Medium Data Structure MCQs
11. What is the advantage of external hashing over open addressing?
(a) Less space is used
(b) Deletion operation is easier.
(c) The time complexity is lesser
(d) All of the above
Ans. (b) Deletion operation is easier.
Explanation. The open addressing scheme has a limitation that we cannot delete the item if the empty bucket is between the search, while external hashing is free from this.
12. What is the time and space complexity to delete a node from the singly linked list?
(a) Time complexity: O(1), Space complexity: O(1)
(b) Time complexity: O(1), Space complexity: O(n)
(c) Time complexity: O(n), Space complexity: O(1)
(d) Time complexity: O(n), Space complexity: O(n)
Ans. (c) Time complexity: O(n), Space complexity: O(1)
Explanation. To search for the node, we need to traverse the full linked list; hence time complexity will be O(n), and space complexity will be O(1). As to keep track, we only require a temp variable.
13. What is the complexity of searching in direct addressing?
(a) O(1)
(b) O(log(n))
(c) O(n)
(d) O(n2)
Ans. (a) O(1)
Explanation. Searching in direct addressing takes constant time since every key has a unique array position.
14. Which among the following sorting algorithm is the most optimal one to sort a random linked list?
(a) Merge sort
(b) Insertion sort
(c) Quick sort
(d) Heap sort
Ans. (a) Merge sort
Explanation. Both insertion and merge sort can be used to sort a random linked list.
Merge sort takes O(N log N) time to sort, and insertion sort takes O(N*N).
Must Read Difference between ArrayList and LinkedList, hash function in data structure.
15. How many edges are present in the complete graph of n vertices?
(a) n(n-1)/2
(b) n(n+1)/2
(c) n
(d) n/2
Ans. (a) n(n-1)/2
Explanation. n complete graph, all the edges are connected to each other; hence the maximum number of edges is calculated by nC2, which is equal to n(n-1)/2.
16. What is the time complexity of performing the enqueue operation in the Queue?
(a) O(1)
(b) O(log(n))
(c) O(n)
(d) O(n*n)
Ans. (a) O(1)
Explanation. The queue is based on the FIFO principle, and the insertion is done from the rear, which can be accessed directly, so it requires O(1) time.
17. What is the maximum number of edges possible in a directed graph having 6 vertices and no self-loops?
(a) 6
(b) 30
(c) 36
(d) 216
Ans. (b) 30
Explanation. The graph having n vertices can be connected to n-1 vertices, so the total number of edges possible is n*(n-1).
18. What is the maximum depth of a trie with n strings of length m?
(a) n
(b) log2 n
(c) m
(d) log2 m
Ans. (c) m
Explanation. The trie is used to store the strings on the basis of common prefixes. Hence the maximum string length is the maximum depth of the trie.
19. How many nodes does a full binary tree with n leaves contains?
(a) 2*n - 1
(b) 2n
(c) n
(d) n - 1
Ans. (a) 2*n - 1
Explanation. A full Binary tree has 0 or 2 children. So, a binary tree having n leaves contains 2*n - 1 node.
20. What is the condition of the overflow of a linear queue implemented using an array?
(a) Rear = front + 1
(b) Rear = front
(c) Rear = MAX_SIZE
(d) Rear = MAX_SIZE - 1
Ans. (d) Rear = MAX_SIZE - 1
Explanation. We can only insert the elements till the maximum size of the array; hence Rear = MAX_SIZE - 1 should be checked to avoid the overflow condition.
Hard Data Structure MCQs
21. Which of the following is the postfix of the expression A+B/C*(D-A)?
(a) ABC/DA-*+
(b) +A/B*C-DA
(c) ABCDA/-*+
(d) +*-/ABCDA
Ans. (a) ABC/DA-*+
Explanation. In the postfix operation, all the operators appear after the operand.
22. What output does the following code give?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int arr[5]={1,2,3,4,5};
printf("%d", arr[5]);
return 0;
}
(a) Garbage Value
(b) 5
(c) 1
(d) Error
Ans. (a) Garbage Value
Explanation. Since the indexing of the array starts from 0, so the elements of an array can be accessed as arr[0] to arr[4]. The arr[5] will try to access some memory location outside the array, hence printing the garbage value.
23. What is the cost of searching for an AVL tree?
(a) O(n)
(b) O(log (n))
(c) O(n*n)
(d) O(n*log(n))
Ans. (b) O(log(n))
Explanation. AVL tree is a balanced tree. First, we check the current node value and then recur the left or right subtree accordingly. The number of comparisons is limited by height n; the time complexity is O(log(n)).
24. What is the time complexity of the delete operation from the rear end of the deque?
(a) O(1)
(b) O(N)
(c) O(N*N)
(d) O(N*log(N))
Ans. (b) O(N)
Explanation. The time complexity is O(n) as we have to traverse the n elements to delete it from the rear end.
25. Which is faster in search operation among the AA trees and Red-black trees?
(a) AA-tree
(b) Red black tree
(c) Equally faster
(d) None of these
Ans. (a) AA-Tree
Explanation. AA-tree is faster than Red black time in searching because it is flatter.
26. Consider the following numbers 8,1,2,4,3,9,6,5 to be inserted into the empty binary search tree. What will be the sequence of in-order traversal of the resultant binary search tree?
(a) 8 1 3 5 6 9 2 4
(b) 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9
(c) 5 6 9 3 4 2 1 8
(d) 8 1 2 4 3 9 6 5
Ans. (b) 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9
Explanation. The in-order traversal of a BST gives increasing order of the elements.
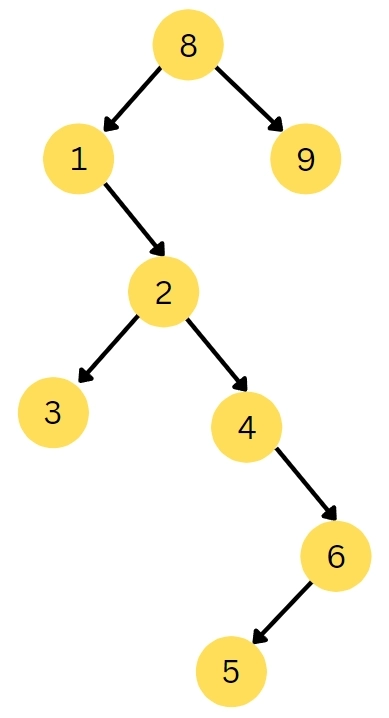
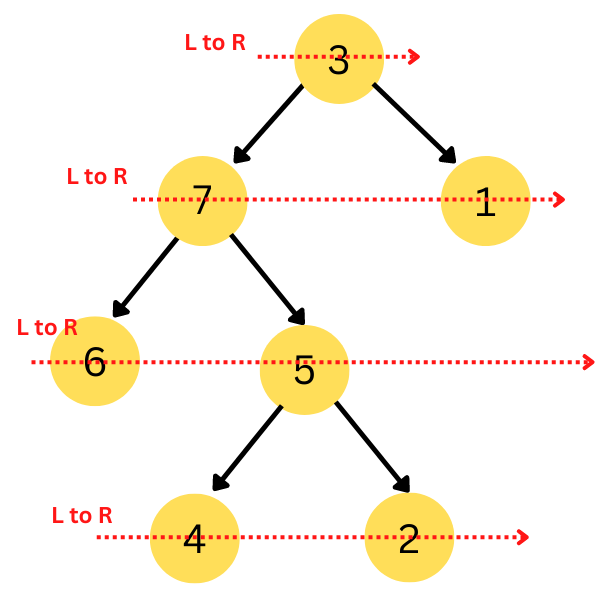
27. What is the level-order traversal of the following tree?
(a) 3, 7, 6, 5, 4, 2, 1
(b) 6, 7, 4, 5, 2, 3, 1
(c) 3, 7, 1, 6, 5, 4, 2
(d) 3, 1, 7, 5, 6, 2, 4
Ans. (c) 3, 7, 1, 6, 5, 4, 2
Explanation. n level-order traversal, all the nodes on each level are traversed, and then we move on to the next level.
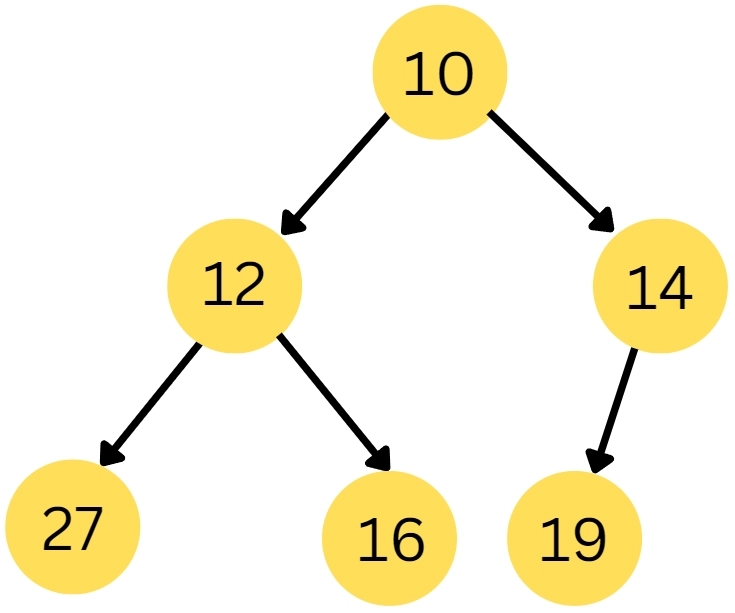
28. Which among the following array depict a binary min-heap?
(a) 14 12 10 27 16 19
(b) 27 19 16 14 12 10
(c) 16 19 27 12 14 10
(d) 10 12 14 27 16 19
Ans. (d) 10 12 14 27 16 19
Explanation. A min heap has data in such a way that every node value is smaller than its children’s value.
29. What is the output of the program after performing the following functions?
push(10);
push(20);
pop();
push(15);
pop();
pop();
top();
push() - It is used to push an element into the stack
pop() - It is used to pop the top element of the stack
top() - It returns the top element of the stack
(a) 20
(b) 10
(c) 15
(d) Stack Underflow
Ans. (d) Stack Underflow
Explanation. push (10) and push(20) will push 10 and 20 into the stack. Now pop() will remove the top element, i.e., 20. Now, push(15) will push 15 into the stack. pop() will remove 15 and then 10. Now the stack is empty, hence Stack underflow.
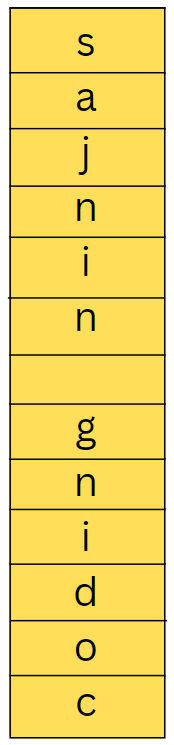
30. What output does the following code produce?
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s = "Coding Ninjas";
stack<char> st;
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
st.push(s[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<s.size();i++){
cout<<st.top();
st.pop();
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
(a) Coding Ninjas
(b) sajniN gnidoC
(c) Ninjas Coding
(d) gnidoC sajniN
Ans. (b) sajniN gnidoC
Explanation. We have put all the characters of the string in the stack; the stack will reverse the string.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 types of data structures?
- Arrays: Ordered collections with fixed sizes.
- Linked Lists: Linear data structures with nodes.
- Stacks: LIFO structures for managing data.
- Queues: FIFO structures for managing data.
- Trees: Hierarchical structures used for organizing and searching data.
What is the use of data structure Mcq?
Data structure MCQs are a tool for assessing a person's understanding of the concepts of data structures, including arrays, linked lists, and graphs. They are commonly used in computer science education to evaluate students' knowledge and mastery of these concepts.
Which categories are available in data structure Mcq?
Data structure MCQs are typically categorized into different topics, such as arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. Each category focuses on a specific data structure and tests the respondent's understanding of its properties, operations, and applications.
Why is practicing Data Structure MCQ important?
Practicing Data Structure MCQ is important because it helps individuals reinforce their understanding of data structures concepts and improve their problem-solving skills. It also prepares them for exams and technical interviews, where knowledge of data structures is often tested.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have gone through some most important Data structures MCQ questions. We have discussed them in detail with their explanation.
Related articles
Refer to our Guided Paths on Coding Ninjas Studio to learn more about Data structures and algorithms, Competitive Programming, JavaScript, System Design, etc. Enroll in our courses and refer to the mock test and problems available.