Introduction
A smart city is a framework for developing, deploying, and promoting sustainable development techniques to solve growing urbanization problems. The basic goal of a smart city is to use smart technology and data analysis to improve the quality of life by improving city functions and boosting economic growth. It mainly uses information and communication technologies (ICT).
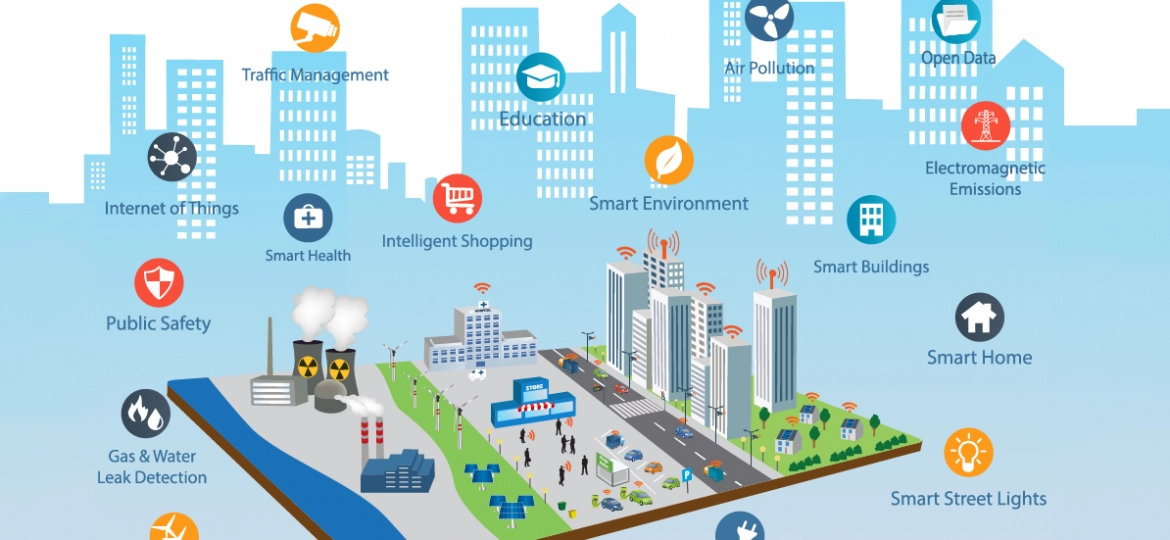
An important aspect of this ICT framework is an intelligent network of connected objects and devices (also known as a digital city) sending data via wireless technologies and the cloud.
In real-time, cloud-based IoT applications receive, analyze, and manage data to assist municipalities, businesses, and individuals in making smarter decisions that improve quality of life.
Citizens interact with smart city ecosystems in various ways, including through their smartphones and connected cars and residences. Connecting devices and data to a city's physical infrastructure and services can help save money and increase sustainability.
With the help of the IoT, communities may enhance energy distribution, speed trash collection, reduce traffic congestion, and improve air quality.
Role of IoT in Smart Cities
Smart cities use various software, user interfaces, communication networks, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The Internet of Things is the most important of these. The IoT is a network of interconnected devices that communicate and share data. Vehicles, home appliances, and on-street sensors are all examples of this. Data collected from these devices are kept in the cloud or on servers, allowing both public and private sector efficiencies to be improved, resulting in economic advantages and improvements to people's lives.
Edge computing is used by many IoT devices to ensure that only the most relevant and important data is sent through the communication network. A security system is also in place to safeguard, monitor, and regulate data transfer from the smart city network and prevent unauthorized access to the IoT network of the city's data platform.
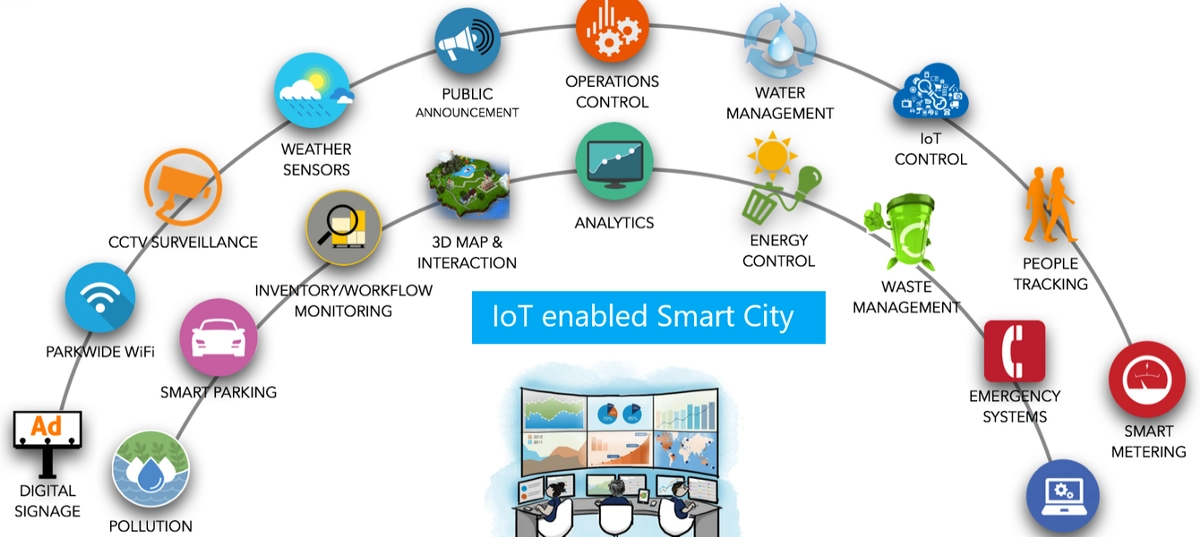
Here are five smart city components and their influence in the Internet of Things era:
- Smart Infrastructure
- Cities must create the conditions for long-term growth: digital technologies are becoming more vital, and urban infrastructure and buildings must be developed more effectively and sustainably.
- CO2 emissions should be minimized by investing in electric cars and self-propelled vehicles.
- Smart cities use sophisticated technologies to create an energy-efficient and ecologically beneficial infrastructure.
- To save electricity, smart lights should only turn on when someone passes past them, such as by setting brightness levels and recording daily usage.
2. The City Air Management Tool (CyAM)
- CyAM is a cloud-based software with a dashboard that displays real-time air quality data from sensors throughout a city and forecasts values for the next three to five days.
- Cities can simulate the next three to five days.
- CyAM is built on MindSphere, Siemens' cloud-based, open Internet of Things operating system (IoT)
3. Traffic Management
- The optimization of traffic is a challenge for large smart cities.
- Sensors embedded in the pavement give real-time traffic flow updates to a central traffic management platform, which analyses the data and adapts traffic signals to the current situation in seconds.
- It makes traffic predictions based on previous data, with no human intervention.
4. Smart Parking
- Smart Parking is now a reality, requiring no complicated infrastructure or significant expenditure, making it appropriate for a mid-sized Smart City.
- When a car leaves a parking space, intelligent parking systems detect it.
- The sensors on the ground inform the driver, via their smartphone, of available parking spaces.
5. Smart Waste Management
- Garbage management systems help improve waste collection efficiency, lower operational costs, and better address the environmental challenges of inefficient waste collection.
- A level sensor is installed in the waste container, and when a particular threshold is achieved, a notification is sent to the truck driver's management platform via smartphone.






