Implementation of Combinatorics
In this section of the blog, we will understand combinatorics optimization algorithms by solving the famous traveling salesman problem.
The TSP(Traveling Salesman Problem) is a well-known and extensively researched optimization issue over 90 years. As one might imagine, it has a wide range of applications, including logistics and delivery services.
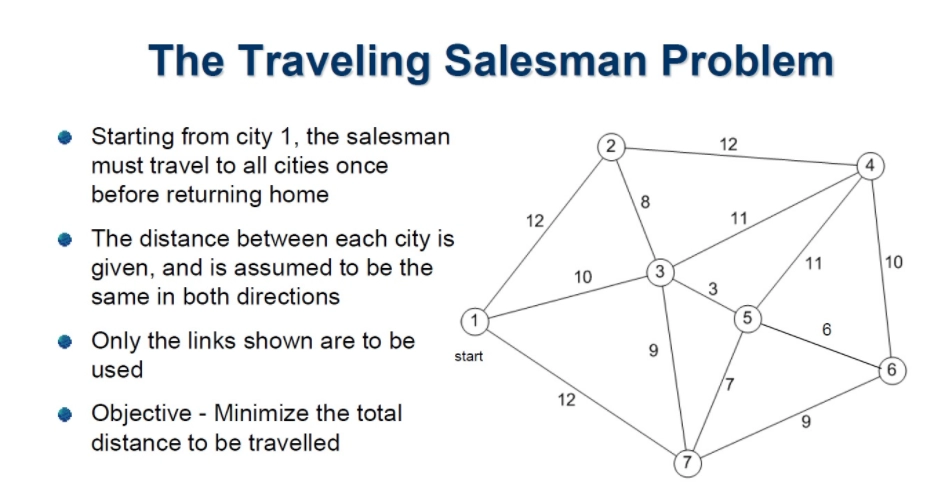
Source: Link
Indeed, many organizations in our present times, such as UPS, Amazon, and others, employ fully optimized TSP solutions (albeit these organizations would be working at the Vehicle Routing Problem, a subtype of TSP). The Vehicle Routing seeks to solve a problem involving a fleet of cars (which we will not discuss today).
This problem can be overcome by creating heuristics that do not require human interaction. The notion of constructing heuristic algorithms without human interaction may be endlessly expanded thanks to neural networks and reinforcement learning.
In the below illustration, we would be using a simple greedy algorithm to optimize the given problem.
Code
Step 1: Import the mathematical libraries.
import numpy as np
Step 2: Creating a function defining the use of the algorithm
def algorithm(cities):
best_order = []
best_length = float('inf')
Step 3: Define the limitations and the specific boundaries in accordance with the algorithm that should filter.
for i_start, start in enumerate(cities):
order = [i_start]
length = 0
i_next, next, dist = get_closest(start, cities, order)
length += dist
order.append(i_next)
while len(order) < cities.shape[0]:
i_next, next, dist = get_closest(next, cities, order)
length += dist
order.append(i_next)
#print(order)
if length < best_length:
best_length = length
best_order = order
return best_order, best_length
Step 4: Create a function to find the closest city so the salesman can select his route accordingly.
def get_closest(city, cities, visited):
best_distance = float('inf')
for i, c in enumerate(cities):
if i not in visited:
distance = dist_squared(city, c)
if distance < best_distance:
closest_city = c
i_closest_city = i
best_distance = distance
return i_closest_city, closest_city, best_distance
Step 5: Apply the mathematical optimization part of the greedy algorithm.
def dist_squared(c1, c2):
t1 = c2[0] - c1[0]
t2 = c2[1] - c1[1]
return t1**2 + t2**2
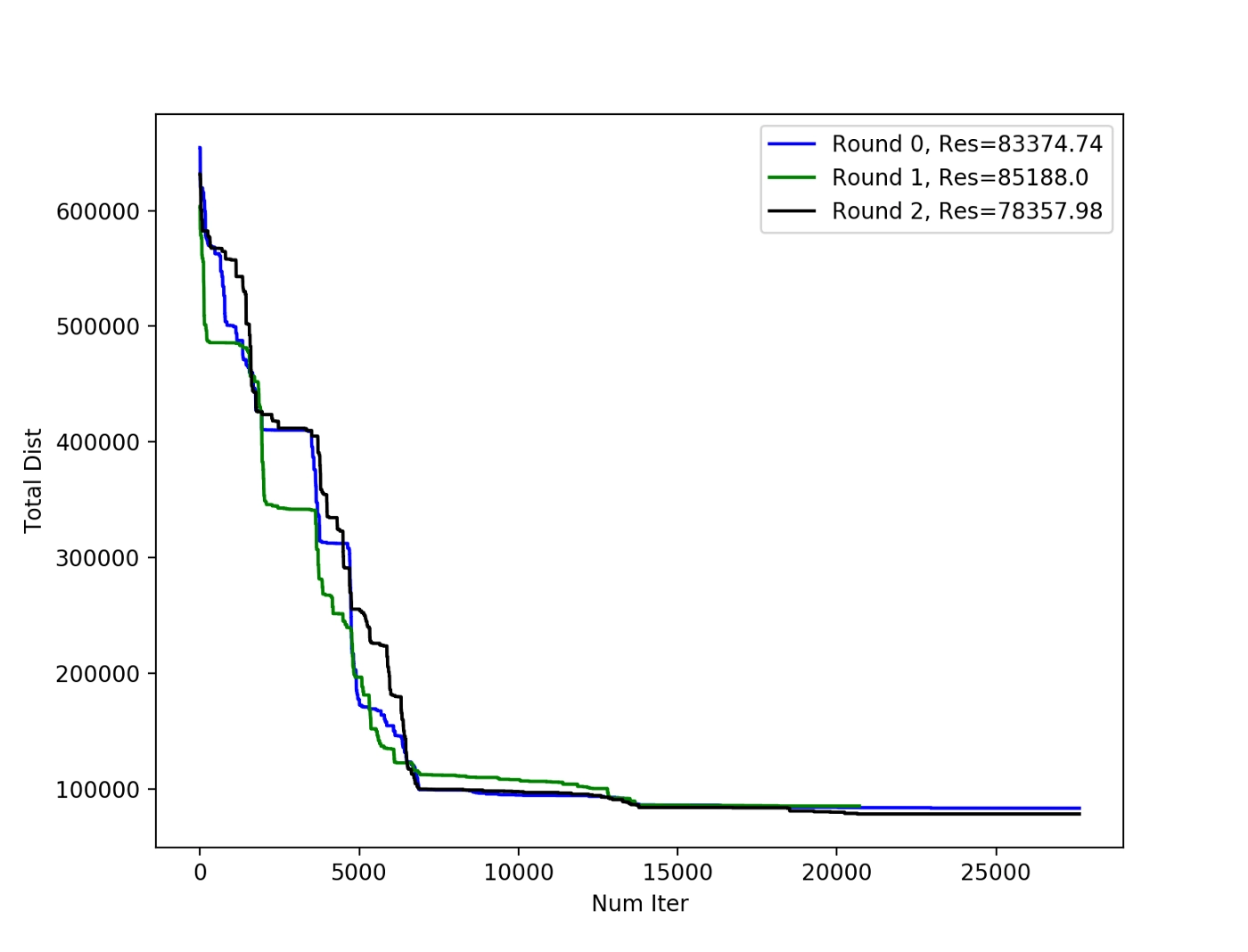
3 runs of the salesman using the combinatorics method with randomized initial points
Use of combinatorics in machine learning
Combinatorics in Machine Learning can select the correct machine learning model. Permutations and combinations can give us the necessary stats to choose the best model.
Combinatorics is also helpful in optimizing the data before applying it to our model.
Also See, Agents in Artificial Intelligence
Subfield and their Application in Combinatorics
Enumerative combinatorics
The most traditional branch of combinatorics is enumerative combinatorics. It primarily focuses on calculating the number of different combinatorial items. Despite the fact that counting the number of items in a set is a somewhat wide mathematical issue, many of the difficulties that emerge in implementations have a fairly simple combinatorial explanation.
Analytical combinatorics
Analytical combinatorics is concerned with the identification of combinatorial structures using advanced analysis and probability theory methods. The field of mathematics known as complex analysis studies the properties of complex numbers. This article does not include probability theory because it is a very broad topic. Unlike enumerative combinatorics, which utilizes explicit formulas and functions, analytical combinatorics concentrates on deriving asymptotic formulae.
Graph Theory
In combinatorics, graphs are important objects. Enumeration (e.g., the set of graphs on n vertices with k edges), existing structures (e.g., Hamiltonian cycles), and algebraic representations. Graph theory and combinatorics are often conceived of as independent sciences, despite the fact that they have strong connections. While combinatorial techniques may be utilized to solve many graph theory issues, the two disciplines are often employed to solve problems of distinct sorts.
Partition Theory
Partition theory is strongly connected to q-series, special functions, and orthogonal polynomials, and it investigates different enumeration and asymptotic issues relating to integer partitions. It was once regarded as a component of integer theory and analysis but is today considered a branch of combinatorics or a separate discipline. It has linkages to statistical mechanics and involves the bijective method as well as different techniques in analysis and analytic number theory.
Design Theory
Combinatorial designs, which are arrangements of subsets with specified intersection qualities, are the subject of design theory. Block designs are a subset of combinatorial designs. This is one of the earliest branches of combinatorics, as evidenced by Kirkman's 1850 schoolgirl problem.
Must Read, Descriptive Statistics
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of combinatorial optimization in AI?
When an exhaustive search is not possible, combinatorial optimization is a collection of methods for finding the best item from a finite number of options. Regardless of the program's eventual role, these optimization processes form the foundation of most AI algorithms.
Is Combinatorics Convex?
The convex combinatorial optimization problem, a broad expansion of the conventional linear combinatorial optimization problem, We prove that it can be solved in strongly polynomial time over any edge-guaranteed family and explore a few applications.
What is Combinatorial Explosion in terms of AI?
The accelerated growth rate at which most programs expand is known as combinatorial explosion. The objective of AI is to minimize the problem of combinatorial explosion. The combinatorial explosion problem happens when the number of entities is increased, resulting in a large number of potential combinations.
Conclusion
The terms "machine learning" and "optimization" are often used interchangeably. Machine learning's primary idea is to minimize a loss function, which might be cost or distance in the case of an optimization issue. When machine learning is used with meta-heuristics methodologies like tabu search and LNS to learn and develop heuristics, breakthroughs in combinatorial optimization are made.
We have discussed in this blog the fusion of combinatorics along with a simple application of it in python to understand the concepts better along with the sub-implementation of combinatorics. You can also consider our Machine Learning Course to give your career an edge over others.