parenthesis. We can decompose an Array as part of more significant multiple assignments. Since each decomposition is considered its multiple assignments, we can also use * to gather arguments in the decomposition.
CODE
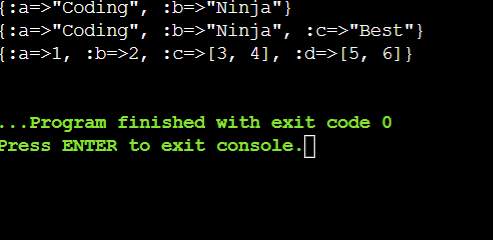
(a, b) = ["Coding", "Ninja"]
puts a: a, b: b # prints {:a=> Coding, :b=>Ninja}
a, (b, c) = "Coding", ["Ninja", "Best"]
puts a: a, b: b, c: c # prints {:a=>Coding, :b=>Ninja, :c=>Best}
a, (b, *c), *d = 1, [2, 3, 4], 5, 6
puts a: a, b: b, c: c, d: d
# prints {:a=>1, :b=>2, :c=>[3, 4], :d=>[5, 6]}

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
OUTPUT
CODE OUTPUT
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ruby?
Ruby is an open-source dynamic language with natural and easy-to-read/write syntax. Ruby is a careful balance language and a perfect blend of five different languages.
Ruby is said to be a combination of which five languages?
Ruby, an open-source dynamic language, is a perfect blend of five different languages (Perl, Smalltalk, Eiffel, Ada, and Lisp).
What do you understand by assignment in ruby?
Nonoverridale = operator does Assignment in Ruby. It helps us to assign value to a particular variable. For example, look into the below value assignment in ruby. Value 1 is assigned to variable x
X = 1

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
Is Ruby Case Sensitive?
Ruby is a case-sensitive language, which means lowercase identifiers in ruby are different from uppercase identifiers. E.g. Like_This is entirely different from LIKE_THIS. Similarly, Start is different from START.
What do you understand by parallel assignment in ruby?
Parallel Assignment in ruby means supporting more than one value and variable in assignment expression. Ruby Ruby does support parallel assignments Eg.
x, y = 1, 2 # This Expression is similar to saying x = 1; y = 2

You can also try this code with Online Ruby Compiler
Conclusion
In this article, we have studied the value assignment in Ruby in detail and also briefly explored multiple types of value assignment in ruby covering all about it.
Also, visit our Guided Path in Coding Ninjas Studio to learn about Ruby. If you are preparing for an interview, visit our Interview Experience Section and interview bundle for placement preparations. Upskill yourself in Ruby on Rails, Backend Web Technologies, Hadoop, SQL, MongoDB, Data Structures and Algorithms, JavaScript, System Design, and much more!. Please upvote our blogs if you find them engaging and helpful! I wish you all the best for your future adventures and Happy Coding.
To learn more, refer to Operational Databases, Non- relational databases, MongoDB, Top-100-SQL-problems, interview-experience, Introduction to ruby on rails, Directory Structure in Ruby, Ruby on Rails, Ruby vs Python. You can also refer to the Official Ruby, Ruby, Official Documentation, Ruby FAQ, Ruby Koans, Ruby Doc, Why Ruby?
We expect that this article must have helped you enhance your knowledge on the topic of Ruby. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.











