Introduction
So are you wondering what Cloud Asset Inventory is? and how can it help in boosting your business?
Don’t worry Ninja! Just follow the article till the end. This blog will discuss the importance of cloud asset inventory and its management and the commercial advantages it may bring to your company.

As we know that the overall internet traffic is increasing at a rate of approximately 100% annually. By distributing incoming traffic among several servers, networks, or other resources, load balancing helps organisations fulfil workload demands while enhancing performance and guarding against service interruptions.
Cloud Asset Inventory provides inventory services based on a time series database that allows you to view, monitor, and analyse all your GCP and Anthos assets across projects and services.

The metadata for Google Cloud assets is stored here for a period of five weeks. This provides each asset's history of creation, modification, and deletion over the past five weeks. The most recent status of an asset is retained by Cloud Asset Inventory even if it was created five weeks ago and hasn't been changed or removed in that time.
Key Features of Cloud Asset Inventory
Now that we know what Cloud Asset Inventory is. It’s time to discuss key feature of Cloud Asset Inventory which are:
Search Assets
You can use a custom query language to search asset metadata included within a project, folder, or organisation using the Cloud Asset Inventory search service.
Let’s see how the cloud asset inventory Utilises a custom query language to search asset metadata and Export to BigQuery.
You may perform data analysis on your inventory after exporting the asset metadata for your project, folder, or organisation to a BigQuery table. Without the need for custom scripts, BigQuery offers users a SQL-like experience for data analysis and the generation of insightful findings.
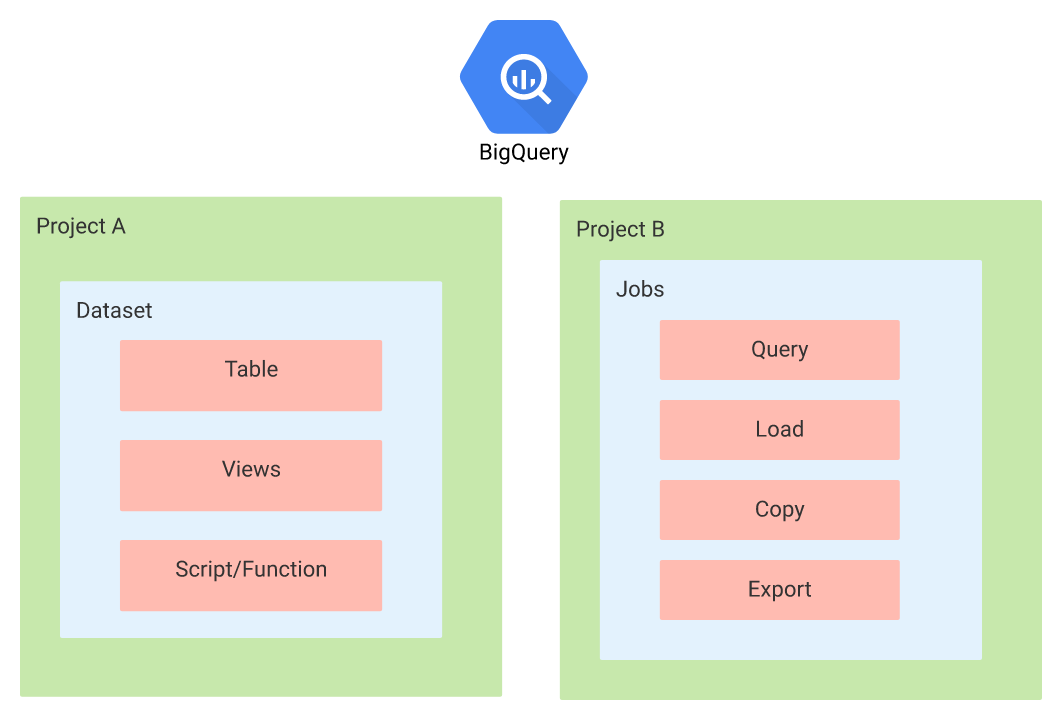
For exporting the big query follow the given steps-
-
Enable the Cloud Asset Inventory API by following the steps mentioned in the first point.
-
Using either the gcloud CLI or the API, configure the permissions necessary to access the Cloud Asset Inventory API.
-
Set up your environment.
Keep in mind that the billing project is used as the consumer project by the gcloud CLI. Check to see if the billing project is distinct from the core project if you get a permission refused message:
gcloud config list
To set the billing project to the consumer project:
gcloud config set billing/quota_project CONSUMER_PROJECT_NUMBER
1. The following roles must also be granted to the specified service account in the destination project if you're exporting to a BigQuery dataset in a project where the Cloud Asset Inventory API is not enabled.
service-${CONSUMER_PROJECT_NUMBER}@gcp-sa-cloudasset.iam.gserviceaccount.com
-
BigQuery Data Editor role (roles/bigquery.dataEditor)
-
BigQuery User role (roles/bigquery.user)
The service account will be created by making a single API call, or you may manually create the service account and grant the service agent role using the following commands:
gcloud beta services identity create --service=cloudasset.googleapis.com --project=PROJECT_ID
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding
PROJECT_ID --member=serviceAccount:service-PROJECT_NUMBER@gcp-sa-cloudasset.iam.gserviceaccount.com
--role=roles/cloudasset.serviceAgent
5. Create a BigQuery dataset.
Export to Cloud Storage
Let’s explore how to export your project's asset metadata to a Cloud Storage bucket. This Cloud Storage bucket should be located in the project from which you're exporting the asset metadata.
For exporting to cloud storage , complete the following steps.
-
Where you'll be running the API commands enable the Cloud Asset Inventory API on the project.
-
Use the gcloud CLI or the API to configure the permissions required to call the Cloud Asset Inventory API.
-
For setting up your environment, complete the following steps.
Gcloud -For setting up your environment to use the gcloud CLI and to call the Cloud Asset Inventory API, on your local client install the Google Cloud CLI.
API- For setting up your environment to call the Cloud Asset Inventory API with the Unix curl command, do the following steps-
-
In order to interface with the Google OAuth system, install oauth2l on your local computer.
-
Confirm that the Unix curl command is available to you.
-
On your project, folder, or organisation, be sure to grant your account one of the following roles.The Cloud Asset Viewer role (roles/cloudasset.viewer)
-
The Owner basic role (roles/owner)
- To store the exported snapshot, create a Cloud Storage bucket.
Export Asset History and Metadata
You can export all asset metadata at a specific timestamp to a Cloud Storage file or a BigQuery table using the Cloud Asset Inventory export service. Additionally, you can export the event change histories of numerous assets over a specified period of time. You can view all the creation, remove, and update events for the given assets over time by viewing the exported event change history.
Before you start working with Cloud Asset Inventory, you must enable the Cloud Asset Inventory API, the Google Cloud CLI, and grant permissions. Google Cloud CLI communicates with Cloud Asset Inventory and other Google Cloud services.
In order to enable the Google Cloud CLI and Cloud Asset Inventory API, let's take the following steps.
-
To evaluate how our products perform in realistic scenarios, you must first create an account in Google.
-
Select or create a Google Cloud project in the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page.
-
Now enable the required API.
-
Install and initialise the Google Cloud CLI.
Monitoring Asset Changes
Utilising real-time notifications, Cloud Asset Inventory enables you to keep track of resource and policy changes that you have subscribed to. You can monitor asset changes by subscribing to real-time notifications.

You can create and subscribe to a feed to get instant information about resource and policy changes. You can specify whether you want to track changes of supported resource types, IAM rules, access policies, and organisation policies within an organisation, project, folder, or for particular resources when configuring the feed. You may also add conditions to your feed so that you only get notifications for specific kinds of asset changes.
Analyze Assets
You may analyze IAM policies inside of a project, folder, or organisation using the Cloud Asset Inventory analysis service. It also allows to analyze IAM policy to find out who has access to what.
Policy Analizer is used to find out which principles it shows how to use the Policy Analyzer (users, service accounts, groups, and domains), have access to which Google Cloud resources.
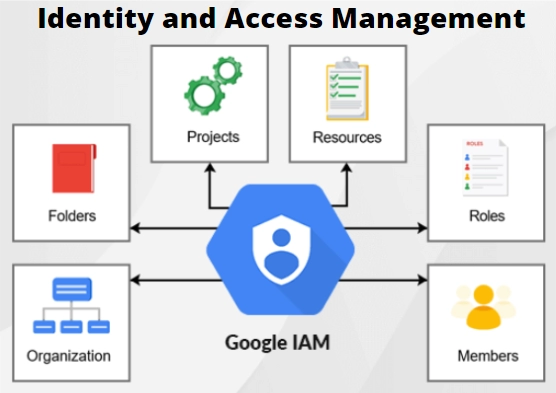
The following roles and permissions are required to analyze allowed policies.
To obtain the permissions that you need to examine an allow policy, you can ask your administrator to grant the following IAM roles on the folder, project, or organization that you will scope your query to:
-
Cloud Asset Viewer (roles/cloudasset.viewer)
-
To analyse policies with custom IAM roles: Role Viewer (roles/iam.roleViewer)
-
To use the Google Cloud CLI to analyse policies: Service Usage Consumer (roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageConsumer)
-
These predefined roles contain the permissions required to analyse an allow policy.
These were some benefits of Cloud Asset Inventory. Now let us talk about Asset inventory management which is generally the way an organization monitors the assets it owns to track and analyze issues such as maintenance requirements, physical location, performance, depreciation, and eventual disposal of the asset.
So let’s discuss the key benefits of Cloud Asset Management.







