Properties of URI
Some of the important properties of a URI are given below.
scheme
The scheme component specifies the protocols that will be associated with the URI. Some schemes require the "//" character, while others do not. Example: HTTP, HTTPS, or file.
http://www.example.comString scheme = uri.scheme;
If we print the scheme of the above Uri, it will give the output as http.
authority
The authentication section, a host, and an optional port number preceded by a ':' comprise the authority component. The authentication section contains the username and password. Any IP address can serve as the host.
http://www.example.com/bananasString authority = uri.authority;
If we print the authority of the above Uri, it will give the output as www.example.com.
Note: The authority can also include user info and port information.
http://user:password@www.example.com:8080/bananasString authority = uri.authority;
If we print the authority of the above Uri now, it will give the output as user:password@www.example.com:8080.
userInfo
This property contains user information.
http://user:password@www.example.comString userInfo = uri.userInfo;
If we print the userInfo, the output will be user: password.
Note: Passwords should not be included in the URI in plain text. This is both a security risk and a deprecated practice.
host
It contains the hostname of the URI.
http://user:password@www.example.com:8080String host = uri.host;
If we print the host of the above Uri, the output will be www.example.com.
port
The port number specifies the protocol port used to communicate with the server specified in the URI. This port number is given after a colon after the host.
http://www.example.com:8080int port = uri.port;
If we print the port value of the above Uri, the output will be 8080.
path
The path is a string that contains the address of the resource on the server.
http://www.example.com/fruit/bananasString path = uri.path;
If we print the path of the above URI, it will give the output as /fruit/bananas.
pathSegments
Because a path frequently has multiple segments, you can obtain them as a list rather than parsing them yourself:
http://www.example.com/fruit/bananasList<String> pathSegments = uri.pathSegments;
If we print the path segments of the above URI, it will give the output as [fruit, bananas].
query
A query is nonhierarchical data that is typically used to search for a specific resource. They are separated from the previous section by a '?'.
http://www.example.com/fruit?q=yellowString query = uri.query;
If we print the query of the above URI, it will give the output as q=yellow.
fragment
Fragments are used to identify secondary resources such as headings or subheadings on a page, and so on.
http://www.example.com/fruit#bananasString fragment = uri.fragment;
If we print the fragment of the above Uri, it'll give output as bananas.
Encoding-Decoding of URI Components
We use the encodeComponent() and decodeComponent() methods to encode and decode all of the string's characters that have a particular meaning in a URI, such as (but not limited to) “/”, “&”, and “:”.
Encoding and decoding fully qualified URIs
Except for characters with special meaning (such as /,:, &, #) in a URI, the encodeFull() and decodeFull() methods are used for encoding and decoding characters in a URI, respectively.
Parsing URIs
We may get the parts of a URI object or a URI string using URI fields like path. We use the parse() static function to generate a URI from a string.
Building URIs
The Uri() constructor can be used to create a URI from individual pieces of scheme, host, path, and fragment.
Below is an example showing its practical application.
Code:
void main(){
var uri = Uri(
scheme: 'https',
host: 'dart.dev',
path: '/foo/bar',
fragment: 'utility-classes');
print(
uri.toString() == 'https://dart.dev/foo/bar#utility-classes');
}
Output:
true
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Dart and Flutter?
Flutter is a Google-developed open-source user interface SDK. It supports the creation of iOS/Android apps and uses the Dart programming language. Dart is a client-side programming language that is open-source. It's simple to learn, reliable, and capable of producing high-performance applications.
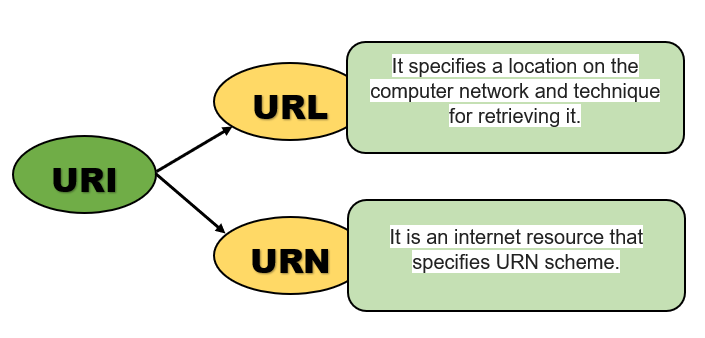
What is the basic difference between a URI and URL?
A URI is a string of characters that identifies a web resource on the internet by its location, name, or both. A URL, on the other hand, is a string of characters that merely serves to identify the location of an internet resource.
What is the difference between Uri.fromParts and Uri.parse??
Uri.fromParts From the given components creates an opaque Uri, and Because this approach encodes the ssp, it can't be used to generate hierarchical URIs. Uri.parse, on the other hand, is simply used to generate a URI from a string
Conclusion
In this article, we learned about Dart URI and its encoding-decoding methods for generating, parsing, and building URIs. However, learning never stops, and there is more to learn. So head over to our Android Development Course on the Coding Ninjas Website to dive deep into Android Development and build future applications.We hope this article has helped you enhance your knowledge as a Dart beginner. If you want to learn more, check out our article on environment setup and Competitive Programming articles. Do upvote this article to help other ninjas grow.