Introduction
The concept of Edge Computing is an extension of Cloud Computing. The Cloud Computing that is most popular nowadays requires the computation of data to be done at the side of resources. That is, let's say we have generated some data in a device that uses cloud computing. The data that is generated is to be transferred to the cloud server far away and get computed, and then revert back to the device as a result/output. But this seems time-consuming, right? Well, Yes, here enters the concept of edge computing. Edge Computing is the opposite of it. Let’s take a closer look at it.
Edge Computing
The computing process should have to take care of three properties, they are
- Bandwidth.
- Latency.
- Cost Saving and Traffic.
A computing concept should be evaluated by briefly looking at the aforementioned concepts.
Edge Computing is a distributed Computing mechanism, an extension of cloud computing, where the resources and compute will move at or near the data source. This can be graphically represented as follows.
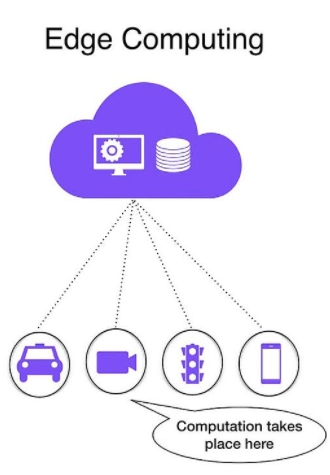
Over here, we can see that the compute, resources, and mini servers will move at the devices in which edge computing is placed, i.e., the device where the data is generated.
The major use-case of Edge Computing is “self-driving cars.
Self-driving cars:
Self Driving cars will generate a huge amount of data due to the presence of sensors. And it requires a huge amount of computational resources as it should be too dynamic in nature. Let’s say the computation as whether a self-driving car should apply a brake when a person is standing on the road. This generates a huge amount of data. But if we use cloud computing here, then the data is to be transferred to the cloud servers, which are far away from the device, and get back the results after computation. This may result in high latency.
What if we use Edge Computing here. This Edge computing makes resources available at the self-driving car itself to decrease the latency tremendously.
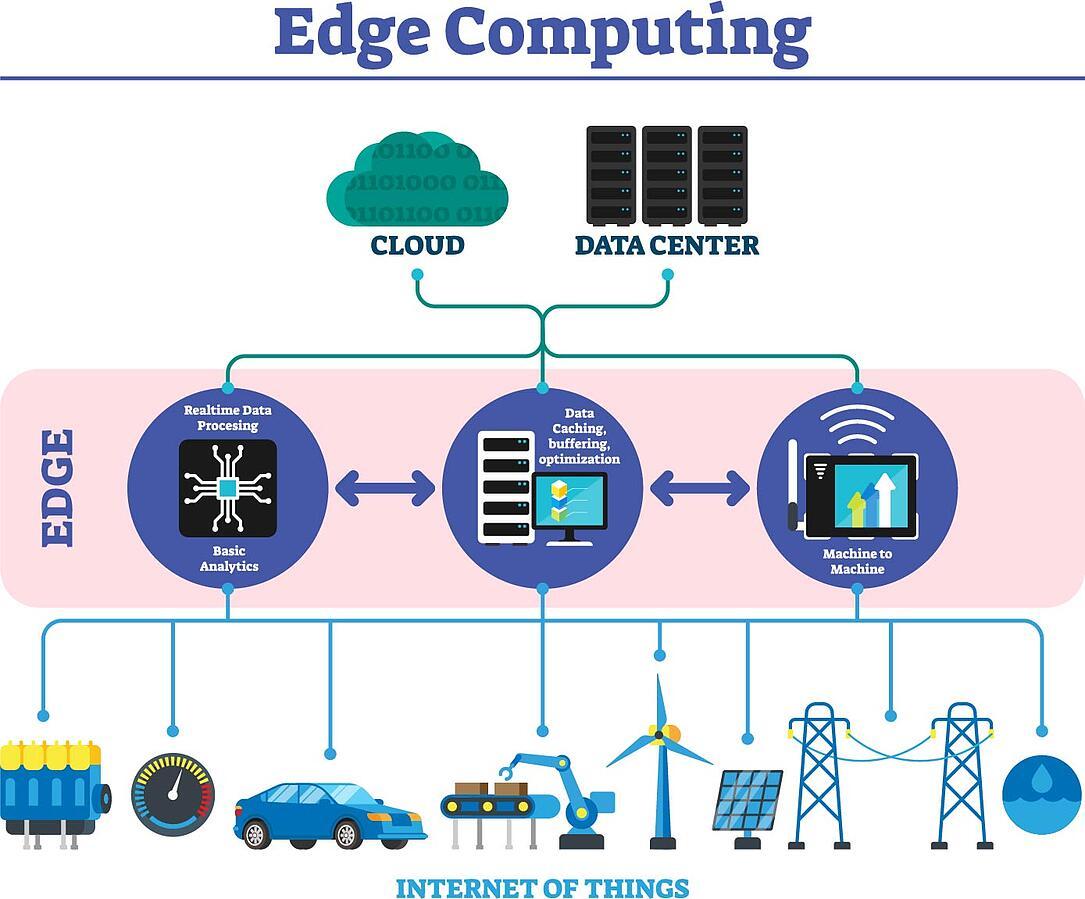
From the architecture diagram, we can say that there are mainly three layers in edge computing. They are,
- The Cloud Edge.
- The local Edge.
- The device Edge.
The Cloud Edge includes all the cloud information, storage resources, data processing resources, etc. Whereas in local edge, the presence of edge servers, etc., can be seen. And the last layer, i.e., the device Edge, will contain the devices, their generated data, the connection lines, etc.
Here basically, edge computing will distribute the computing resources or data processing workload to a localized or integrated computer or device to compute the data at the data generated device itself.
Let's take a brief look at the very important part of edge computing, i.e., Edge server.
The edge server is an important part of edge computing. An edge server is nothing but a device or computer that is located near the edge computing installed device. Edge server will act as an intermediary between the cloud and devices. The best example for edge servers is rugged servers. The main intention of Edge computing is “If you cannot get the data closer to the data center, get the data center closer to the data.”.
So let’s answer the question, “Will Edge Computing replaces cloud computing?”.
Well, as we said earlier, edge computing is just a compliment or an extension of cloud computing as this edge computing may not suit all the IoT devices well due to architecture and implementation problems.
Thus we can easily say that edge computing will not replace cloud computing.




