Working with Java Command-Line Arguments
Working with command-line arguments refers to the process of handling and utilizing arguments passed to a program when it is executed from the command line or terminal. In Java, these arguments are provided to the main method of the program as an array of strings (String[] args).
Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
- Passing Arguments: When a Java program is executed from the command line, you can pass one or more arguments after the name of the class file to customize its behavior or provide input data.
- Accessing Arguments: Inside the main method of your Java program, these arguments are accessible via the args parameter. This parameter is an array where each element corresponds to one of the command-line arguments provided when the program was started.
- Array Handling: The args array can be iterated over to process each argument individually. It holds string representations of whatever was typed on the command line after the program's name.
- Usage Examples: Command-line arguments are commonly used to specify file paths, configuration settings, or any other parameters that may affect how the program operates. They provide a flexible way to customize program behavior without modifying its source code.
- Error Handling: Developers typically include validation and error handling mechanisms to ensure that command-line arguments are correctly formatted and appropriate for the program's expected input.
How to Pass and Access Command Line Arguments in Java?
Suppose the class name is CommandLineExample, compile and run it like this:
javac CommandLineExample.java
java CommandLineExample Hello World
Output:
First argument: Hello
Second argument: World
Diagram: Command-Line Arguments Flow
+---------------------+
| User Input (Shell) |
| java CommandLineExample Hello World |
+---------------------+
|
v
+------------------------------------+
| args[] = {"Hello", "World"} |
| |
| Accessed via args[0], args[1], ...|
+------------------------------------+
|
v
+------------------------------+
| Java Program Output |
| First argument: Hello |
| Second argument: World |
+------------------------------+
Example of Command Line Argument in Java
Let’s look at this simple example to understand command line arguments in Java. This program prints all the arguments passed from the command line.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// check if any argument is passed checking the length of args using args.length
if (args.length > 0) {
// traverse the args parameter to access the arguments
for(int i = 0 ; i < args.length ; i++) {
// displays the arguments
System.out.println(args[i]);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Arguments not passed.");
}
}
}
Example of command-line argument that prints all the values
Here's an example of a Java program that prints all the command-line arguments passed to it:
public class CommandLineArgumentsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Print all command-line arguments
System.out.println("Command-line arguments:");
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
System.out.println("Argument " + (i + 1) + ": " + args[i]);
}
}
}
Output
Command-line arguments:
Argument 1: apple
Argument 2: banana
Argument 3: cherry
Steps to Execute the Program
To compile and run the above Java program in the command prompt, follow the following steps:
1. The javac command is used to compile the code, which then creates a .class file.
Syntax:
javac <filename>.java
2. After compilation, the .class file can be executed using the java command.
To simply run the code, use java <classname> Here, the class name is the name of the user’s class. Like in the above case, the user’s class is Main, and “Main” has to be mentioned in the place of the class name.
To pass arguments while running the program, the arguments are mentioned after the class name.
java <classname> arguments
Passing Numeric Command-Line Arguments
The main() method only accepts string arguments, so the arguments passed are stored as Strings in the String array. Hence, it is not possible to directly pass numeric arguments through the command line.
So to have numeric arguments, the string arguments have to be parsed into an integer, double, float, etc., using the parseInt() method, parseDouble() method, parseFloat() method, respectively.
Example:
Let’s look at this simple example to calculate the sum of two numbers.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// check if two arguments are passed
if (args.length == 2) {
// access the first argument
int num1 = args[0];
// access the second argument
int num2 = args[1];
int sum = num1 + num2;
System.out.println("Sum of "+num1+" and "+num2+" = "+sum);
} else {
System.out.println("Enter two numbers.");
}
}
}
In the above example, the arguments are used as such without converting them into it. This produces the incompatible types error.
This can be solved by converting the string argument into an integer using the parseInt() method of the Integer class.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// check if two arguments are passed
if (args.length == 2) {
// access the first argument
int num1 = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
// access the second argument
int num2 = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
int sum = num1 + num2;
System.out.println("Sum of "+num1+" and "+num2+" = "+sum);
} else {
System.out.println("Enter two numbers.");
}
}
}
BMI Calculator using Command-Line Arguments In Java
Let’s write a program to find the BMI using command-line arguments in Java. In this program, the first argument is the name, the second argument is the weight (in kg), and the third argument is the height(in meters).
Formula for BMI
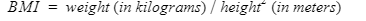
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// check if three arguments are passed
if (args.length == 3) {
// access the first argument
String name = args[0];
// access the second argument
float weight = Float.parseFloat(args[1]);
// access the third argument
float height = Float.parseFloat(args[2]);
float bmi = weight / (float)Math.pow(height,2);
System.out.println("Name: "+name);
System.out.println("BMI: "+bmi);
String bmiCategory;
// assign bmi category
if(bmi < 18.5) {
bmiCategory = "Underweight";
} else if((bmi >= 18.5) && (bmi <= 24.9)) {
bmiCategory = "Normal weight";
} else if((bmi >= 25.0) && (bmi <= 29.9)) {
bmiCategory = "Overweight";
} else {
bmiCategory = "Obesity";
}
System.out.println("BMI Category: "+bmiCategory);
} else {
System.out.println("Enter name, weight, and height in exact order.");
}
}
}
Frequently Asked Questions
What are command-line arguments?
Command-line arguments are external inputs passed to a Java program at runtime, allowing dynamic data input without modifying source code.
How does Java collect command-line arguments?
Java collects command-line arguments through the main(String[] args) method, storing them in the args array for use during program execution.
What is the use of command-line arguments in Java?
The command line arguments in Java are used to pass arguments during the program’s execution.
How to count command line arguments in Java?
To count command line arguments in Java, use args.length within the main method to get the number of arguments passed.
Conclusion
That’s all about the topic! With the help of this knowledge, one can easily create command line applications in Java. It offer a powerful way to make programs more flexible and dynamic. By allowing users to provide input during runtime, they enhance the program’s functionality and usability.
Recommended Reading: