Introduction
This article will discuss the problem of finding the length of a Doubly Linked List. Let's discuss in brief what is the doubly linked list.
Doubly Linked List
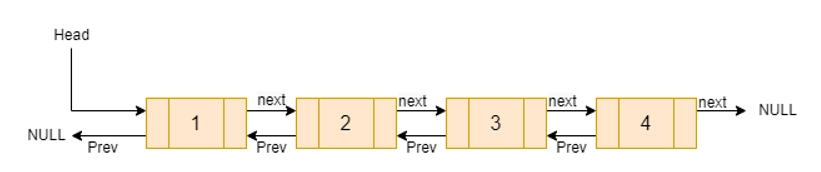
In comparison to Single Linked List, Doubly Linked List is a version of Linked List in which navigation is available in forward and backward directions. The following are some key terms to know to grasp the notion of a doubly linked list.
- A linked list's links can store a piece of data known as an element.
- Each link in a linked list has a Next link that points to the next link.
- Each link in a linked list has a Prev link that points to the previous link.
- A Linked List comprises the connecting links to the first and last links, referred to as First and Last.
Problem Statement
The Problem states that we need to calculate the length of the doubly linked list.
Sample Examples
Input:

Output:
4
Explanation:
The length of the given linked list is 4. Recommended Topic, Floyds Algorithm and Rabin Karp Algorithm
Solution Approach
The idea is very simple, we just keep on moving to the next node, and we will initialize a count variable to keep the number of nodes.
Steps of Algorithm
- Initialize the variable count = 0.
- Keep on moving to the next node until all the linked list nodes are exhausted.
- As we move to the next node, keep on increasing the count.
- Finally, the count variable contains the size, i.e., the number of nodes in the linked list.
Implementation in C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int val;
node *next, *prev;
node(int val)
{
this->val = val;
this->next = NULL;
this->prev = NULL;
}
};
// inserting the node into the doubly linked list
void insert(int val, node *&head)
{
node *newNode = new node(val);
newNode->next = head;
if (head != NULL)
head->prev = newNode;
head = newNode;
}
// function to get the length of the doubly linked list
int length(node *head)
{
// initialising the count variable = 0
int count = 0;
while (head)
{
head = head->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
int main()
{
// initialising the head as NULL
node *head = NULL;
// inserting the values into the linked list
insert(1, head);
insert(2, head);
insert(3, head);
insert(4, head);
cout << length(head) << endl;
}
Output:
4Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N)
We are traversing the doubly linked list only once, to calculate the number of nodes in the linked list.
Space Complexity: O(1)
We are not using any temporary array, so therefore space complexity is O(1).
Also read - Merge sort in linked list




