Introduction
Business Analysts play a crucial role in connecting business needs with technical solutions, making their expertise invaluable to organizations seeking to innovate and improve efficiency. With the demand for skilled Business Analysts on the rise, preparing for job interviews in this field is more important than ever.

If you want to become a business analyst, and you are hustling about what questions to read for your interview. Your hustle to find a variety of quality questions ends here. Here, we have discussed the most common business analyst interview questions that can help you ace your upcoming interview.
Basic Business Analyst Interview Questions
1. What exactly is a Business Analyst?
Ans: A business analyst acts as a link between many organizational stakeholders. They interact with many stakeholders within an organization in order to explain and finalize needs and assist the project team with project planning, design, and validation. They are individual who has good subject expertise and can sort business demands.
2. What qualifications do you have for a business analyst position at our firm?
Ans: The interviewer wants to see if you comprehend the job role and if you meet the company's requirements for the ideal applicant with this type of business analyst interview question.
There are two parts to this question:
Emphasize your education by mentioning coursework relevant to the position.
Show how your background, attitude, and skills make you a good fit for the company.
You can show the interviewer what benefits you will offer to the company by giving instances of your prior work. Make sure your response includes a problem and a solution.
Tip: When showcasing and explaining your expertise and competencies, keep in mind the skills listed in the job advertisement.
3. What are the core competencies of a Business Analyst?
Ans: It's one of the most typical interview questions for business analysts. Although each organization is unique, the essential criteria for a business analyst are relatively consistent. Please read the job description to find the required vital competencies and incorporate them into your response.
You can respond that a business analyst requires excellent communication and negotiation skills. Problem-solving, analytical thinking, and decision-making are also essential skills. Industry expertise, business process management, and technical ability need a business analyst.
4. List some of the tools and abilities that Business Analysts employ.
Ans: You can combine technical and non-technical tools/skills to answer this question. Google Docs, MS Office Suite, database knowledge, ERP systems, SQL, and other technical skills/tools are a few examples.
Business process Management, Requirement elicitation, Documentation, and more are examples of non-technical/business analysis skills.
Pro tip: Tailor your response to highlight your distinct abilities and experience.
5. What exactly is a flowchart? Why is it significant?
Ans: A flowchart uses symbols and diagrams to depict the entire system's flow. It is crucial since it makes the plan understandable for developers and non-technical stakeholders.
Here is the diagram given below for better understanding.
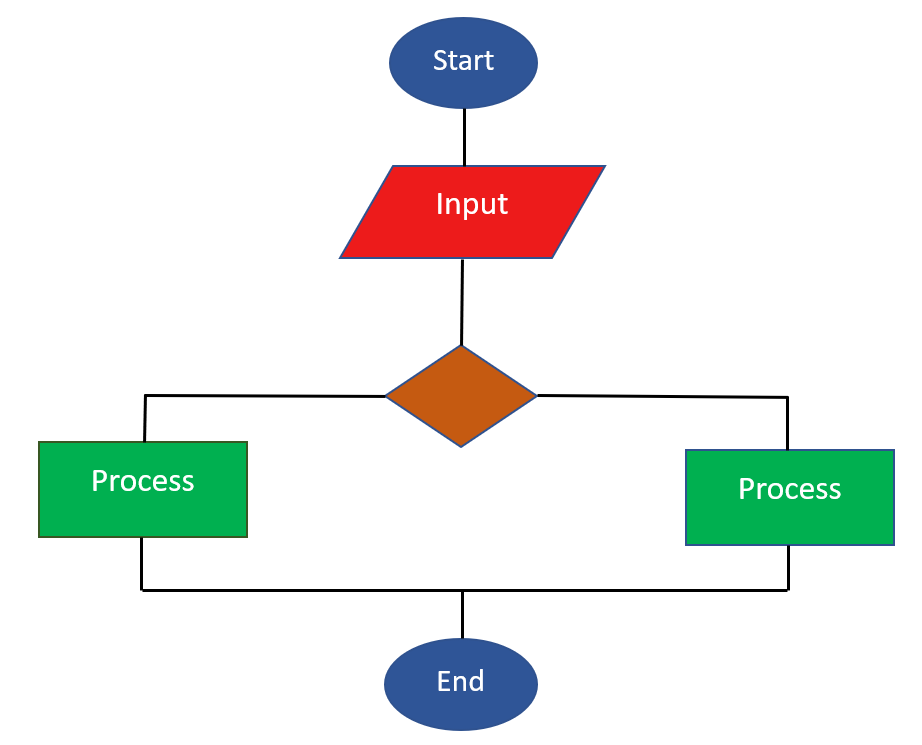
6. What do you mean by SRS?
Ans: A System Requirements Specification (SRS) is sometimes known as a Software Requirements Specification. It is a document or group of documents that describe the features of a system or software app. It has several parts that outline the expected functionality that stakeholders and customers demand to satisfy end-users.
7. What are the main elements of SRS?
Ans: The following are the main components of an SRS:
- Work Description
- Requirements for Function
- Non-functional specifications
- Dependencies
- Modeling Data
- Assumptions
- Constraints
- Acceptance Criteria
8. What is a Use Case Model?
Ans: A use case model depicts a series of events and activities that occur during any process that an actor does. It is an essential aspect of software engineering and software modeling since it specifies the desired functionalities and the resolution of any potential faults that a user may face.
Given below is a use case model for an online shopping system.
9. What is the meaning of scope creep, and how can you prevent it?
Ans: Scope creep, also known as requirement creep, refers to unplanned modifications or deviations in a project's scope within the same resource range, such as within the same schedule and budget. It's a sign of inadequate project management and a potential project danger. A variety of factors can cause scope creep.
Ineffective communication among project stakeholders and Inadequate project requirements documentation
Scope creep can be avoided by doing the following:
- The scope of the project is documented.
- Implementing effective change management.
- Prior notification of the modifications' implications on the persons involved.
- The new requirements should be recorded correctly in the project log.
- Avoid gold plating, which entails adding more features to existing functions.
10. What is BRD? What distinguishes it from SRS?
Ans: A Business Requirements Document (BRD) is a written contract for a product between a customer and an organization.
The following are the differences between BRD and SRS:
| BRD | SRS |
|---|---|
| It is a high-level software functional specification. | It is the software's high-level functional and technical specification. |
| It is a formal document that describes the client's needs (written, verbal) | It outlines the software's functional and non-functional needs. |
| The Business Analyst creates it following direct engagement with the clients. | The System Architect creates it since it requires technical competence. |
| It is calculated depending on the specifications and interactions with the client. | It is derived from BRD. |
11. What does INVEST mean?
Ans: INVEST stands for Independent, Negotiable, Valuable, Estimable, Sized appropriately, and testable. Business analysts and project managers often use this word to define the process of providing high-quality services and products.
12. How do you define extends?
Ans: A dotted line that represents a relationship is called extends. It's most commonly used to describe optional behavior with no independent significance. Help on "Sign on" is an example of how "Sign on" might be extended.
13. How are non-functional requirements documented?
Ans: Non-functional needs are recorded in two documents:
- SDD (System Design Document)
- FRD (Functional Requirement Document)
14. Explain SaaS.
Ans: SaaS stands for Software as a Service. It has something to do with cloud computing. It differs from other software packages in that it does not require installing software on your computer. You only need an Internet connection and a Web browser to utilize it.
15. What is the complete form of OLTP?
Ans: The OLTP stands for Online Transaction Processing. It is a term that refers to the processing of data on a computer network. These systems are designed to complete database transactions quickly. Data entry and database retrieval are the primary functions of these systems.
16. What actions are necessary to turn a product into an idea?
Ans: Market analysis, competitor analysis, SWOT analysis, personas, strategic vision, and feature set are all tasks you must complete. Features, Use Cases, SDLC, Storyboards, Test Cases, Monitoring, and Scalability should be prioritized.
17. What do you mean by personas?
Ans: Instead of real users, personas are employed to help developers and technical teams judge user behavior in various settings. Personas are social roles that any actor or character can play. It comes from a Latin word that means "character." It refers to a group of clients or end-users in marketing terms.
18. What does the acronym FMEA stand for?
Ans: FMEA means Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. It's a failure analysis utilized primarily on product development, system engineering, and operations management. This study determines the severity of various failure modes in any system.
19. What gaps can a business analyst encounter during gap analysis?
Ans: There are mainly four types of the gap –
Performance Gap: The difference between expected performance and the actual performance
Product/Market Gap: The gap between budgeted sales and actual sales is termed a product/market gap
Profit Gap: The variance between the targeted and actual profit of the company.
Manpower Gap: The gap between the required number and quality of the workforce and the actual strength in the organization.
20. What is the 100-point system?
Ans: This strategy gives different steps in a process priority. Each group member is responsible for assigning points to various stages. Finally, all of the issues for each step are totaled. The phase with the most points is the most important.




