Introduction
JavaScript supports dialog boxes. These dialog boxes or popups are used to interact with the user. They are also used to notify a user or to receive some user input before proceeding.
There are three types of dialog boxes:
- Alert Dialog Box
- Prompt Dialog Box
- Confirm Dialog Box
Read More About, Basics of Javascript
Let's explore them one by one with the help of examples.
Getting Started
Alert Ninjas! The ongoing emergence of new technologies in web development keeps the interest in this subject high. But, before you start on the big tasks, we recommend that you understand the fundamentals. With our JavaScript Course, you may jumpstart your web development career by mastering JS principles. It's now the cheapest it's ever been!
These dialog boxes' appearance is defined by the operating system or browser settings. They cannot be changed using CSS. Also, dialog boxes are modal windows, which means that when one is presented, code execution stops and only begins when the dialog box is dismissed.
We'll go through each of these dialog boxes in-depth in the following section.
Alert Dialog Box
An alert dialog box is typically used to provide users with a warning message. For example, if one input field requires text input but does not provide any, use an alert box to display a warning message.
Example:
|
<!DOCTYPE html> onclick="Warning();" /> |
When you will run this code,
Output:

On clicking this “Click” button, you will get a pop-up warning box like this:
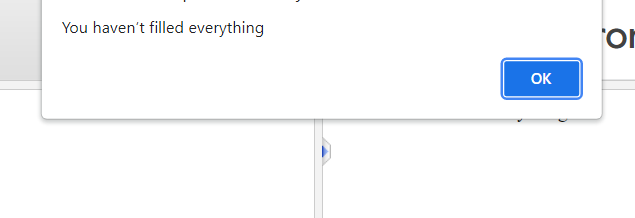
For good practice, you can try it on an online javascript editor.
Prompt Dialog Box
If you want the user to enter a value before proceeding to the next page, a prompt box is a solution.
The prompt() method is used to display this dialog box, and it accepts two parameters: (i) a label to display in the text box and (ii) a default string to display in the text box.
Example:
|
<!DOCTYPE html> |
When you will run this code,
Output:

On clicking this “Click” button, you will get a textbox like this:
There are two buttons in this dialogue box: OK and Cancel. The window method prompt() will return the entered value from the text box if the OK button is pressed or returns null if the user hits the Cancel button. The prompt() method always returns a string value.
Confirm Dialog Box
Confirm Dialog Box allows users to confirm or approve anything. To proceed, the user must click "OK" or "Cancel" when a confirmation window appears. It will return true if the user hits the OK button. If the user presses the Cancel button, confirm() returns false, and null is displayed.
Example:
|
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script> function Confirmation(){ var value = confirm("Do you want to continue? "); if( value == false ){ document.write (" Not Continued!"); return false; } else{ document.write ("Continued!"); return true; } } </script> </head> <body> <p>Click here for results: </p> <form> <input type="button" value="Click" onclick="Confirmation();" /> </form> </body> </html> |
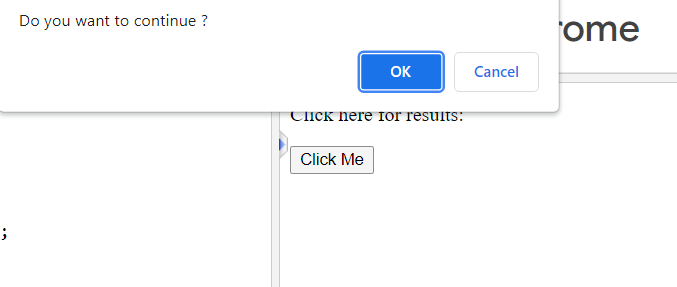
When you will run this code,
Output:

On clicking this “Click” button, you will get a confirmation box like this:
Tip: A newline character or line feed (\n) displays line breaks inside the dialog boxes.







