Introduction
Today’s world is the Internet era. The Internet has helped organisations to grow strongly and rapidly. With this rapid growth, one primary concern is also penetrating: cyber security.
Cybersecurity refers to the process of protecting internet-connected systems such as computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks.
This article will discuss Cyber Security technologies in detail. So, let’s get started:
Also read - active and passive attacks
Cyber Security Technology
The main aim of Cyber security technology is to protect our internet-connected systems from hackers and malicious activities. Every organisation that uses the internet requires cyber security technologies that address the three primary control types - preventive, detective, and corrective - and auditing and reporting.
There are four types of cyber security technology-

Let’s discuss each of these technologies one by one.
Firewall
A firewall is a network device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing data based on predefined rules. It examines the data, and if the data follows the defined set of rules, it allows the data to pass and otherwise blocks it.
The firewall acts as a barrier between the secured internal network and outside untrusted networks like the Internet.
A firewall can be software (host-based) or hardware (network-based), or both.
Firewall can be categorized into four categories-
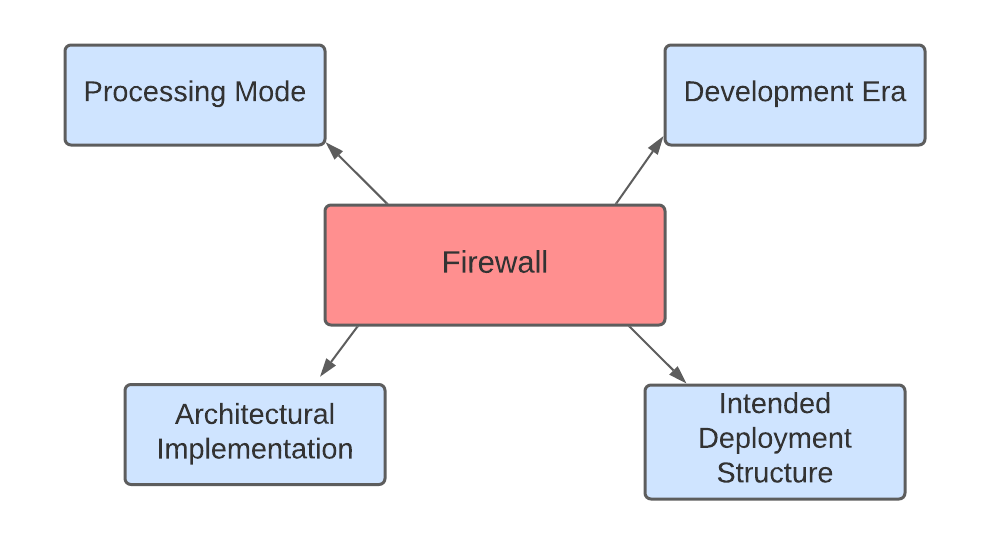
Let’s discuss these categories one by one.
-
Processing Mode
The processing mode category of the firewall technology can be further sub-categorized into five categories.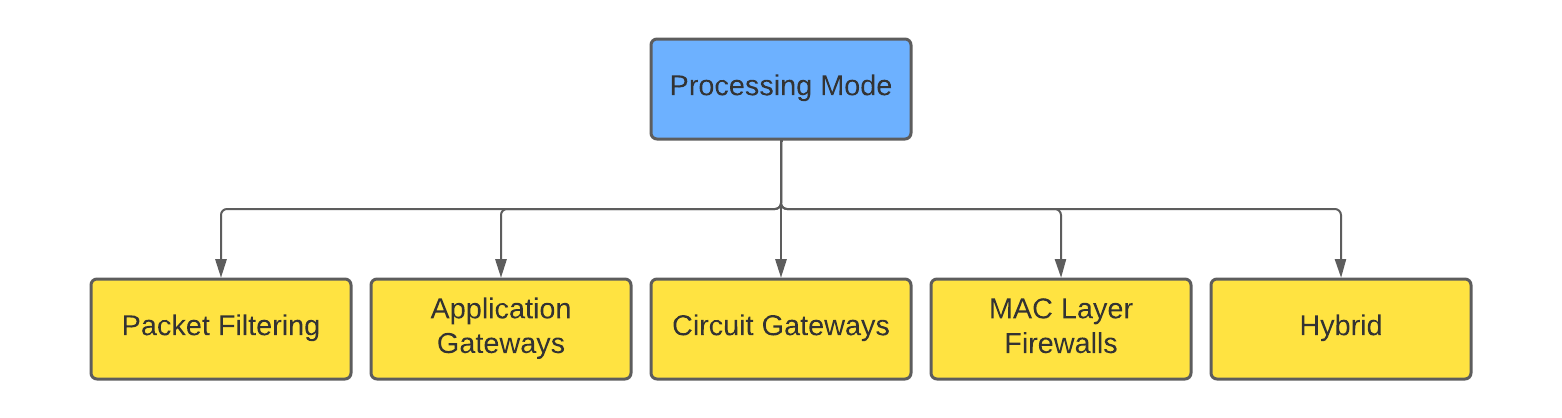
Let’s start with Packet Filtering.
Packet Filtering
A packet filtering is a type of firewall that applies rules to each incoming IP packet and then decides whether to forward it to the next network connection or discard the packet. This firewall is installed on the TCP/IP network.
A packet’s acceptance and abandonment rules are based on the source IP address, destination IP address, protocols and ports.
The packet filtering firewall analyses the traffic at the transport layer. For this purpose, it maintains a filtering table that decides whether the packet will be forwarded or discarded.
Packet filtering firewalls can be further categorised into three types-
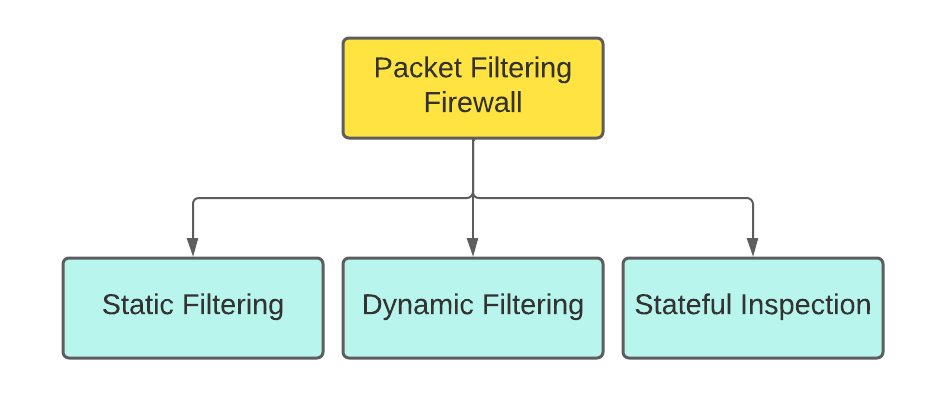
Static Filtering- The system administrator creates the firewall rule in static filtering. These filtering rules govern how the firewall determines which packets are allowed and denied.
Dynamic Filtering- Dynamic filtering enables the firewall to establish some rules for itself, such as dropping packets from an address that sends many wanted packets.
Stateful Inspection- A stateful inspection firewall uses a state table to keep track of each network connection between internal and external systems.
Next, we will discuss application gateways.
Application Gateways
Application-level gateways, also known as a proxy server, contacts users using TCP/IP applications like TELNET, FTP, HTTP, SMTP etc. This firewall is usually installed on a dedicated computer to provide network security.
Application gateways serve as an intermediary between the requester and the protected device. This firewall filters incoming node traffic to specific specifications, which means that only network application data that is transmitted is filtered.
Although application gateways are more secure than packet filtering firewalls, there is a processing overhead.
Next, we will discuss circuit gateways.
Circuit Gateways
A circuit-level gateway is a firewall that uses two TCP connections- one between the internal host and gateway and the other between the external host and gateway. It monitors TCP data packet handshaking and session fulfilment of firewall rules and policies instead of application gateways.
This firewall operates between the transport and application layer, such as the session layer. Here, security checks are done before setting up a connection. Once the connection is established, all the data will be passed.
Next, we will discuss MAC layer firewalls.
MAC Layer Firewalls
The MAC layer firewall is meant to operate at the OSI network model’s media access control layer. It can use the identity of a specific host computer to make filtering decisions. The access control list (ACL) entries are linked to the MAC addresses of particular host computers. This entry specifies the types of packets that can be sent to each host while blocking all other traffic. It will also check a requester's MAC address to determine whether the device used to make the connection is authorised to access the data or not.
Next, we will discuss hybrid.
Hybrid
Hybrid is a type of firewall that combines features from the other four types. These are packet filtering and application gateways components, or packet filtering and circuit gateways, respectively.
2. Development Era
The development era category can be further sub-categorized into five categories.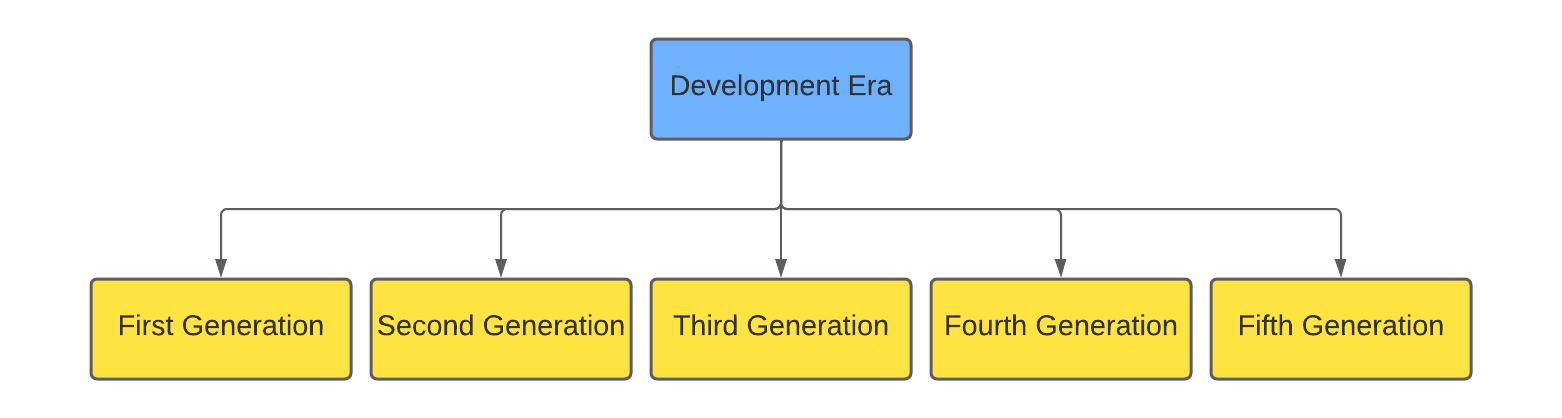
Let’s start with the first generation of the development era.
First Generation- The first generation firewall comes with the static packet filtering firewall. In static packet filtering, the system administrator creates the firewall rule. These filtering rules govern how the firewall determines which packets are allowed and denied. It is the simplest and cheapest firewall protection.
Next, we will discuss the second generation.
Second Generation- The second generation firewall comes with application gateways or proxy servers. It contacts users using TCP/IP applications like TELNET, FTP, HTTP, SMTP etc. This generation ensured more security between trusted and untrusted networks. This firewall filters incoming node traffic to specific specifications, which means that only network application data that is transmitted is filtered.
Next, we will discuss the third generation.
Third Generation- The third generation firewall comes with stateful inspection firewalls. There is more demand for growing support of VPNs, wireless communication, and enhanced virus protection in this generation. It uses a state table to keep track of each network connection between internal and external systems.
Next, we will discuss the fourth generation.
Fourth Generation- The fourth-generation firewall comes with dynamic packet filtering firewalls. It enables the firewall to establish some rules for itself, such as dropping packets from an address that sends many wanted packets. Since dynamic packet filtering firewalls use session information like IP addresses and port numbers, this generation ensures more security than static packet filtering firewalls.
Next, we will discuss the fifth generation.
Fifth Generation- The fifth-generation firewall comes with the kernel proxy firewall. In this firewall, when a packet arrives, a new virtual stack table is created that only contains the protocol proxies required to examine the particular packet. These packets are examined at each stack layer, including the data link header, network header, transport header, session layer information, and application layer data. This firewall works faster than all the application-level firewalls.
3. Intended Deployment Structure
The intended development structure category of the firewall technology can be further sub-categorized into three categories.
Let’s start with commercial appliances.
Commercial Appliances- It consists of a firewall application software that runs on a general-purpose computer and on a custom operating system. It protects medium to large business networks. Using a commercial appliances firewall system requires proper training since it is pretty complex.
Next, we will discuss small office small home firewalls.
Small Office Home Office- As the name suggests, the small office and home office (SOHO) firewalls are designed to protect from internet security threats to small offices and home offices networks. They provide limited resources, so they are simple to use and cheap.
Next, we will discuss residential software.
Residential Software- The residential software firewalls are installed directly on a user’s system. It is basically used to provide protections like antivirus and intrusion detection.
4. Architectural Implementation
The architectural implementation category of the firewall technology can be further sub-categorized into four categories.
Let’s start with packet filtering routers.
Packet Filtering Routers- The packet filtering routers monitor the incoming and outgoing packets. The packet’s source IP addresses, destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports define some rules to allow or block a packet. Thus, controlling the network access.
Next, we will discuss screened host firewalls.
Screened Host Firewalls- The screened host firewalls combine the packet filtering routers with a separate and dedicated firewall. Here, the application gateway also needs only one network interface. It enables the router to pre-screen packets to reduce network traffic and load on an internal proxy. It also protects the harmful protocols from reaching the application gateway.
Next, we will discuss dual-homed host firewalls.
Dual Homed Host Firewalls- The computer system needs to have at least two NICs for using the dual-homed host firewalls. One NIC is connected to the external network, and the other is connected to the internal network providing additional protection. Thus, all the traffic must pass through this firewall to move between the internal and external networks.
Next, we will discuss screened subnet firewalls.
Screened Subnet Firewalls- In this firewall, an additional layer of security is added to the screened host architecture as a perimeter network. This further isolates the internal network from the Internet. In the screened host architecture, there are two screening routers. One router is connected to the perimeter and the internal network, and the other to the perimeter network and external network. This firewall ensures a high-security check on the internal networks and does not compromise its security.
VPNs
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. This technology is widely used to establish a secure and encrypted Internet connection between our device and a network. Using VPNs prevents hackers from keeping track of our information and helps maintain our privacy on a private network. This type of connection helps to ensure that our sensitive data is safely transmitted.
VPNs sound similar to firewalls, but they are different in that firewalls protect data that is local to a device, whereas VPNs protect online data. Data travels through secure tunnels to ensure safe internet communication, and VPNs users use an authentication method to gain access over the VPNs server.
VPNs are mostly employed in the corporate world. They are used by remote users who need to access corporate resources, consumers who want to download files, and business travellers who need to access a geo-restricted site.
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a security system that monitors computer systems and network traffic. It keeps a check on the traffic, prevents possible hostile attacks from the outsider and insider, and prevents system misuse.
There is a difference between firewall and intrusion detection systems. On the one hand, a firewall protects an organisation's sensitive information from malicious activities. In contrast, IDS, on the other hand, alerts the system administrator when someone attempts to breach the firewall’s security and gain access to any network on the trusted side.
The intrusion detection system can be categorised into four categories-
Let’s discuss these categories one by one.
-
NIDS
NIDS stands for Network Intrusion Detection System that monitors the incoming and outgoing traffic to and from all network devices.
-
HIDS
HIDS stands for Host Intrusion Detection System. It runs on all network devices. It has direct access to both the internet and the enterprise internal network. It can detect abnormal network packets that originate within the organisation and malicious traffic that a NIDS has missed. HIDS can also detect malicious traffic generated by the host.
-
Signature-based Intrusion Detection System
The signature-based intrusion detection system detects an attack by looking for specific patterns like byte sequences in network traffic or known malicious instruction sequences used by malware.
This IDS is derived from antivirus software that can detect attacks. However, this IDS fails in detecting new attacks for which no pattern exists.
-
Anomaly-based Intrusion Detection System
The anomaly-based intrusion detection system was introduced to overcome the disability of signature-based IDS, i.e. detection of new attacks. This IDS warns the administrators about the malicious activities. It monitors network traffic and compares it to a predefined baseline. It finds out what is typical for a network in terms of bandwidth, protocols, ports and other devices.
Access Control
Access control is the process of restricting access to a system. Its primary focus is to reduce the risk of unauthorised access to a business or organisation. Users are granted access permission and certain privileges to a system and its resources. So for this purpose, users must provide the credential to gain access to a system. These credentials can be in any form, including passwords, keycards, biometric readings, and so on. Access control ensures the use of security technology and access control policies to safeguard sensitive information such as customer data.
Access control can be categorised into two categories-
Let’s discuss them one by one.
-
Physical Access Control
This type of access control can only be used in buildings, rooms, campuses and physical IT assets.
-
Logical Access Control
This type of access control establishes connections to computer networks, system files and data.
One more method of access control is more secure, known as two-factor authentication. The first factor is that a user wishing to gain access to a system must present credentials, and the second factor could be an access code, password, or biometric reading.
Authorisation and authentication are the two main components of access control. Authentication is a process that verifies and grants access to a user, whereas authorisation determines whether a user should be allowed or denied access to a system.




