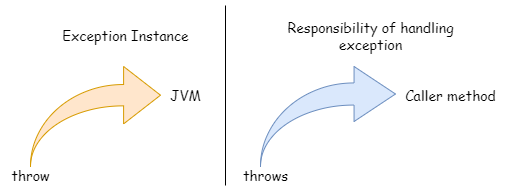
What is Throw Keyword in Java?
Throw in Java is used to explicitly throw an exception from a method or constructor. We can throw either checked or unchecked exceptions in java by throw keyword. The "throw" key-word is mainly used to throw a custom exception. The only object of the throwable class or its subclasses can be thrown. When a throw statement is encountered, program execution is halted, and the nearest catch statement is searched for a matching kind of exception.
Syntax of Throw in Java:
throw new ArithmeticException("Arithmetic Exception");
void myMethod() {
try {
//throwing arithmetic exception using throw
throw new ArithmeticException("Something went wrong!!");
} catch (Exception exp) {
System.out.println("Error: " + exp.getMessage());
}
}
Example of Throw in Java:
Java
public class Main {
public static void validateMarks(int marks) {
if (marks<80)
throw new ArithmeticException("Not Oracle certified");
else
System.out.println("Oracle certified ");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
validateMarks(86);
System.out.println("welcome ...");
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output:

Explanation:
In this example, we have created the validateMarks() method that takes an integer value as a parameter. If the marks is less than 80, we are throwing the ArithmeticException otherwise, print a message that you are Oracle certified.
What is Throws Keyword in Java?
Methods may throw exceptions during the execution of the program using the throws keyword. If a method is able to cause exceptions is called, it must list all the exceptions that might occur during execution. This is so that the caller knows how to handle the exceptions. To do this, a method should use the throws keyword.
Syntax of Throws in Java:
throws ArithmeticException;
//Declaring arithmetic exception using throws
void sample() throws ArithmeticException{
//Statements
}
Example of Throws in Java:
Java
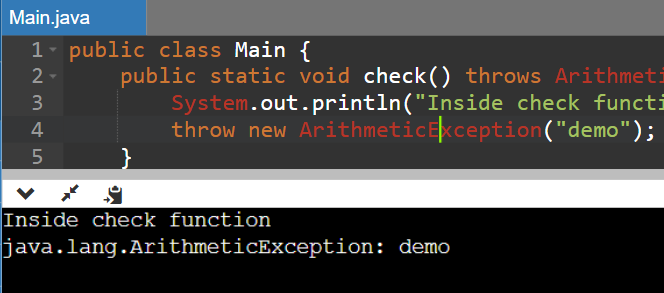
public class Main {
public static void check() throws ArithmeticException {
System.out.println("Inside check function");
throw new ArithmeticException("demo");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
check();
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}

You can also try this code with Online Java Compiler
Output:
Try it on online java compiler.
Explanation:
In this example, the programmer makes a prior announcement that the code may be risky, so throws exception with the method itself. The above codes will throw an exception if the file as mentioned above is not created first or gets deleted.
Throw Vs Throws in Java
- Purpose:
- throw is used to explicitly throw an exception from a method or block.
- throws is used to declare exceptions that a method might throw.
- Usage:
- throw is followed by an exception object.
- throws is followed by exception class names.
- Placement:
- throw is used within the method body.
- throws is used in the method signature.
- Number of Exceptions:
- throw can throw only one exception at a time.
- throws can declare multiple exceptions separated by commas.
- Syntax Example:
- throw new IOException("File not found");
- public void readFile() throws IOException, SQLException { ... }
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the keywords used in exception handling?
There are five keywords used in Java exception. catch, try, throw, throws and finally
What is the difference between throw throws and throwable?
In Java, throw is used to explicitly throw an exception. throws declares that a method can throw specified exceptions. Throwable is the superclass for all errors and exceptions, encompassing both Exception and Error classes.
What are the Benefits of Java Exception Handling?
- Separating Error-Handling code from regular business logic code
- Grouping and differentiating error types
- Propagating errors up the call stack
When to use throws in Java?
Use the throws keyword in Java to indicate that a method can potentially throw an exception. It's required when dealing with checked exceptions that the method does not handle internally, thereby making exception handling mandatory for the caller.
Why do we use throws and throws?
In Java, throw is used to explicitly throw an exception, while throws declares exceptions a method might throw. They help in exception handling, ensuring robust code by preventing runtime errors and enforcing proper error management in programs.
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the difference between Throw and Throws in Java. Understanding the distinction between throw and throws is crucial for effective Java exception handling. throw is used to manually trigger exceptions, while throws indicate potential exceptions a method might encounter.
Recommended Reading: