Introduction
Interceptor is an object that is called at the time of preprocessing and postprocessing a request.
We used Interceptor to perform different operations like validation, exception handling, etc.
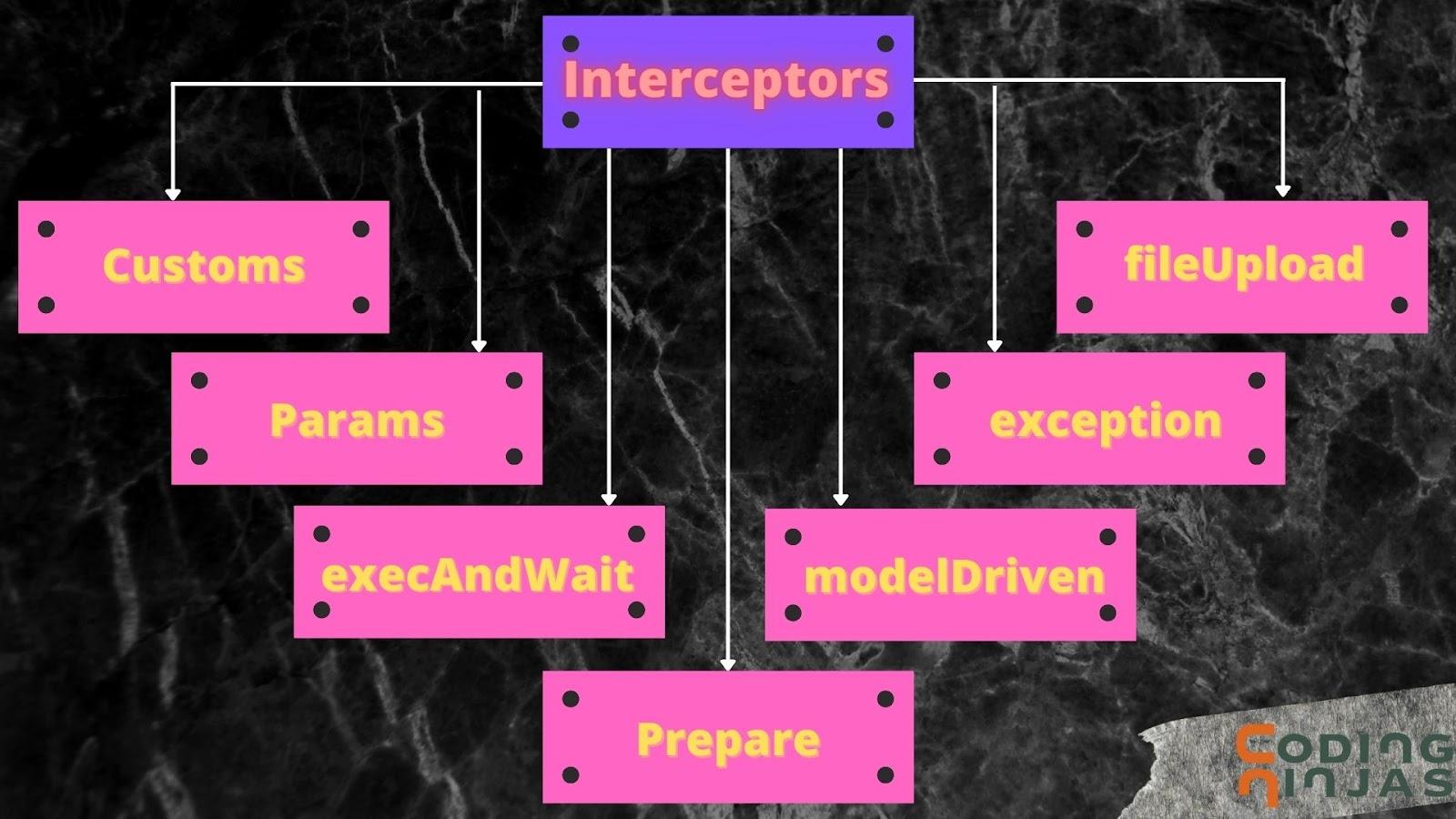
You can refer to this blog to know more about Struts2 and Interceptors.
We have already discussed the fileUpload Interceptor and params Interceptor. You can also check out that.
In this blog, we will discuss the exception interceptor.
Exception Interceptor
Exception handling allows us to map an exception to a result code so that the result code will not throw an unexpected exception.
Since exceptions in our application may occur at any point, therefore struts2 provides a mechanism of global exception handling to overcome the problem where we can display a global result to the user. It will redirect to an error page when an exception has occurred.
Internal Working of an Exception Interceptor

If the exception occurs, it is wrapped in ExceptionHolder and pushed in the valuestack so that we can easily access the exception object from the result.
Parameters of Exception Interceptor
Following are the parameters of Exception Interceptor
- logEnabled - It specifies whether the log is specified or not. It takes boolean values. Therefore, it can be either true or false.
- logLevel - It specifies the log level (trace, debug, info, warn, error, fatal), and the default log level is debug.
- logCategory - It specifies the log category. (eg. com.mycompany.app)
Example
In this example, we define the global-result and global-exception-mappings in the struts.xml file, which specifies the global-result and exception mapping for all the actions of this package, respectively.
We are using the exception, the parent of many exception classes such as IOException, ArithmeticException, etc., which means that if any exception occurs, a specified result will be invoked.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts
Configuration 2.1//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.1.dtd">
<struts>
<package name="aa" extends="struts-default">
<global-results>
<result name="myresult">globalresult.jsp</result>
</global-results>
<global-exception-mappings>
<exception-mapping result="myresult" exception="java.lang.Exception"></exception-mapping>
</global-exception-mappings>
<action name="login" class="com.Login">
<result>welcome.jsp</result>
<result name="error">error.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
Let's see how we can display the exception.
Displaying Exception
We can display the exception on the browser either by printing the exception or by exceptionStack. The exception object only publishes the name of the exception, whereas exceptionStack prints the details of the exception.
Now, let's talk about some frequently asked questions related to them.






