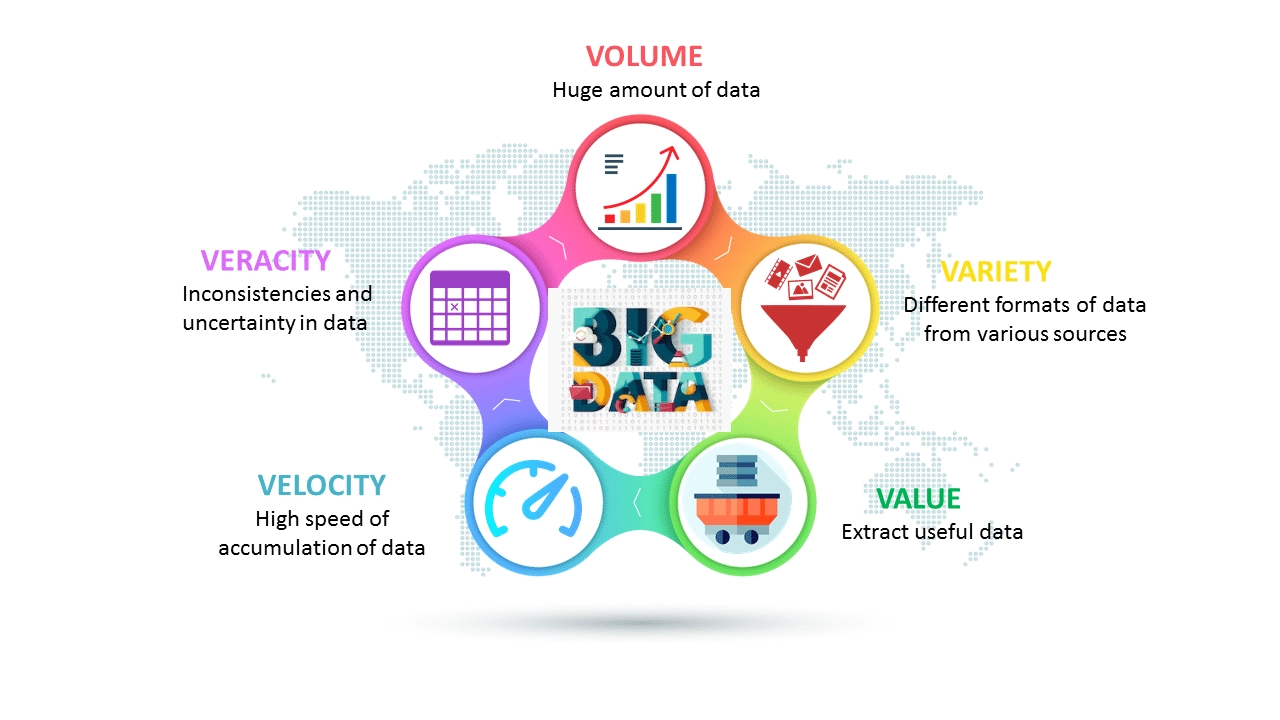
Characteristics of big data
Volume
The size of big data is enormous. The size of data plays a very important role in determining the value of data.
Variety
It refers to the heterogeneous sources and nature of data which can be structured and unstructured.
Velocity
It refers to the speed of generation of data and how fast it is generated and processed to meet the demands.
Variability
It refers to the inconsistency shown by the data at some times.
 source
source
Grasping the fundamental of big data
Handling the data at a large scale became easy for the organizations when the concept of big data occurred. Businessmen struggle to manage their customers' information, product, and services. For example, if a company is selling the goods and all the customers are buying the same goods, it is easy to manage. But when the demand for the goods increases and companies start selling more goods, there are many opportunities for the customers to select any good. Still, in that case, it will become challenging to manage all the customers' data with small data, but when the big data is introduced, it will become effortless for them to manage the data.
We are dealing with a lot of complexity in managing the data. some data are structured, while others are unstructured, which leads to the manipulation of the database at a very high complexity. (We have already discussed the types of data above in this article.)
In today's scenario, the challenge is how companies can make sense of the intersection of all different types of data when dealing with so much information.
Understanding the waves of Data Management
Every data management wave was born to tackle a specific type of data management problem. When the new technology comes into effect in the market, it requires the discoveries of new approaches with a set of tools to allow the company/market to study the relationship between the data elements. Suppose you are the company leader that provides browser surfing. In that case, you have access to the large scale of data that needs monitoring, so to prevent them from any damage, new inventions become a must to prevent the data from hacking.
The evolution of data management over the last five decades has led us to comprehend big data. To do so, you must first understand the foundations of earlier waves. You should also be aware that as we move from one wave to the next, we do not discard the tools, technology, or processes that we have been employing to address a different set of issues.
Wave 1: Creating Manageable Data Structures
Wave 2: Web and content management
Wave 3: Managing big data
In this blog, we will be discussing Wave 1: Creating Manageable Data Structures in detail.
Creating Manageable Data Structures
In the 1970s, the introduction of the related data model and the related website management system (RDBMS) changed the things which set out the framework and approach to improve performance.
Making things worse, a lot of data duplicity was there, and the actual business value of that data was difficult to measure. Most Importantly, the relationship model adds a level of inaccessibility (scheduled query language [SQL], report producers, and data management tools). It fills a growing need to help companies better organize their data and be able to compare emerging sales from one place to another. Entity-Relationship (ER) model emerged, which added additional releases to maximize data usage. It was easy for program planners to meet growing business needs and subtract value from data. In addition, it helped business executives who wanted to explore information such as innovation and compare it with the customer order information for decision-making purposes.
Data repositories and data markets have solved many problems for companies that require a consistent approach to manage large-scale data. These data marts focused on specific business issues and were more targeted and supported the business need for faster queries than massive data storage.
How will the companies adapt their traditional data management systems to capture the growing volume of random data elements? As with any data management wave, the warehouse has evolved to support emerging technologies such as integrated data systems and electronics. Data storage enabled the IT organization to select a subset of data stored such that it would be easier for a business to try to get information. Object information sites enter the programming language, and the structure of the data objects makes it easy to manage a variety of data items without reorganizing the complex joins. The data warehouse helps the companies cope with the growing volume of systematic data they need to analyze minimally.
As many data organizations need to manage and grow control, data storage provides the solution. A random data item can be stored on a related website as a single component of integrated data. Today, content management systems and data repositories can benefit from developing hardware robustness, virtualization technology, and creative ability integrated hardware and software programs, also known as electronic devices. The answer was an additional development of data managed by data marts. Data warehouses are often fed at collection times, usually weekly or daily, to complicate matters, which is excellent for planning, financial reporting, and culture marketing campaigns but slows down in the real-time growing business and consumer locations. The Web site stores BLOB as a set of customizable pieces that look at what was inside, unlike the BLOB, an independent unit connected to a common relationship site, provided with a database of the item and an integrated approach to dealing with informal data.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is big data used in our daily lives?
There are 2.5 quintillion bytes of data produced every day in today's world, and it is increasingly at a very high rate. When a user is using social media, so to know their likes and dislikes, it is the data that is continuously changing and recording the actions of the users to show the relative contents.
What data tools can be used for data recovery?
- Tableau. VS. Qlik Sense.
- Wolfram Mathematica. VS. Looker.
- amoCRM. VS. SyncSpider.
- Phocas Analytics. VS. TIBCO Spotfire.
- Elastic Stack. VS. JMP.
What is the primary purpose of data discovery?
Data acquisition aims to present relevant data, communicate this information to business users in a way that is accessible to non-technical users, and ultimately improve business processes.
Conclusion
We gained insights on Creating Manageable Data Structures through this article and specifically about big data in detail. To know more about Data Warehouse, Hadoop, Cloud, AWS, Data Mining, Database, Non-Relational Databases, and Big data, click on the links. For more such topics, visit Coding Ninjas. We hope that this blog helped you enhance your knowledge regarding Redundant Physical Infrastructure.
Peeps out there who want to learn more about can refer to our guided paths on Coding Ninjas Studio to learn more about DSA, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, etc. Enroll in our courses and refer to the mock test and problems available, interview puzzles, look at the interview experiences, and interview bundle for placement preparations. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Thank you for reading.
Until then, Keep Learning and Keep improving.