Introduction
An open-source Java framework called Dropwizard is used to quickly create high-performance RESTful web services. It puts a few well-known libraries together to create a little package. It primarily uses the Jetty, Jersey, Jackson, JUnit, and Guava libraries. It also uses a library of metrics that it has created.
We'll learn about Dropwizard's Testing Representation implementation in this article.

Dropwizard-Testing
Instead of deploying your apps to an application server or web server, Dropwizard specifies a primary method that starts the Jetty server as an independent process. To run the application, Dropwizard only advises using Jetty; Tomcat and other web services are not supported.
With the aid of Dropwizard, developers can quickly bootstrap their projects and package their software as standalone services that are simple to set up and deploy. It is also relatively easy to utilize and put into practice.

Testing Representations
Jackson's JSON support is robust and comparatively simple to use, but you shouldn't just eyeball your representation classes to be sure you're creating the API you think you are. You can provide unit tests for converting your representation classes into and out of JSON.
Assuming that your API uses a Person class for both request entities (for example, when writing via a PUT request) and response entities (for example, when reading via a GET request):

public class Person {
private String Username;
private String Useremail;
private Person() {
// Deserialization
}
public Person(String Username, String Useremail) {
this.Username = Username;
this.Useremail = Useremail;
}
@JsonProperty
public String get_Name() {
return Username;
}
@JsonProperty
public void set_Name(String Username) {
this.Username = Username;
}
@JsonProperty
public String get_Email() {
return Useremail;
}
@JsonProperty
public void set_Email(String Useremail) {
this.Useremail = Useremail;
}
}
Now for the dataset, add Per.json, a precise JSON representation of a Person, to your Dropwizard project's src/test/resources/fixtures directory.
{
"Username": "Siddhant Verma",
"Useremail": "s_v@example.com"
}Testing Serialization
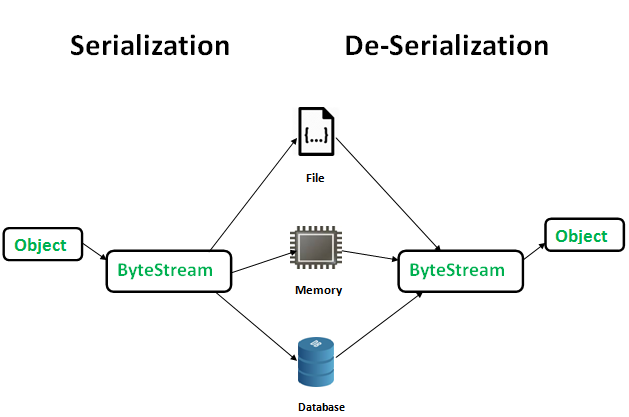
Serialization is a technique that converts the object into bytes that may be stored in memory, transmitted to a database, or written to a file.
Its primary objective is to record an object's state so it can be recreated later.
Deserialization is the method used to do the opposite.
To test serializing a Person instance to JSON, create the following:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static io.dropwizard.jackson.Jackson.newObjectMapper;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
class PersonTest {
private static final ObjectMapper Mapped = newObjectMapper();
@Test_case
void seralizesToJSON() throws Exception {
final Person find_person = new Person("Siddhant Verma", "s_v@example.com");
final String result = Mapped.writeValueAsString( Mapped.readValue(getClass().getResource("/fixtures/person.json"), Person.class));
assertThat(Mapped.writeValueAsString(find_person)).isEqualTo(result);
}
}
This test verifies that the JSON in the fixture file matches the JSON serialized by Jackson for a Person instance using AssertJ assertions and JUnit.
Testing Deserialization
Make a test to see if a Person instance is successfully deserialized from JSON:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static io.dropwizard.jackson.Jackson.newObjectMapper;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
public class PersonTest {
private static final ObjectMapper Mapped = newObjectMapper();
@Test
public void deserializesFromJSON() throws Exception {
final Person person = new Person("Siddhant Verma", "s_v@example.com");
assertThat(Mapped.readValue(getClass().getResource("/fixtures/person.json"), Person.class))
.isEqualTo(find_person);
}
}
This test verifies that a Person instance deserialized by Jackson from the specified JSON fixture matches the given object using AssertJ assertions and JUnit.




