Introduction
The computers we see today have evolved from a few basic concepts derived by people like us. It was not as advanced an idea back then but gave a kickstart to this digitised world. We will look at architecture concepts that paved the way or provided a basis for today’s super-advanced machines.
Classification of computers
There exist two major classifications of computers:
- Stored Program Control Concept
- Flynn’s Classification of Computers
Recommended Topic - Shift Registers in Digital Electronics and Difference Between Jfet and Mosfet
Stored Program Control Concept
This concept simply refers to storing the instructions to execute them in sequence. John Von Neumann introduced this idea in the late 1940s; he proposed that programs be stored electronically in binary format to modify instructions on repeated instruction executions. Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer(ENIAC) is one of the examples that came up during the early 1940s.
Following are further classifications in the Stored Program Concept
- Von-Neumann Model
- General Purpose System
- Parallel Processing
Von Neumann Model
The computer achitecture design proposed by Von Neumann came in 1945 following the concept of stored program control. It consists of an Arithmetic and Logical memory unit(ALU), Registers. Control unit and input/output. Its working is based on a single processor, uses single memory for both instructions and data and does program execution using fetch, decode and execute cycle.
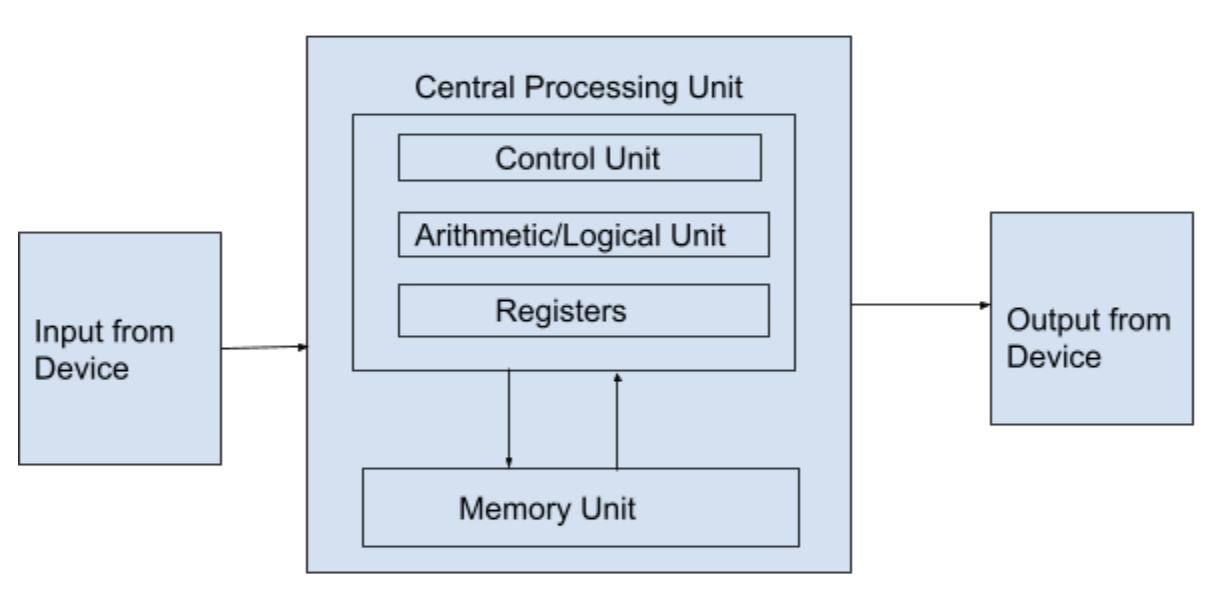
Following are components inside the von-Neumann model:
- Central processing unit
- Buses
- Memory unit
Let’s discuss each one in brief.
Central Processing unit
It processes all of the data operations coming from the instructions from the input/output. There are three significant components inside the CPU: arithmetic logic unit(ALU), Control Unit (CU), and Registers. ALU does all the micro-tasks relating to operations on the instructions, like arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction), logical operations (AND, OR, NOT). The Control Unit only controls the functions of ALU, memory, input and output. Registers contain high-speed storage separate from memory, used to prioritise data processing.
Below is the list of different types of registers.
| Registers | Descriptions |
| Memory Address Register | Holds memory location of data needing to be held |
| Memory Data Register | Holds data being transferred. |
| Program Counter | Holds the address of the next instruction to be processed. |
| Accumulator | Holds logical results |
| Current Instruction Register | It has instructions currently being processed |
Buses
It is a path to interchange information between registers.
| Bus | Description |
| Databus | It acts as a carrier of data between the processor, input/output and memory unit. |
| Address bus | Contains addresses of data between memory and processor. These are addresses and not the data itself |
| Control bus | It carries commands as well as signals coming from CPU |
Memory Unit
It has storage cells bound together in the form of circuits responsible for storing data and feeding it to input/output and processors.
You can also read about Input-Output Processor here.
It consists of two types:
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Read-Only Memory (ROM)
General-purpose system
It consists of ALU, Control units and processors which are interconnected by bus for purpose of exchange of information.
Also read, microprogrammed control unit
Parallel processing
It enables us to achieve multitasking by providing multiple data processing at the same time. Parallel processing systems provide the ability to perform multiple functions like addition, subtraction, increment, decrement at the same time.
Recommended topic: Cloud Computing