Introduction
In this blog, we will learn about Boot Block and Bad Block with their types and cover frequently asked questions about them. The operating system is in charge of various additional elements of disk management, including disc configuration, boot block, or disk booting. Following is a short description of them.
The boot block is an important component of an operating system that resides in a region of a hard disk or any other storage device and contains all important data and instructions required for initiating the booting process.
Whereas a bad block is a sector of a data storage device that can't be utilized because of permanent damage or malfunction. hence it is not reliable to store data

Also see, Types of Computer Memory (RAM and ROM), Multiprogramming vs Multitasking
We are done with the brief introduction, let's move on to the detailed discussion about them.
You can also read about the - Memory hierarchy in computer network
Boot Block
When a computer boots up or reboots to obtain an instance, it requires an initial application to run. The Bootstrap program is the initial software that must initialize all parts of the system, such as:
- Start the operating system after initializing the CPU registers, device controllers, and main memory.
- The bootstrap software locates the operating system kernel on disk and loads it into memory to complete its task.
- Finally, it returns to the original address to commence operating-system execution.
The bootstrap program is kept in read-only memory (ROM). This placement is helpful since ROM needs no setup, and it is at a fixed point that the CPU may start processing when powered up or reset. Because ROM is read-only memory, computer viruses cannot infect it. The issue is that updating the bootstrap code necessitates replacing the ROM and hardware chips. As a result, systems contain a tiny bootstrap loader software in the boot ROM, whose function is to get a complete bootstrap program from the disk.
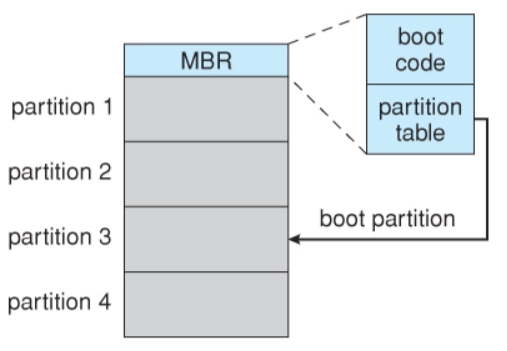
The whole bootstrap software may be changed fast, and a new version is saved to disk. The whole bootstrap software is saved in "the boot blocks" at a specific position on the disk. A disk that has a boot partition is termed a boot disk or system disk.
The code in the boot ROM asks the disk controller to read the boot blocks into memory (no device drivers are installed at this stage) and then executes that code. The bootstrap software is more advanced than the boot ROM's bootstrap loader. It can start the Operating System by loading the entire operating system from a non-fixed point on a disk.
We are done with the boot block, let's move on to Bad Block.
You can also read about the Multilevel Queue Scheduling, Multiprogramming vs Multitasking