Introduction
Deadlock is a situation when all processes are holding one resource each while they wait for another process to acquire a different resource. Starvation is a situation that prevents low-priority processes from acquiring resources. Starvation occurs when processes with high priorities constantly consume resources.
To begin with, we all know how important the role of operations between processes has in any operating system.
A computer system can handle numerous tasks at once. At the moment of execution, a process loads into memory. Processes are continually produced and destroyed. Deadlock and starvation are two common issues that are attributed to processes.
So, to understand the difference between the two, we have to first understand both the terms in detail. Are you excited to dive into the deep concepts of operating systems? So, let’s get started.
Also see, Types of Operating Systems and Open Source Operating System.
What is Deadlock?
Whenever a process enters a waiting state since the other waiting process is holding the requested resource, it is called a deadlock. A major difficulty in multi-processing is a deadlock, which occurs when numerous processes share a mutually exclusive resource known as a soft lock or software.
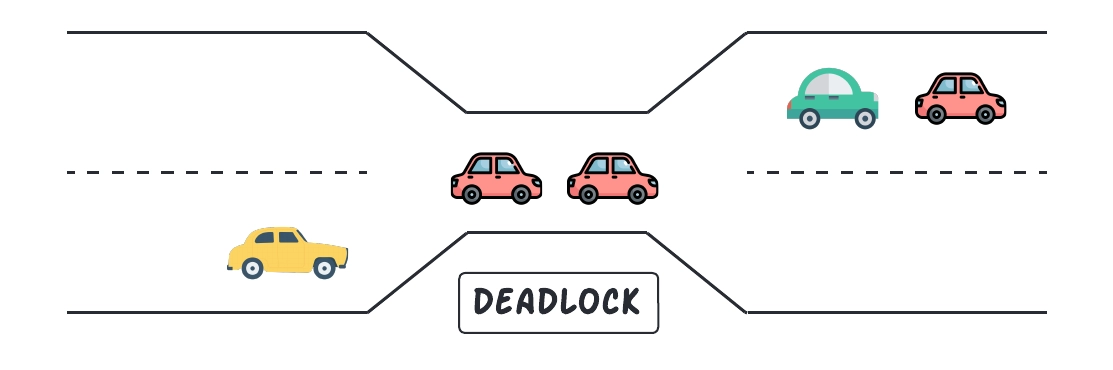
To understand more, let’s take a real-life example of running traffic, which only moves in one way. And, a bridge is a resource in this case. So, In this situation, we can see that the problem can be solved if one car backs up or a process backs up in the operating system. When a deadlock occurs, it is readily resolved when we Preempt resources and rollback.
So, did u get the concept or not? As it was more about the real world and less about the computer world, so let us take a much more brief and more relatable example that directly relates to the operating processes.
So, Let's assume that P1 and P2 are the two processes we have. Process P1 is currently holding resource R1 and waiting for resource R2. And, at the very same time, process P2 is using resource R2 while waiting for resource R1.

As a result, process P1 is waiting for process P2 to give up its resource while process P2 is also waiting for process P1 to free its resource. And no resources are being released. As a result, they are each waiting for the other to relinquish the resource. This results in endless waiting and no work being done. This is known as deadlock.
Below are the four conditions that may occur in deadlock. These are as follows:
- Mutual Exclusion
- Hold and Wait
- No preemption
- Circular Wait
Mutual exclusion
If another process requests the same resource, it must wait until the resource is released by the process that is now using it.
Hold and Wait
A process must be holding a resource while awaiting the acquisition of another resource held by another process.
No Preemption
The resource-holding process cannot be stopped or preempted. When the process holding the resource has completed its duty, it must relinquish the resource willingly.
Circular wait
In a cyclical form, the process must wait for resources. Assume there are three processes: P0, P1, and P2. P0 must wait for the resource owned by P1; P1 must wait for process P2 to acquire the resource held by P2, and P2 must wait for P0 to acquire the process.
Now, let us discuss Starvation in detail:






