Introduction
In the early days, when someone started a business, they needed to set up their whole computing system and plan for the maintenance of those systems. But this has become a thing of the past. Now, we have Cloud Computing. We pay for the computing power we use, and the service provider does the maintenance and other work. Cloud Computing has opened a whole new world of opportunities. The concept of cloud computing is not that difficult to understand, but we can not say the same for the economics of cloud computing. Many variables need to be considered. But don't worry; this article will make the economics of cloud computing a piece of cake. So, let's begin!!
Economics of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing Economics is the study of its costs and benefits and the economic principles behind them. It explores the key points of the business. Some of the topics that are considered are:
- What will be the return on investment of migrating to cloud computing?
- Benefits of switching to a different cloud provider
- Comparing the cost of cloud computing to the traditional setup of computing power
Economic planning for organizations
Cloud computing has become a viable option for organizations with technological advancements. Any organization looking to shift to cloud computing has to do some research to know the new system's effectiveness—some of the things that organizations lookout for are given below.
The total cost of ownership: The organization first estimates their expenditure if they deploy an in-campus system. Based on that, the cost estimation of the cloud computing setup is done.
Cost of the current data center: If an organization is moving from an existing data center to cloud computing, then it is necessary to include the maintenance costs, IT hardware costs, software licenses, supplies, spare parts, and everything else that the organization needs to pay to keep the operations up and running.
Cost of estimated cloud infrastructure: After assessing the current infrastructure, the organization compares it to the pricing of the cloud computing setup. The pricing of cloud computing varies widely depending on the service provider and many other factors.
Cost of cloud migration execution: The cost incurred to migrate the operations from the current infrastructure to cloud computing is considered. These include the consulting fees, software licensing costs, software testing, integration costs, etc.
Additional post-migration cost: There are certain costs associated with maintenance of the cloud computing infrastructure like skilled labor force, improving the cloud environment, administration, etc. These costs are also taken into consideration.
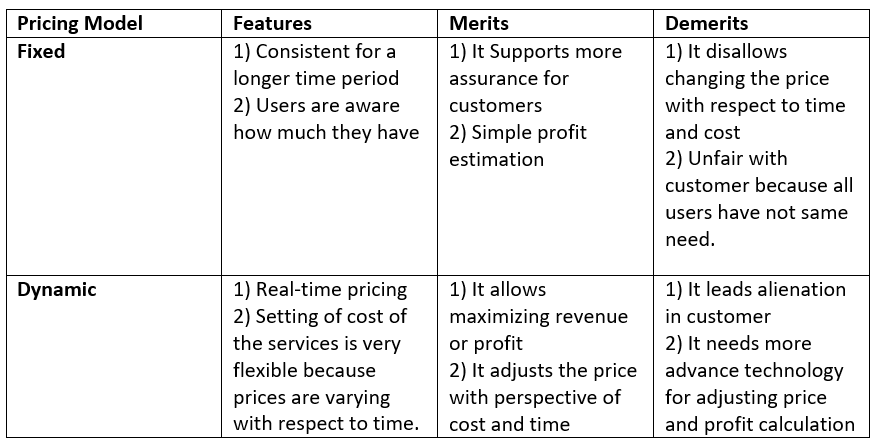
Pricing of cloud computing
The cloud computing service providers have many different pricing strategies for their services. Some of them are fixed pricing models, and some are dynamic. The advantages and disadvantages, along with some of their features, are discussed below.
Economic Characteristics of cloud
Cloud Computing is an economically feasible option for computing resources. The new start-ups don't have enough funding and resources in the initial stages to set up an in-campus computing infrastructure. Cloud computing has given a perfect and economical option for organizations like these. Some of the characteristics of cloud computing are discussed below.
Scalability: Cloud Computing offers a flexible option to expand operations as and when required. It allows access to unlimited computing resources without thinking about the economic aspects. The key to this feature requires good planning.
Low Entry Barrier: Users can access good computing resources based on their needs starting at a low price point. They don't need to invest a massive amount of money in beginning their basic operations.
Utility: Cloud Service providers provide pricing models to match the needs ad resources to the pricing. This allows the client to only pay for the resources that they need. This eliminates wastage of resources and, in turn, reduces the end-user cost of services and products.
Flexibility: The users can resize their resources based on their needs. They offer high economic flexibility.






