Introduction🤔
Sometimes, when dealing with graph data structure, we often witness an edge in a graph on removal, which disconnects the graph. But the question arises of how to check if removing a given edge disconnects a graph or not.
So, let us learn to check if removing a given edge disconnects a graph or not.

Are you ready❓
Check out also Application of graph data structure
Check If Removing a Given Edge Disconnects a Graph🎯
An edge is a bridge in an undirected connected graph, if removed, disconnects the graph.
For example1🪢 -
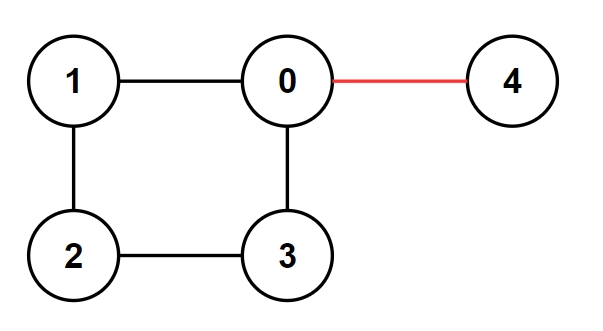
In the above graph, the bridge (highlighted with red) is between (0,4), which means 0 and 4.
For example2🪢 -
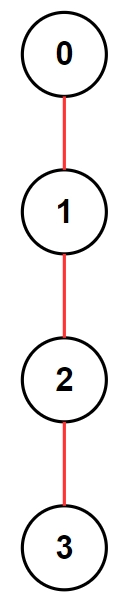
In the above graph, the bridge (highlighted with red colour) is between (0,1), (1,2), and (2,3).
One way to check whether removing a given edge disconnects a graph is by determining whether or not a specific edge is a bridge.
We can always find if an undirected graph is connected or not by finding all reachable vertices from any vertex (say, the first vertex). The graph is connected if the count of reachable vertices equals the number of vertices in the graph. Else, it is disconnected. All the reachable vertices can be found either using the BFS or the DFS Algorithm.
Algorithm👨💻
Let us look at the algorithm
- Remove the given edge
- Find all the reachable vertices from any vertex.
- If the count of reachable nodes is not V, return 'Yes'. Else return 'No' [not a bridge].
Implementation🦾
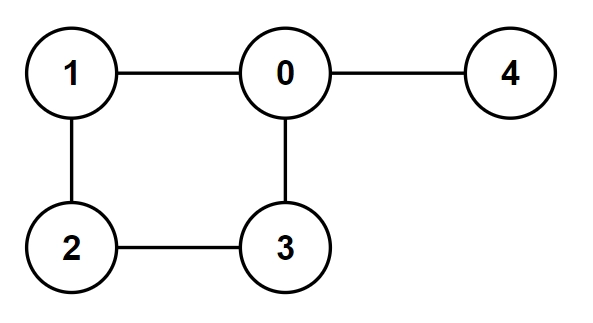
In the above graph, we need to check if removing a given edge disconnects a graph using code implementation.
Code in C++📄
/*C++ program to check if removing a given edge disconnects a graph*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* A directed graph using representation -> adjacency list */
class Graph{
/* vertices*/
int Vert;
list<int> *adj_adjacent;
void DFS(int vert, bool visited[]);
public:
/* The constructor*/
Graph(int Vert);
/*Add an edge to the graph using the function*/
void add_an_edge(int vert, int next_vert);
/* if graph is connected -> Returns true*/
bool isConnected();
bool isBridge(int vert_prev, int vert);
};
Graph::Graph(int Vert){
this->Vert = Vert;
adj_adjacent = new list<int>[Vert];
}
void Graph::add_an_edge(int vert_prev, int vert){
adj_adjacent[vert_prev].push_back(vert);
adj_adjacent[vert].push_back(vert_prev);
}
void Graph::DFS(int vert, bool visited[]){
/*Marking and printing the current node as visited*/
visited[vert] = true;
/* Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex*/
list<int>::iterator i;
/* Loop*/
for (i = adj_adjacent[vert].begin(); i != adj_adjacent[vert].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFS(*i, visited);
}
/* If a given graph is connected return true else return false*/
bool Graph::isConnected(){
bool visited[Vert];
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
/*Find all reachable vertices from the first vertex*/
DFS(0, visited);
/*If the set of reachable vertices includes all, return true.*/
for (int i=1; i<Vert; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
/* This function assumes that edge (vert_prev, vert) exists in graph*/
bool Graph::isBridge(int vert_prev, int vert){
/* Remove edge from the undirected graph*/
adj_adjacent[vert_prev].remove(vert);
adj_adjacent[vert].remove(vert_prev);
bool res = isConnected();
/* Adding-> edge back*/
add_an_edge(vert_prev, vert);
/* Return true if graph gets disconnected after removing the edge.*/
return (res == false);
}
/* Main code- the driver*/
int main(){
/*Creating a graph as given above*/
Graph g(5);
g.add_an_edge(0, 1);
g.add_an_edge(0, 3);
g.add_an_edge(0, 4);
g.add_an_edge(1, 2);
g.add_an_edge(2, 3);
cout << "\n Is there a bridge between (0,4)- ";
g.isBridge(0, 4)? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No";
cout << "\n";
cout << "\n Is there a bridge between (1,2)- ";
g.isBridge(1, 2)? cout << "Yes" : cout << "No";
cout << "\n";
return 0;
}
Output📋
Is there a bridge between (0,4)- Yes
Is there a bridge between (1,2)- No
Time Complexity🌐 - O(V + E) [Where V-vertices and E-edges in the graph]
Code in Java📋
/*Java program to Check if removing a given edge disconnects a graph*/
import java.util.*;
/*A directed graph Using representation -> adjacency list*/
class Graph {
/*vertices*/
int Vert;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > adj;
private void DFS(int vert, boolean[] visited){
/*Marking and printing the current node as visited*/
visited[vert] = true;
/* Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex*/
for (Integer i : adj.get(vert)) {
if (!visited[i]) {
DFS(i, visited);
}
}
}
public Graph(int Vert){
this.Vert = Vert;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < Vert; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
public void add_an_edge(int vert_prev, int vert){
adj.get(vert_prev).add(vert);
adj.get(vert).add(vert_prev);
}
/*Returns true if Given graph is connected else return false*/
public boolean isConnected()
{
boolean[] visited = new boolean[Vert];
/*Find all reachable vertices from the first vertex*/
DFS(0, visited);
/* return true. if the set of reachable vertices includes all*/
for (int i = 1; i < Vert; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
/*Function assumes that edge (vert_prev, vert) exists in graph*/
public boolean isBridge(int vert_prev, int vert){
/* From undirected graph -> Remove edge*/
adj.get(vert_prev).remove(Integer.valueOf(vert));
adj.get(vert).remove(Integer.valueOf(vert_prev));
boolean res = isConnected();
/*Adding-> edge back*/
add_an_edge(vert_prev, vert);
/*Return true if graph gets disconnected after removing the edge.*/
return (res == false);
}
/*Driver code*/
public static void main(String[] args){
/*Creating a graph as given above*/
Graph g = new Graph(5);
g.add_an_edge(0, 1);
g.add_an_edge(0, 3);
g.add_an_edge(0, 4);
g.add_an_edge(1, 2);
g.add_an_edge(2, 3);
System.out.print("Is there a bridge between (0,4) - ");
if (g.isBridge(0, 4)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
}
else {
System.out.println("No");
}
System.out.print("Is there a bridge between (1,2) - ");
if (g.isBridge(1, 2)) {
System.out.println("Yes");
}
else {
System.out.println("No");
}
}
}
Output📋
Is there a bridge between (0,4) - Yes
Is there a bridge between (1,2) - NoCode in Python📋
# Python program to
# check if removing
# a given edge
# disconnects a graph
# A directed graph
# using representation
# -> adjacency list
class Graph:
def __init__(self, Vert):
self.Vert = Vert
self.adj = [[] for i in range(Vert)]
def add_an_edge(self, vert_prev, vert):
self.adj[vert_prev].append(vert)
self.adj[vert].append(vert_prev)
def DFS(self, vert, visited):
# Marking and printing
# the current node
# as visited
visited[vert] = True
# Recur for all
# the vertices adjacent
# to this vertex
i = 0
while i != len(self.adj[vert]):
if (not visited[self.adj[vert][i]]):
self.DFS(self.adj[vert][i], visited)
i += 1
# Returns true if
# the given graph
# is connected
# else return false
def isConnected(self):
visited = [False] * self.Vert
# Find all reachable
# vertices from the
# first vertex
self.DFS(0, visited)
# If the set of
# reachable vertices
# includes all
# then return true.
for i in range(1, self.Vert):
if (visited[i] == False):
return False
return True
# This function assumes
# that edge (vert_prev, vert)
# exists in the graph
def isBridge(self, vert_prev, vert):
# From undirected graph
# -> remove edge
indU = self.adj[vert].index(vert_prev)
indVert = self.adj[vert_prev].index(vert)
del self.adj[vert_prev][indVert]
del self.adj[vert][indU]
res = self.isConnected()
# Adding -> edge back
self.add_an_edge(vert_prev, vert)
# Return true if graph
# gets disconnected after
# removing the edge.
return (res == False)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Creating the graph
# as given above
g = Graph(5)
g.add_an_edge(0, 1);
g.add_an_edge(0, 3);
g.add_an_edge(0, 4);
g.add_an_edge(1, 2);
g.add_an_edge(2, 3);
print("\n Is there a bridge between (0,4)- ")
if g.isBridge(0, 4):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
print("\n Is there a bridge between (1,2)- ")
if g.isBridge(1, 2):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
Output📋
Is there a bridge between (0,4) - Yes
Is there a bridge between (1,2) - No
Now we have understood how to check if removing a given edge disconnects a graph or not.




