Introduction
Just like every other language (C, C++, Java), there is also the concept of data types in dart. To store a variable in a programming language, we use data types to specify the type of variable we are using. When we create a variable, we also provide some amount of memory to it. That amount of memory also varies for different data types.
Dart also provides dynamic data types feature means when the variable type is not mentioned explicitly. We can use the dynamic data type by using the keyword dynamic.
Types of Data Types
There are several types of data types in the dart, such as:
Number
This data type is used to store numeric data like integer, double, etc.
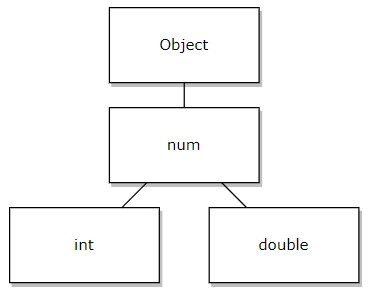
Keywords: int, double, num (inherited data type of int and double).
int: The int keyword in the Dart programming language represents an integer. Integers, as we all know, are made up of whole numbers (i.e., non-decimal positive and negative numbers). In the RAM, four bytes are assigned for each integer.
double: Double is a data type in the Dart programming language that stores decimal values (fractional numbers). Eight bytes are allocated in memory for each double variable. Any integer value you try to assign to the double variable will be cast to the double data type by default.
num: All numbers in Dart are part of the common Object type hierarchy, and there are two concrete, user-visible numeric types: int and double, which represent integer and fractional values, respectively. Those numeric types have distinct, hidden implementations depending on the platform. But now in new versions, you will not face any problems implementation-wise.
Dart Dev
Declaration and Initialization:
int x;
x = 100;
double y;
y = 10.5;
//We can also do both the step at once.
int x = 100;
double y = 10.5
Code:
void main() {
// declare an integer
int x = 100;
// declare a double value
double y = 10.5;
print(x);
print(y);
//passing string
var x_new = num.parse("100");
var y_new = num.parse("10.5");
print(x_new);
print(y_new);
}
Output:
100
10.5
100
10.5String
The most common application of strings is to represent text. A string can be single or multiline in nature. Matching single or double quotes are used to write single line strings, and triple quotes are used to write multiline strings.
Keywords: String
Syntax:
String s1 = 'Coding Ninjas';
String s2 = "Coding Ninjas";
String s3 = '''This is an example showing
multiline string using single quotes.''';
String s4 = """This is an example showing
multiline string using double quotes.""";
//All above given strings are valid.
Code:
void main() {
String s1 = 'Coding';
String s2 = " Ninjas";
String s3 = s1 + s2;
print(s3);
}
Output:
Coding NinjasBooleans
This data type is used to represent boolean type data mean either true or false.
Keywords: bool
Syntax:
bool goodArticle = true;
Code:
void main() {
bool goodArticle = true;
print(goodArticle);
}
Output:
trueLists
An array is a highly popular collection in programming. Arrays are represented in Dart as List objects. A list is essentially a collection of objects that are arranged in a certain order. The List class in the dart:core library allows you to create and manipulate lists.
Keywords: List
Syntax:
List<int> l1 = [1,2,3];
Code:
void main() {
List<int> l1 = [1,2,3];
List<String> l2 = ['Ninja1','Ninja2'];
print(l1);
print(l2);
}
Output:
[1, 2, 3]
[Ninja1, Ninja2]Map
Map is used to store the key-value pairs. Each key present in the map must be unique, whereas the values can occur multiple times. Every key is associated with only one value. We can declare a map data structure using curly braces {} and each entry is separated by a comma (,).
Keywords: Map
Syntax:
Map<int,String> cn = {};
Code:
void main() {
//Declaring a map
Map<int,String> cn = {};
//Inserting elements inside the map.
cn[1] = "Coding";
cn[2] = "Ninjas";
cn[3] = "is";
cn[4] = "good";
print(cn);
}
Output:
{1: Coding, 2: Ninjas, 3: is, 4: good}Set
Set is a data structure that contains a sequence of data having the same data types. Set consists of unique elements (duplicate elements are not allowed) and unordered in nature means it does not preserve the input order.
Keywords: Set
Syntax:
Set<data_type> st = {};
//OR
var st = <data_type>{};
Code:
void main()
{
//Declaring and Initializing a set.
Set<String> st = {"Pen","Paper","ball","Pen","Ink","Lense","Ball","Ink"};
//Notice there are repeated elements in the set.
print("Set: $st");
}
Output:
Set: {Pen, Paper, ball, Ink, Lense, Ball}




