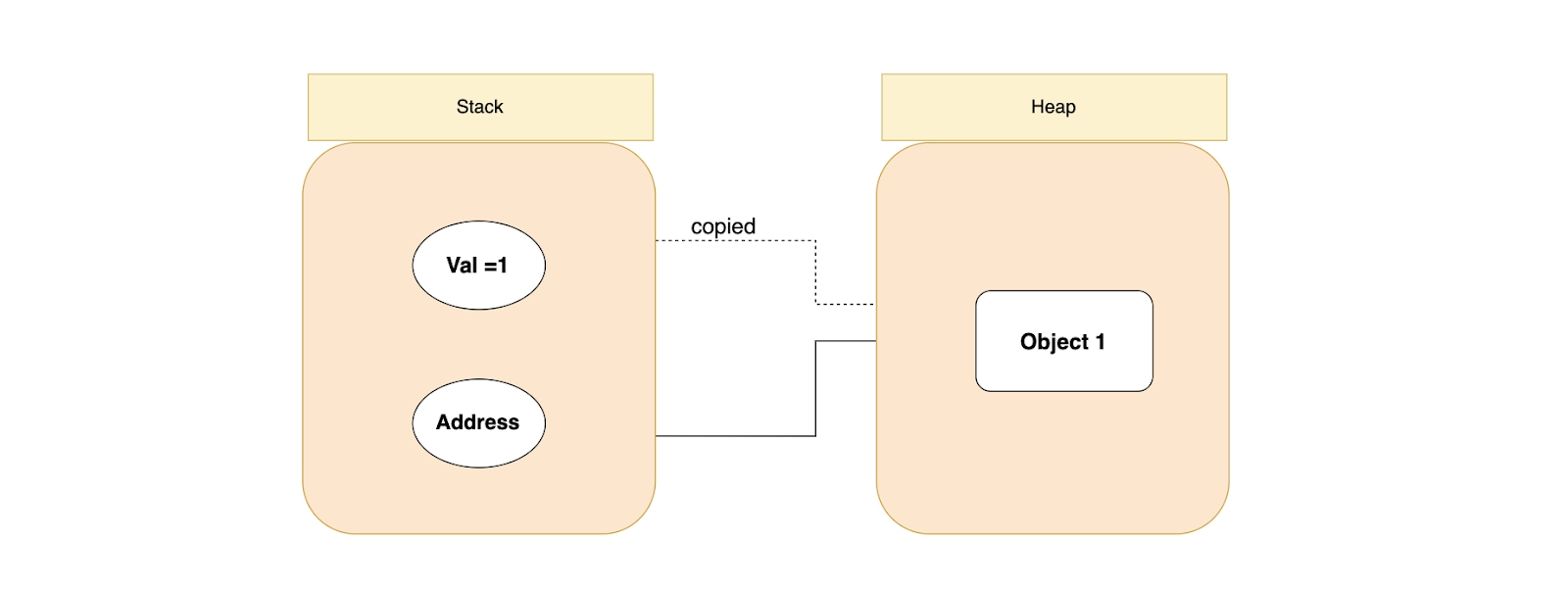
Advantages of Boxing
When a value type transform into a Base object or an interface, boxing comes in handy. The value type is subsequently converted to a reference type by the CLR (Common Language Runtime). CLR allocates heap memory before copying the value type instance to it.
Disadvantages of Boxing
Boxing is a costly procedure since it copies an object from a stack to a heap, which takes a lot of processing cycles and heap space.
The same object can appear in two separate places in memory, each with a different state.
Unboxing
It is the process of converting an object type to a value type. Unboxing is the complete opposite of boxing. Unboxing is altering the type object to any value type explicitly.
Only variables that have already been boxed can be unboxed. It's crucial to understand that Unboxing necessitates an object type that has been boxed from value type to object type. The unboxing process verifies that the given value type matches the type contained in the object type. An error is a mismatch.
An unpacking operation entails determining whether the object instance is a boxed value of the specified value type and then copying the value from the instance.
Example
object box = 12;
int i = (int)box;
conceptually correspond to,
object box = new int_Box(12);
int i = ((int_Box)box).value;
The value of the source argument must reference an object that was previously formed by boxing a value of that value-type for an unpacking conversion to that value-type to proceed at run-time. An InvalidCastException is issued if the source parameter is null or a reference to an incompatible object.
Advantages of Unboxing
Unboxing is explicit conversion. The item from the heap memory is copied to the value from the stack memory.
Disadvantages of Unboxing
We must guarantee that the value type is large enough to hold the object's value when unpacking a value. A run-time error may occur if the operation is not compile correctly.
Also read, Ienumerable vs Iqueryable
Frequently asked questions
What's the distinction between the ref and out parameters?
A ref argument is initialized before being supplied to a method, whereas a parameter does not initialize before pass.
What is the distinction between an array and an array list?
Only elements of the same kind can be store in an array. The array's size is predetermined. An array list is identical to an array. However, it has no defined size.
What is the distinction between a DLL and an EXE?
EXE is an OUT-of-Process component, while Dll is an IN-Process component.
Exe is for one-time use only, whereas DLL can be used several times.
DLLs cannot be started as standalone executables.
What does serialization entail?
When we wish to send an item over the internet, we must first turn it into a stream of bytes. Serialization is the process of transforming an object into a stream of bytes. Serializable, an object must inherit the ISerialize Interface.
De-serialization is the process of converting a stream of bytes into an object.
What's the difference between object pooling and connection pooling?
You can manage the number of connections in object pooling. You can control the maximum number of links reached with connection pooling. If there is nothing in the pool when employing connection pooling, a connection is made because the creation is on the same thread. In object pooling, the collection decides whether or not to create an object based on whether or not the highest reaches, in which case the next available object is return. However, if the thing is hefty, this may increase the time complexity.
Also Read About - singleton design pattern in c#
Conclusion
This article has gone through Boxing and Unboxing. Value Types (int, char, etc. ), Reference Types (object), and Pointer Types are the three data types in the C# Type System. It essentially converts a Value Type to a Reference Type and back. Boxing and Unboxing provide a unified view of the type system, allowing any type value to be handled as an object.
Check out the Introduction in C#. It will clear the concept.
If you want to know the Difference between Argument and Parameter check out this article.
Are you planning to ace the interviews of reputed product-based companies like Amazon, Google, Microsoft, and more?
Please go check out our C# practice course.
Attempt our Online Mock Test Series on Coding Ninjas Studio now!
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding C# and if you would like to learn more, check out our course. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow. Happy Coding!
Ninja, have a great time learning.