Introduction 🌼
Linux is An Operating System similar to Unix based on the Linux kernel that directly handles the hardware and resources of a system, such as the CPU, memory, and storage. It lies between applications and hardware, connecting all of your software to the actual resources that do the work.
Linus Torvalds introduced it in 1991, and Linux is usually distributed as a package. As it is an operating system, most operations are performed on the files. It has some Directories, also known as folders in Linux, that are organized in the form of a tree. These directories, however, are also a form of a file. There are three kinds of files in Linux: regular files, directories, and special files.

Let's learn some fundamental commands to perform operations on Linux file systems.
File Management Commands
pwd Command
Pwd returns the full path name of the current remote working directory. In the above example, the command output is /home/amisha_26, which implies that we are working in the amisha_26 directory, which is inside the home directory.
Syntax:
$ pwd -L: Prints the symbolic path.
$ pwd -P: Prints the actual path.
Example:

cd Command
The command cd also sometimes called as chdir , it allows you to move between directories. The cd command accepts an argument, generally the name of the folder to which you wish to move. Thus the entire command is cd your-directory.
Syntax :
$ cd <directory_name> (Will move to the desired directory)
$ Cd .. (will move back to the previous directory)
Example:

ls Command
The “ls” command lists files that present the directory you want to work with, except for hidden files.
In the above example, ls list all the files present in the directory named as amees.
Syntax :
$ ls
Example:

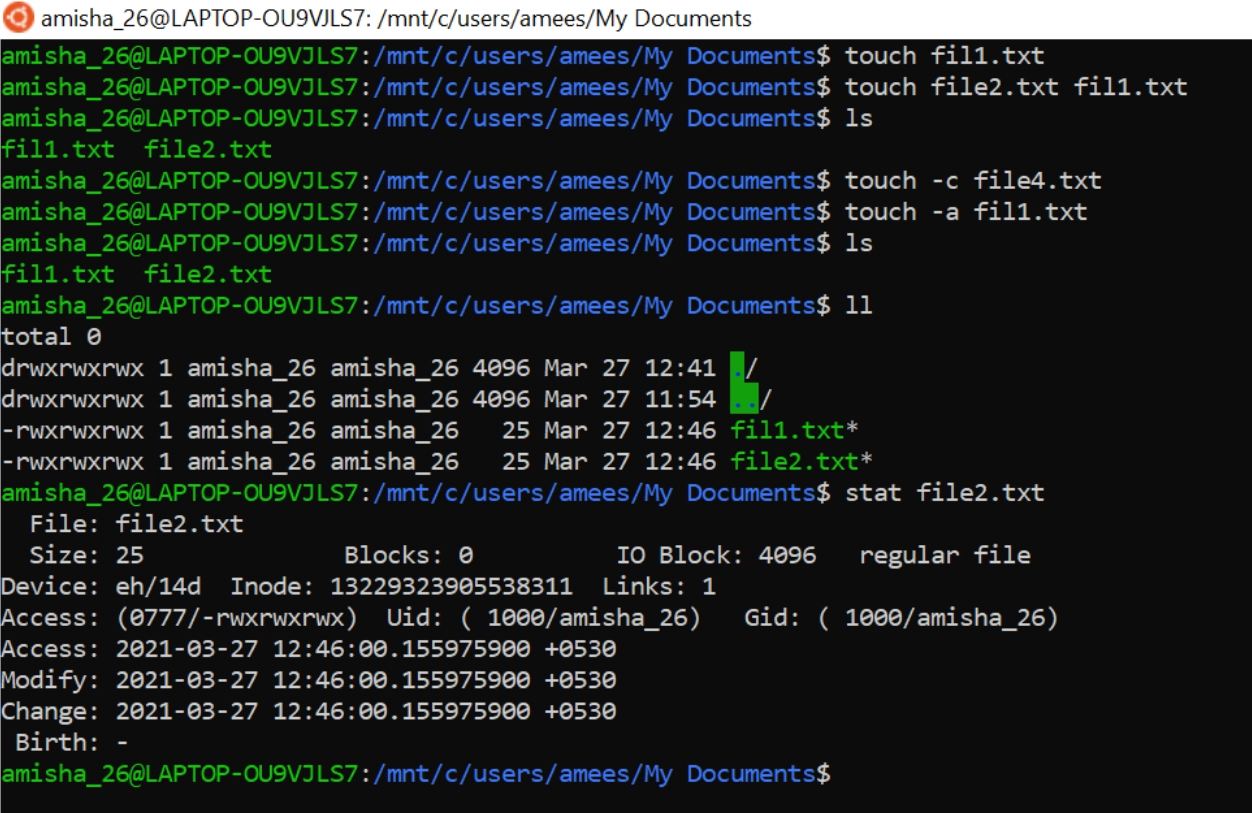
touch Command
The primary use of the touch command is to alter a timestamp. The function is commonly used for file creation, even though this is not its core role. The terminal program may modify and access times for any specified file. The touch command only creates a file if it does not already exist.
Syntax:
$ touch <options> <file or directory name>OPTIONS |
MEANING |
-a |
Changes the access time |
-c |
if the file does not exist, do not create it
|
|
-d
|
update the access and modification times |
-m |
change the modification time only
|
-r |
use the access and modification times of the file
|
-t |
creates a file using a specified time |
Example:
cat Command
Cat or concatenate is often used in Linux. It reads the files' content and gives the content's output on the terminal screen. In the above example, we used the command cat to read the file1.txt and you can see the In the above example, we used the command cat to read the file1.txt and see the output below the command.
Syntax:
$ cat <filename>
Example:

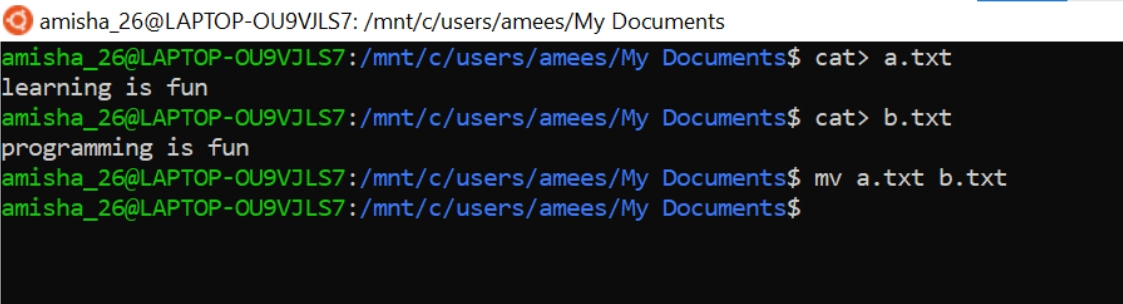
mv Command
The mv command is often used in Linux; this command is used to move a file from one directory to another directory. There is also a second use of the mv command. We can change the name of any existing file to a new name, whichever we desire.
In the above example, we are changing the name of a.txt to b.txt.
Here we are using the mv command, which will change the name of the file a.txt to b.txt.
Syntax:
$ mv <filename> <new file name>
Example:
cp Command
Cp means to copy. The command is used to copy files or groups of files. In the above example, we are using the cp command to copy the content of file3.txt and will paste it into the file named file1.txt.
Syntax:
cp <file/directory-sources> <destination>
Example:

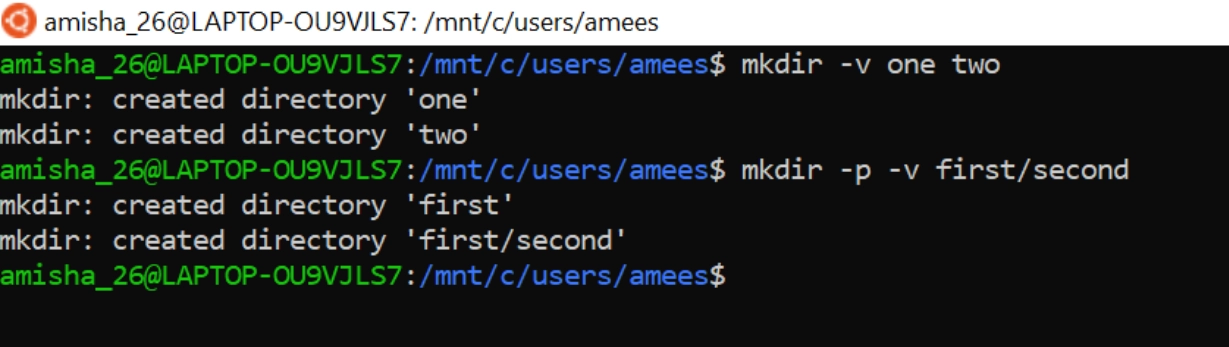
mkdir Command
“mkdir” also known as “ make directory”. This command is used to create single or multiple directories.
Syntax:
mkdir <options> <directories>OPTION |
MEANING |
-v |
print a message for each created directory |
-p |
no error if existing |
Example:
rm Command
“rm” also know as “remove”.This command is used to remove a file. If we use the rm command, the file will be permanently deleted. In GUIs, we got recycle bin and trash for recovering files. So we need to take extra care while using the rm command.
Example:

Read about: gzip command in linux





