Class Hierarchy
java.lang.Object
→ java.util.AbstractCollection<E>
→ java.util.AbstractSet<E>
→ java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet<E>
Syntax
public class CopyOnWriteArraySet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Serializable

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Here, E is the type of elements stored in the Collection. It implements Serializable, Iterable<E>, Collection<E>, Set<E> interfaces.
Constructors of CopyOnWriteArraySet
1. CopyOnWriteArraySet(): This creates an empty set.
CopyOnWriteArraySet<E> c = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<E>();
2. CopyOnWriteArraySet(Collection c): This creates a set containing all of the elements of the specified collection.
CopyOnWriteArraySet<E> c = new CopyOnWriteArraySet<E>(Collection c);
Program
// Java Program to Illustrate CopyOnWriteArraySet Class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
// Main class
class ConcurrentDemo extends Thread {
static CopyOnWriteArraySet s = new CopyOnWriteArraySet();
// Method
public void run()
{
// Child thread trying to add a new element in the Set object
s.add("Element4");
}
//Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Adding elements using add() method
s.add("Element1");
s.add("Element2");
s.add("Element3");
// Creating a child thread that is going to modify CopyOnWriteArraySet s.
ConcurrentDemo t = new ConcurrentDemo();
// Running child thread using start() method
t.start();
// Waiting for thread to add the element
// Try block to check the exceptions
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
// Catch block to handle the exceptions
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Print statement
System.out.println("Child is going to add the element");
}
System.out.println(s);
// Now we iterate through the CopyOnWriteArraySet without getting exception.
Iterator itr = s.iterator();
while (itr.hasNext()) {
String s = (String)itr.next();
System.out.println(s);
if (s.equals("Element3")) {
// Here we will get RuntimeException
itr.remove();
}
}
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output
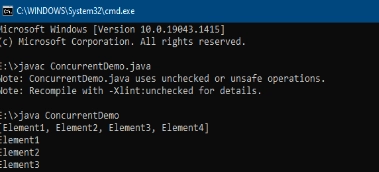
Try it by yourself on java online compiler.
Iterating over CopyOnWriteArraySet
Iteration over the elements contained in this set in the order in which these elements were added can be done using the iterator() method. The iterator returned provides an immutable snapshot of the state of set when iterator was constructed. Synchronization is not required while iterating. The iterator does not supports remove method.
Program
// Java program to Illustrate Iterating Over CopyOnWriteArraySet class
// Importing required classes
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArraySet;
public class Tester {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// create an array list
CopyOnWriteArraySet<Integer> set = new CopyOnWriteArraySet();
System.out.println("Initial size of set: " + set.size());
int count[] = {34, 22,10,60,30,22};
// add elements to the array list
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
set.add(count[i]);
}
System.out.println("Size of set after additions: " + set.size());
// display the set
System.out.println("Contents of set: " + set);
// Remove elements from the array list
set.remove(10);
System.out.println("Size of set after deletion: " + set.size());
System.out.println("Contents of set: " + set);
try {
Iterator<Integer> iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
catch(UnsupportedOperationException e) {
System.out.println("Method not supported:");
}
System.out.println("Size of set: " + set.size());
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output
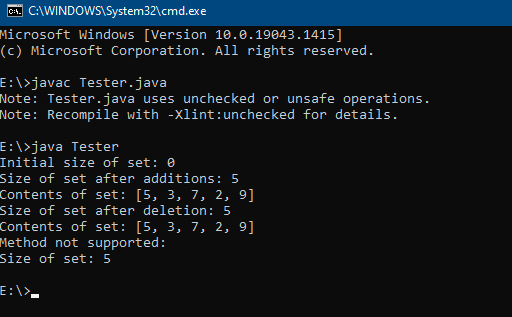
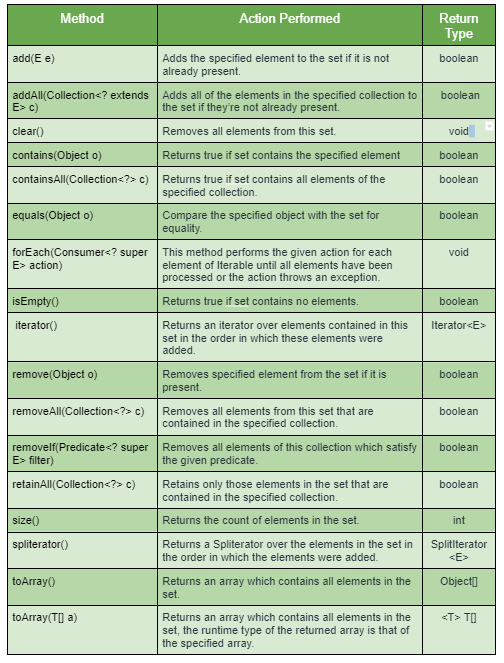
Methods in CopyOnWriteArraySet
FAQs
-
When is CopyOnWriteArraySet useful to achieve thread-safe HashSet?
It is useful when you have a small set of elements for a thread-safe collection.
-
What is the hashCode() method?
It is a method inherited from class java.util.AbstractSet, which returns the hash code value for the set.
-
Which is fast among HashSet and CopyOnWriteArraySet?
HashSet is fast as it is not synchronised while in comparison, CopyOnWriteArraySet is slow as it is synchronised.
-
Which methods are inherited from interface java.util.Collection?
parallelStream() and stream() methods are inherited from interface java.util.Collection.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have discussed CopyOnWriteArraySet. We discussed the syntax, constructors of the CopyOnWriteArraySet. Then we discussed the way of iteration over CopyOnWriteArraySet and various other methods of the class CopyOnWriteArraySet.
Recommended problems -
We hope that this blog helped you enhance your knowledge regarding CopyOnWriteArraySet. Learning never stops, and to learn more and become more skilled, head over to our practice platform Coding Ninjas Studio, to practice top problems, attempt Mock Tests, read informative blogs and interview experiences. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Learning!








