Getting started using Elastic Beanstalk
Setting up: Create an AWS account
If you are not already an AWS customer, you must create an AWS account. Signing up gives you access to Elastic Beanstalk and other AWS services.
Link for signup page: LINK.
Create an application and an environment
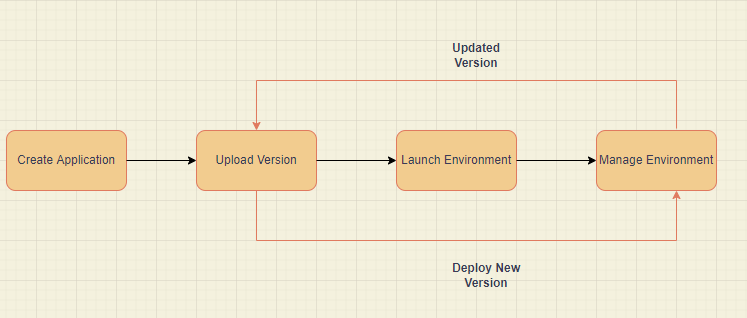
You'll utilize the Create a web app console wizard to build your sample project. It launches an environment within an Elastic Beanstalk application. The collection of AWS resources required to run your application code is referred to as an environment.
Explore your environment
Use the environment page in the Elastic Beanstalk console to get a quick overview of your Elastic Beanstalk application's environment. The top-level information about your environment is displayed in the environment overview window. This information comprises the application's name, URL, current health status, name of the currently deployed application, and platform versions.
Deploy a new version of your application
You may need to deploy a new version of your program regularly. As long as no other update activities are in process on your environment, you can deploy a new version at any time. Sample Application is the application version with which you began this training.
Configure your environment
You can tailor your environment to your application's needs. You can modify the type of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance executing your application, for example, if it is a compute-intensive application. Elastic Beanstalk does an environment update to implement configuration changes.
Clean up
Congratulations! You've successfully deployed a sample application to the AWS Cloud, updated its configuration to add a second Auto Scaling instance, and published a new version. Delete all application versions and terminate the environment to avoid being charged for services you aren't utilizing.
Service roles, instance profiles, and user policies
AWS Elastic Beanstalk prompts you to supply the following AWS Identity and Identity Access Management (IAM) roles when you build an environment.
Elastic Beanstalk service role
Elastic Beanstalk adopts a service role when it calls to other services on your behalf. Elastic Beanstalk, for example, employs a service role to acquire data from the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), Elastic Load Balancing, and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling APIs. This data might include the health of its AWS resources, allowing for better health monitoring.
Elastic Beanstalk instance profile
In your Elastic Beanstalk environment, an instance profile is an IAM role that is applied to instances that are launched. When you create an Elastic Beanstalk environment, you choose the instance profile that will be utilized when your samples are launched. If your web application requires access to other AWS services, provide statements or managed policies in the instance profile that grant access.
Elastic Beanstalk user policy
To prevent utilizing your root account or sharing credentials, create IAM users for each user who uses Elastic Beanstalk. Only provide these users permissions to access services and features they require as a security best practice. Not only does Elastic Beanstalk need permissions for its API actions, but it also needs access to multiple other AWS services.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk security
At AWS, cloud security is a principal focus. As an AWS customer, you have access to a data center and network architecture designed to fulfill the needs of the most security-conscious businesses.
Security of the Cloud: AWS is in charge of safeguarding the infrastructure that underpins all of the AWS Cloud's services and providing you with secure access to those services. At AWS, security is the top priority.
Security in the Cloud: The AWS service you use, as well as other criteria such as the sensitivity of your data, your organization's requirements, and applicable laws and regulations, define your responsibilities.
Following are the some of the security configurations you should consider when using Elastic Beanstalk:
Identity and access management
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a service provided by Amazon Web Services that allows administrators to manage access to AWS services securely. Authentication (signing in) and authorization (having permissions) to use AWS Elastic Beanstalk resources are controlled by IAM administrators. IAM is a free AWS feature that you can use whenever you want.
Logging and monitoring in Elastic Beanstalk
Monitoring is essential for keeping AWS Elastic Beanstalk and your AWS solutions reliable, available, and performant. If a multipoint failure occurs, you should collect monitoring data from all aspects of your AWS solution to more readily diagnose it. AWS provides some tools for monitoring and responding to any events with your Elastic Beanstalk resources.
Compliance validation
Third-party auditors evaluate the security and compliance of AWS Elastic Beanstalk as part of numerous AWS compliance programs. SOC, PCI, FedRAMP, HIPAA, and others are among them. AWS keeps a list of AWS services covered by specific compliance programs up to date at AWS Services in Scope by Compliance Program.
Resilience
AWS Regions and Availability Zones form the foundation of the company's global infrastructure. Multiple physically separated and isolated Availability Zones are joined by low-latency, high-throughput, and highly redundant networking in AWS Regions.
You may create and operate applications and databases that automatically failover between Availability Zones without interruption using Availability Zones.
Infrastructure security
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is safeguarded as a managed service by the AWS global network security protocols detailed in the whitepaper Amazon Web Services: Overview of Security Processes.
To connect to Elastic Beanstalk over the network, you use AWS published API methods. Clients must also implement cipher suites that provide perfect forward secrecy (PFS), such as Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman (DHE) or Elliptic Curve Ephemeral Diffie-Hellman (EC-DHE) (ECDHE).
Configuration and vulnerability analysis
AWS and our customers are responsible for ensuring that software components are secure and compliant. AWS Elastic Beanstalk's managed updates capability aids you in fulfilling your part of the shared responsibility model. This capability automatically upgrades an Elastic Beanstalk-supported platform version with patches and minor updates.
Security best practices for Elastic Beanstalk
AWS Elastic Beanstalk gives numerous security options to consider when developing and implementing your security policies. The best practices listed here are only guidelines and do not constitute a complete security solution. Because these best practices may or may not be relevant or sufficient for your situation, think of them as suggestions rather than prescriptions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Elastic Beanstalk?
Amazon Web Services' Elastic Beanstalk is an orchestration solution for delivering applications that orchestrate multiple AWS services such as EC2, S3, Simple Notification Service, CloudWatch, autoscaling, and Elastic Load Balancers.
What is Elastic Beanstalk's service role?
Elastic Beanstalk adopts a service role when it calls to other services on your behalf. Elastic Beanstalk, for example, employs a service role to acquire data from the Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), Elastic Load Balancing, and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling APIs.
What is Compliance validation?
Third-party auditors evaluate the security and compliance of AWS Elastic Beanstalk as part of numerous AWS compliance programs. SOC, PCI, FedRAMP, HIPAA, and others are among them. AWS keeps a list of AWS services covered by specific compliance programs up to date at AWS Services in Scope by Compliance Program.
Conclusion
In this article, we have briefly discussed AWS Elastic Beanstalk. Further, we will learn how to use it and AWS Elastic Beanstalk subtopics.
I hope you have gained some insight into this topic of AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and by now, you must have developed a clear understanding of them. You can learn more about such topics on our platform Coding Ninjas Studio.
You can refer to our guided paths on Coding Ninjas Studio to learn more about DSA, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, SQL problems, etc. Enroll in our courses and refer to the mock test and problems available, interview puzzles, look at the interview experiences, and interview bundles for placement preparations.
Thank you for reading.