Introduction
Imagine having multiple resources running such as Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon S3 buckets, or Amazon RDS instances, managing all of them without any user interface will be a challenging task. AWS Systems Manager gives you a consistent user interface for viewing operational data from numerous AWS services and automating operational operations across all of your AWS resources. You may organize resources by application, such as Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon S3 buckets, or Amazon RDS instances, examine operational data for monitoring and troubleshooting, and take action on your groups of resources with the System Manager.
In this blog, we will learn about AWS system manager, and the different tools and all the features it provides.
Features of AWS System Manager
Now, there are various features available in System manager which you can use like: The Run Command, you can automate your process, and much more. Below is the list of tools and features that are available in AWS System Manager.
The Run Command
AWS System Manager Run Command allows you to manage the configuration of your managed instances remotely and securely. Any EC2 instance, on-premises server or virtual machine (VM), or any cloud VM in your hybrid environment that has been configured for Systems Manager is referred to as a managed instance. You can use Run Command to automate routine administration chores and make ad hoc configuration changes at a large scale.
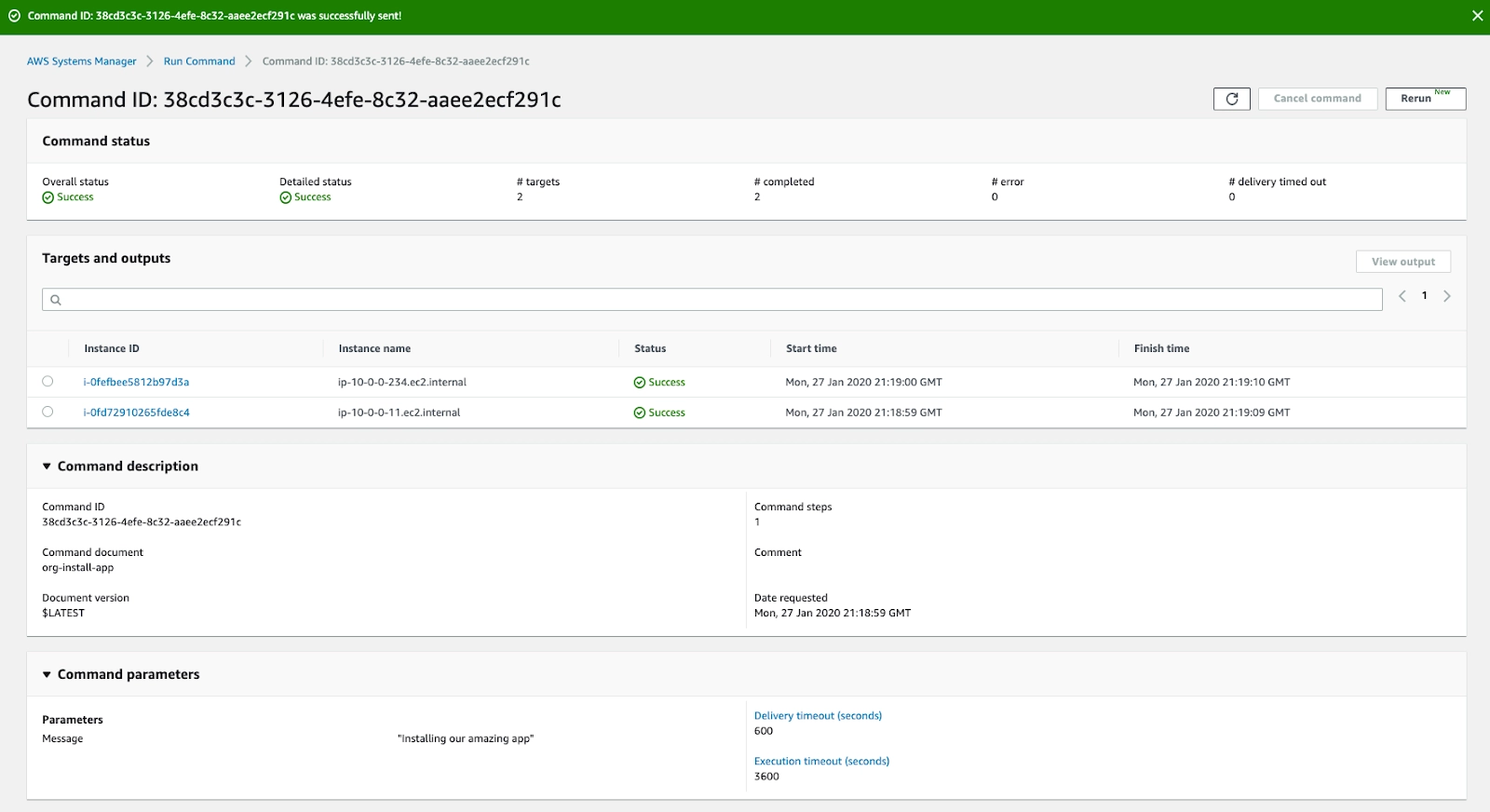 Command Status of the Run Command (Source: Amazon AWS Docs)
Command Status of the Run Command (Source: Amazon AWS Docs)
Automation
Systems Manager Automation automates standard EC2 instance and AWS resource management and deployment operations.
You can do various things using automation such as:
- To configure and manage instances and AWS resources, automated processes can be created.
- Create your own processes or use AWS's pre-defined workflows.
- Amazon CloudWatch Events can be used to get notifications about Automation activities and workflows.
-
Using the Amazon EC2 or AWS Systems Manager console, you can keep track of automation progress and execution details.
Imagine you are the person who is responsible for handling 10,000 instances that are spread across three regions. The finance team collaborated with Enterprise Support on a Cost Optimization investigation, which revealed that 2,500 instances were running larger instance types than were required for the workload. You've been given the responsibility of resizing them. Automation and Maintenance Window may now turn an unpleasant chore into a planned maintenance that can be completed by one person in a timely manner.
State manager
AWS Systems Manager State Manager is a scalable and secure configuration management service that automates the process of maintaining a defined state for your Amazon EC2 and hybrid systems.
Several tasks can be performed using state manager such as:
- Agents, including SSM Agent, are downloaded and updated on a set basis.
- Set up your network settings.
- A Windows domain can be used to join instances (Windows Server instances only).
- Throughout their lives, patch instances with software upgrades.
- Scripts can be run on Linux and Windows managed instances at any time during their lifecycle.
Distributor
AWS Systems Manager Distributor allows you to package your own software for installation on AWS Systems Manager managed instances, as well as find AWS-provided agent software packages like AmazonCloudWatchAgent and third-party packages like Trend Micro. Distributor distributes resources to AWS Systems Manager-managed instances, such as software packages. Specific versions of the package's document—a Systems Manager document that you create when you add the package in Distributor—are advertised to managed instances identified by managed instance IDs, AWS account IDs, tags, or an AWS Region when you publish a package.
After creating a package in Distributor ( Which will create an AWS System Manager document ), the package can be installed in one of the following ways:
- One time, using AWS Systems Manager Run Command.
- On a schedule, using AWS Systems Manager State Manager.
Session Manager
Session Manager is a fully managed AWS Systems Manager capability that allows you to control your EC2 instances, on-premises instances, and virtual machines (VMs) using a one-click interactive browser-based shell or the AWS CLI. Without the need to open incoming ports, maintain bastion hosts, or handle SSH keys, Session Manager enables safe and auditable instance management.
While giving end-users with simple one-click cross-platform access to your managed instances, Session Manager also makes it simple to comply with corporate regulations that need regulated access to instances, stringent security standards, and fully auditable logs containing instance access data.
The IAM user or role must have Session Manager permissions as well as access to the target managed instances in order to create a session. On the instances you want to connect to using sessions, you must have SSM Agent version 2.3.68.0 or later installed.
Post Forwarding with Session Manager
When demonstrating Session Manager to newcomers to Systems Manager, it's common to hear that it doesn't support RDP sessions. SSH tunnelling is used by Port Forwarding to create a secure tunnel between localhost and a remote service
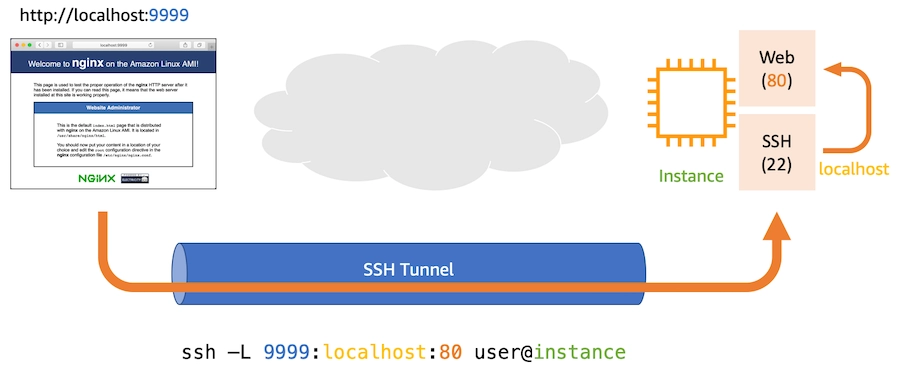
Port Forwarding: Session Manager (Source: Amazon AWS Docs)
This command instructs SSH to connect to the instance as ec2-user, open port 9999 on my local laptop, and route all traffic to localhost:80 on the instance. After the tunnel is formed, I can access to my private web server on port 80 by going to http://localhost:9999 in my browser.
Patch Manager
Patch Manager makes use of patch baselines, which comprise auto-approval procedures and a list of authorized and refused patches. We can use a Systems Manager Maintenance Window task to arrange patching on a regular basis. Patch Manager works with AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), AWS CloudTrail, and Amazon EventBridge to deliver a safe patching experience with event notifications and auditing.
Note: Patches for Windows Server and Linux are not tested by AWS before being made available in Patch Manager. Patch Manager also doesn't handle large operating system upgrades, such as from Windows Server 2016 to Windows Server 2019, or from SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 12.0 to SLES 15.0. Patches should always be properly tested before being deployed to production settings. This is a responsibility that belongs to the client.
Maintenance Window
This section allows you to set a timetable for when to undertake potentially disruptive actions on your instances, such as operating system upgrades, driver updates, and software or patch installations. It also allows you to plan activities on a variety of additional AWS resource types, including Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets, Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queues, and AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) keys, among others.
A schedule, a maximum length, a collection of registered targets (the instances or other AWS resources that are acted upon), and a set of registered tasks are all part of each maintenance window. When you create or change your maintenance windows, you can include tags. (Tags are keys that allow your organization's materials be identified and sorted.) You can also define the dates before and beyond which a maintenance window should not run, as well as the international time zone on which the maintenance window schedule should be based.
Change Calendar
This section allows you to establish date and time ranges during which activities you specify (for example, in Systems Manager Automation documents) in your AWS account may or may not be done. These ranges are referred to as events in Change Calendar. When you generate a Change Calendar entry, you're actually producing a ChangeCalendar Systems Manager document. The document Change Calendar stores iCalendar 2.0 data in plaintext format. The events you enter in the Change Calendar section become a part of the document.
There are two types of Change Calendar entries:
- DEFAULT_OPEN: actions can run by default, but are blocked from running during associated events
- DEFAULT_CLOSED: actions do not run by default, but can run during events associated with the calendar entry
Compliance
You may use AWS Systems Manager Configuration Compliance to check for patch compliance and configuration discrepancies across your fleet of managed instances. You can collect and aggregate data from many AWS accounts and Regions, then drill down into non-compliant resources. Configuration Compliance, by default, shows current compliance statistics for Patch Manager patching and State Manager relationships in Systems Manager. Additional capabilities and benefits of Systems Manager Compliance include:
-
Using AWS Config, you can see the compliance history and change tracking for Patch Manager patching data and State Manager relationships.
-
Create your own compliance types in Systems Manager Compliance based on your IT or business needs.
-
Use Systems Manager Run Command, State Manager, or Amazon CloudWatch Events to fix problems.
-
Generate fleet-wide reports by porting data to Amazon Athena and Amazon QuickSight.
OpsCenter
Operations engineers and IT professionals can use OpsCenter to view, investigate, and resolve operational work items (OpsItems) connected to AWS resources. OpsCenter is intended to shorten the time it takes to resolve issues with AWS resources. This Systems Manager feature collects and standardises OpsItems across services while also providing contextual investigative data on each OpsItem, associated OpsItems, and related resources. You can use Systems Manager Automation manuals (runbooks) provided by OpsCenter to swiftly fix issues. For each OpsItem, you may specify searchable, bespoke data. You can also see summary reports for OpsItems that are automatically generated based on their state and source.
Explorer
AWS Systems Manager Explorer is a configurable operations dashboard that displays data about your Amazon Web Services resources. Explorer shows a consolidated view of operations data (OpsData) for all of your AWS accounts and regions. OpsData in Explorer contains information about your EC2 instances, patch compliance information, and State Manager association compliance information. AWS Trusted Advisor and AWS Compute Optimizer information, as well as information about your AWS Support issues, are all included in OpsData.
Explorer shows how OpsItems are spread across your business units or apps, how they have changed over time, and how they differ by category. In Explorer, you can group and filter information to focus on topics that are important to you and demand action. When high-priority issues are identified, Systems Manager OpsCenter can be used to execute Automation runbooks and quickly resolve them.
Inventory
AWS Systems Manager Inventory gives you a comprehensive view of your Amazon EC2 and on-premises computing environments. Inventory can be used to gather metadata from your managed instances. You may store this metadata in a central Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket, then query the data using built-in tools to rapidly determine which instances are running the software and configurations needed by your software policy, as well as which instances need to be updated. With a single click, you can configure Inventory on all of your managed instances. You can also use different AWS Regions and accounts to configure and see inventory data.
Parameter Store
The AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store provides secure, hierarchical storage for managing configuration data and secrets. Passwords, database strings, Amazon Machine Image (AMI) IDs, and licencing codes can all be stored as parameter values. Values can be stored as plain text or as encrypted data. By utilising the unique name that you gave when creating the parameter, you can reference Systems Manager parameters in your scripts, instructions, SSM documents, and configuration and automation workflows.
AppConfig
AWS AppConfig allows you to manage and monitor application configuration deployments in the same manner that code deployments do, but without the need to re-deploy the code whenever a configuration value changes. You can deploy configurations to any number of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances, containers, AWS Lambda functions, mobile apps, IoT devices, or on-premises instances with AWS AppConfig, which expands with your infrastructure.
AWS AppConfig allows you to alter configurations by using the API or the AWS Management Console to make changes. AWS AppConfig allows you to check those changes semantically and syntactically to ensure that configurations are in line with the expectations of their particular apps, reducing the risk of downtime.




