Introduction
Have you ever wondered why everyone around us is obsessed with getting a perfect space on their devices? Why are RAM sizes generally smaller than hard drives?
What are these devices, how much data can they store? How are they connected, what type of hierarchy do they follow? So many questions; well, we will discuss them all in this article.

Database are the collection of data that provide the ultimate view of the stored data. We all know that data is stored in bits and bytes in different storage devices. At the physical level, actual data is stored in some devices in electromagnetic form. Storage systems can be classified into three types of storage devices now; let's understand these types thoroughly:
Must Recommended Topic, Schema in DBMS,Lock based protocol in DBMS and Checkpoint in DBMS
Types of Data Storage
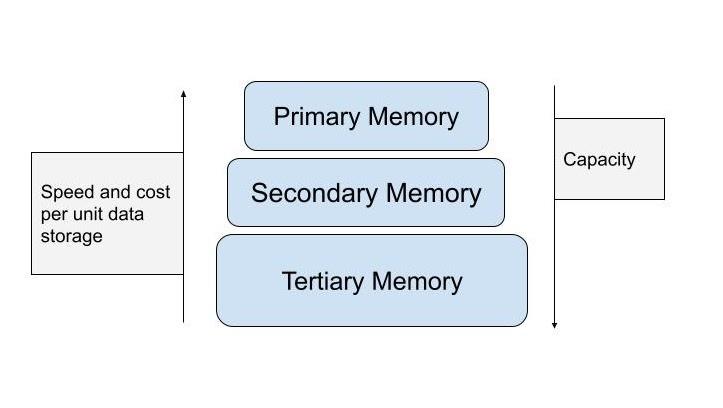
There are three types of data storage devices namely primary, secondary and tertiary storage. The relationship between them in terms of storage capacity, cost, and speed is shown in the diagram given below. Now let’s study each type in detail
Primary Storage
It is the memory storage that is directly accessible to the CPU. It provides quick access to the stored data. These types of storage devices temporarily store the data, and therefore, they are also termed volatile storage. Volatile means that if the system gets off(restarts, gets a power cut, or crashes), the data in these devices are lost permanently, and the space becomes again free, which can be utilized for other purposes.
Since these devices are directly accessible to the CPU, they are placed on the motherboard. These devices are typically small and ultra-fast. CPU's internal memory(registers), cache memory, and main memory(RAM) are all directly accessible to the CPU and are placed on the motherboard's chipset. CPU's main memory and cache are two important primary devices. Let us discuss them right away:
Main memory
The main memory handles the instructions of the computer. It is generally termed RAM(Random Access Memory). RAM stores operating system software, software applications, and other information for the CPU to have direct access when needed.

source:pexels.com
Cache
It is a tiny storage media that is maintained by computer hardware only. A cache is much faster than RAM and makes data retrieving easier and more efficient.

Secondary Storage
Secondary storage is the storage area that allows you to save and store data permanently, and it is also called 'Online storage.' Secondary storage is 'non-volatile storage, i.e., unlike primary storage, it doesn't lose data if the system restarts, crashes, or gets a power cut. Secondary storage devices work alongside primary computer storage(i.e., cache and RAM), and they are not as fast as primary storage. Some commonly described secondary storage media are:
Hard Drive
A hard drive, hard disk, HDD, or HD is a non-volatile data storage device. It is usually installed on the computer and directly connected to the motherboard. It contains one or more platters housed inside the air-sealed casing; data is written on these platters with a magnetic head/heads that move to and fro as platters spin. These can be of various sizes and can store data as per the user's need. There are two types of HDDs, namely internal HDD and external portable HDD.

source:pexels.com
Magnetic Disk storage
A magnetic disk is a flat disk covered with a magnetic coating and uses a magnetization process to read, write and access data. It stores data in the form of tracks, spots, and sectors. Floppy disks and zip disks are typical examples of magnetic disks.

Tertiary Storage
Tertiary storage devices are devices to store immense amounts of data. These storage devices are external to the computer system and slowest. Generally, these devices are used to back up an entire system. Optical disks(optical storage) and magnetic tapes(tape storage) are commonly used tertiary storage devices. These two types of storage are explained below:
Tape Storage
In a tape storage system, magnetic tape is used as a recording media to store data. Generally, magnetic tapes are used for archiving and backup data for long-term storage.

Optical Storage
In optical storage, data is read and written with a laser. Typically data is written on a Digital Versatile Disc(DVD) or Compact Disk(CD). Optical media is more durable and less vulnerable to environmental conditions than tape storage.

Source:pixabay.com
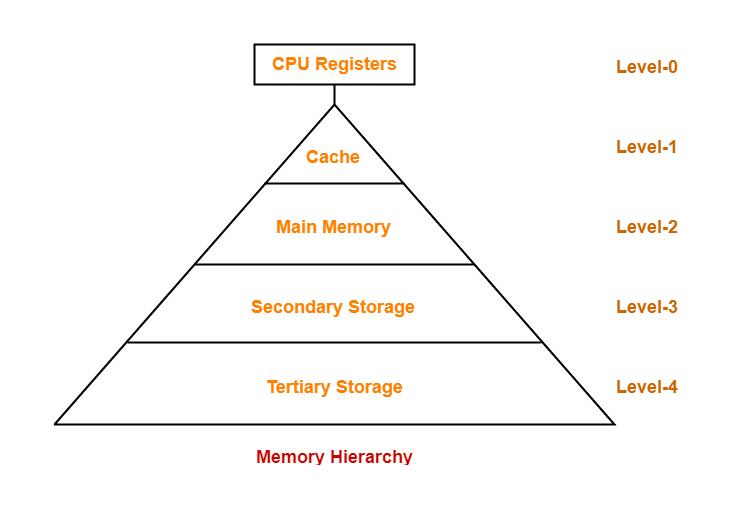
Now that we’ve gained a depth of understanding of different storage devices, let us now look at the hierarchy they follow:
Recommended Topic - Specialization and Generalization in DBMS And Recursive Relationship in DBMS