Creating a Github Account
The simplest way to get started with GitHub is to sign up for a free account on Github.
Choose a username (for example, Spider123), enter your email address and password, and click ‘Sign up’ for GitHub. Once you've logged in, it will look like this:
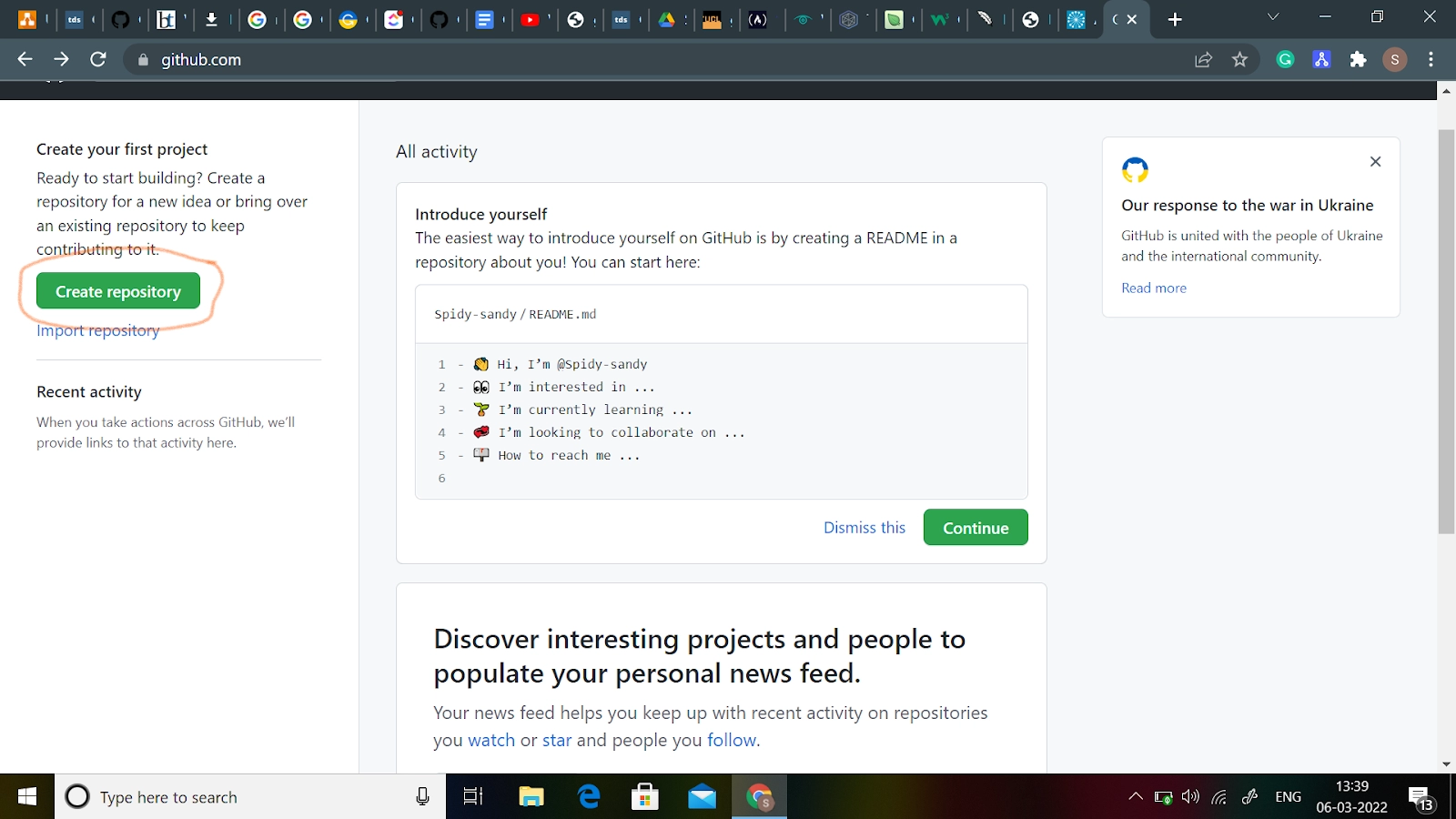
Creating a new repository
A repository is a location or container where something is kept; in this case, we're making a Git repository to save code. To create a new repository, choose New Repository from the + sign dropdown menu as shown in the upper-right corner of the image given above.
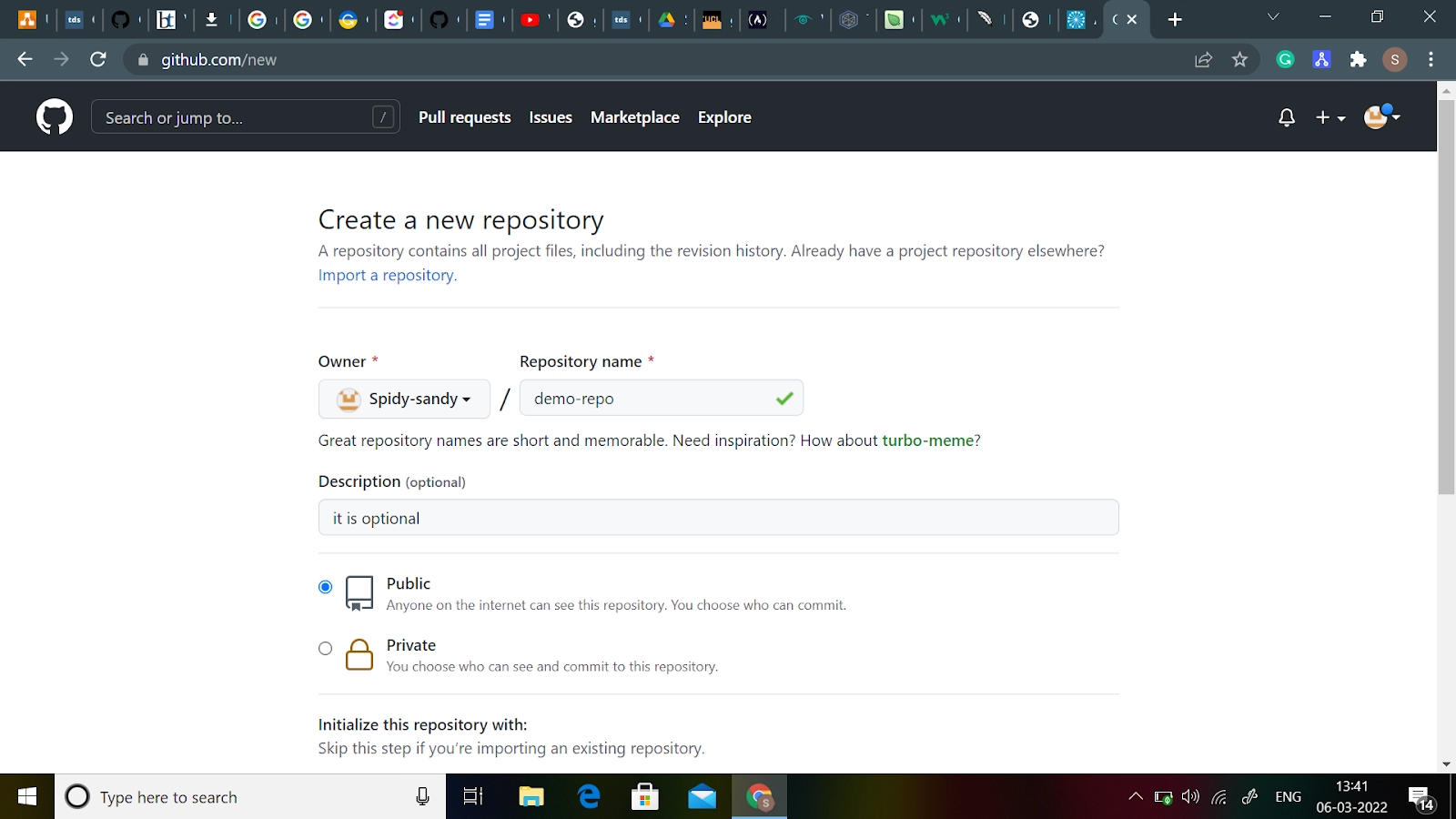
Give your repository a name (for example, "demo-repo"). Initialize your repository with a README file, if you want to include it. (I would highly recommend doing this! It’s the very first thing people are going to look at when they are checking out your repository. It is also a great place to add information that you need in order to understand or run the project.)
Now, click on Create Repository. Don't be concerned about changing any of the other options on this page.
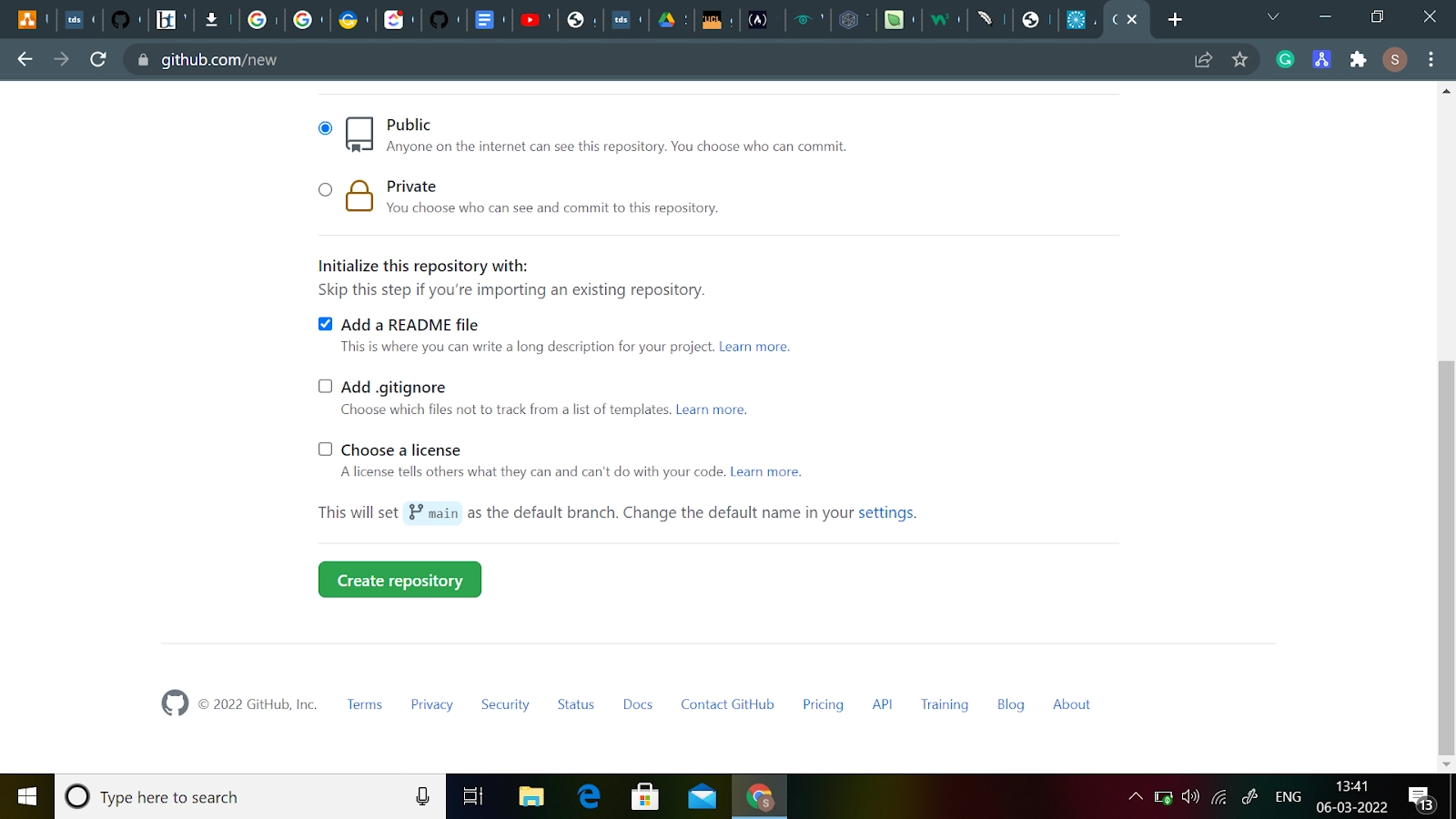
Congratulations! You've created your first GitHub repository.
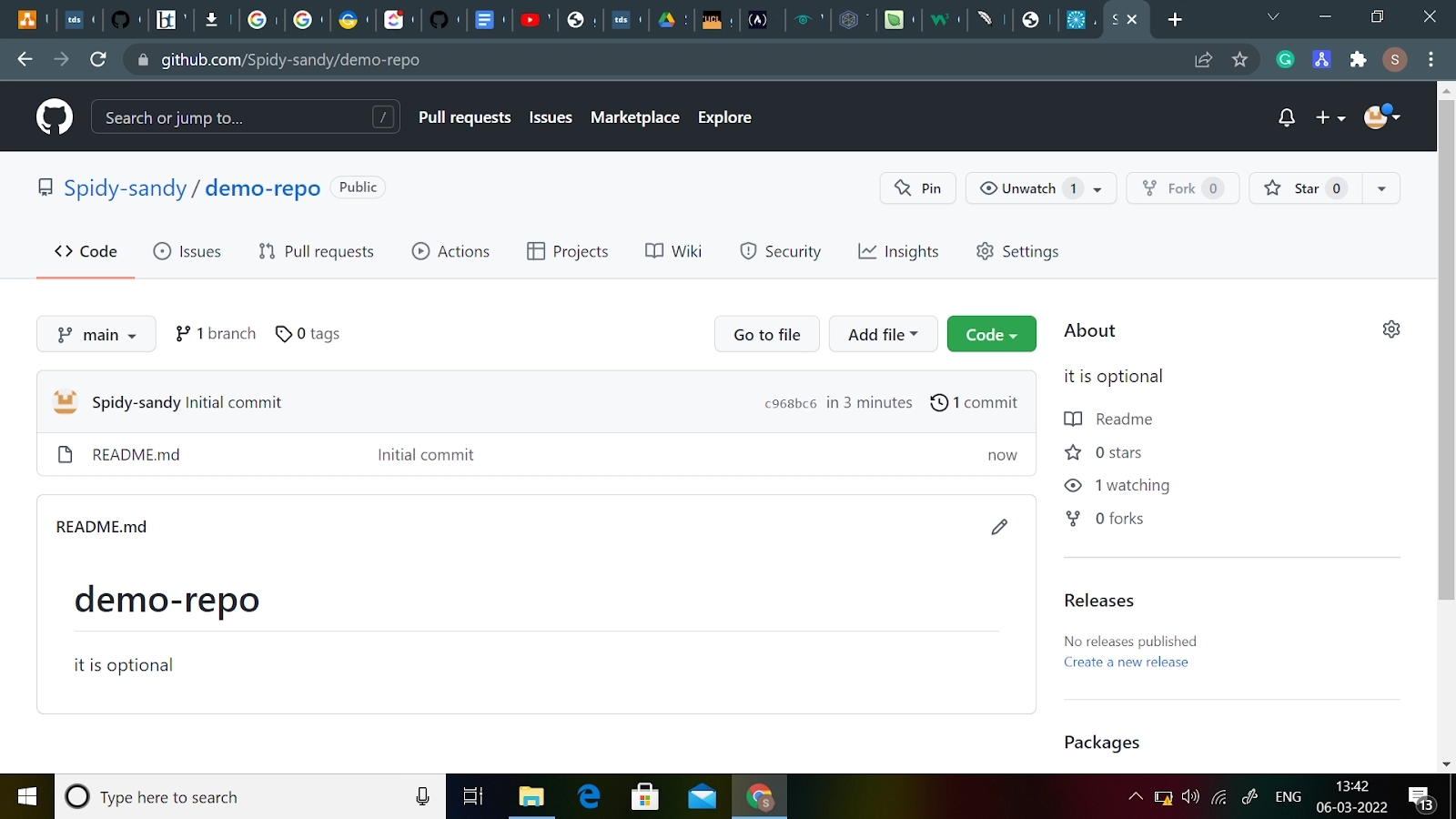
Cloning a Repository
If a project has already been set up in a central repository, the most common way for users to obtain a development copy is with the git clone command. Cloning, like git init, is typically a one-time operation.
Once they have received a working copy, all version control operations and collaborations are managed through a developer's local repository. It is primarily used to point to an existing repo (repository) and create a clone or copy of that repo in a new directory in a different location.
The original repository can be on the local file system or a remote machine that supports the supported protocols. The git clone command duplicates an already existing Git repository.
Cloning a repository means taking a repository from the server and cloning it to your computer, similar to downloading it. You must obtain the "HTTPS" address from the repository page.
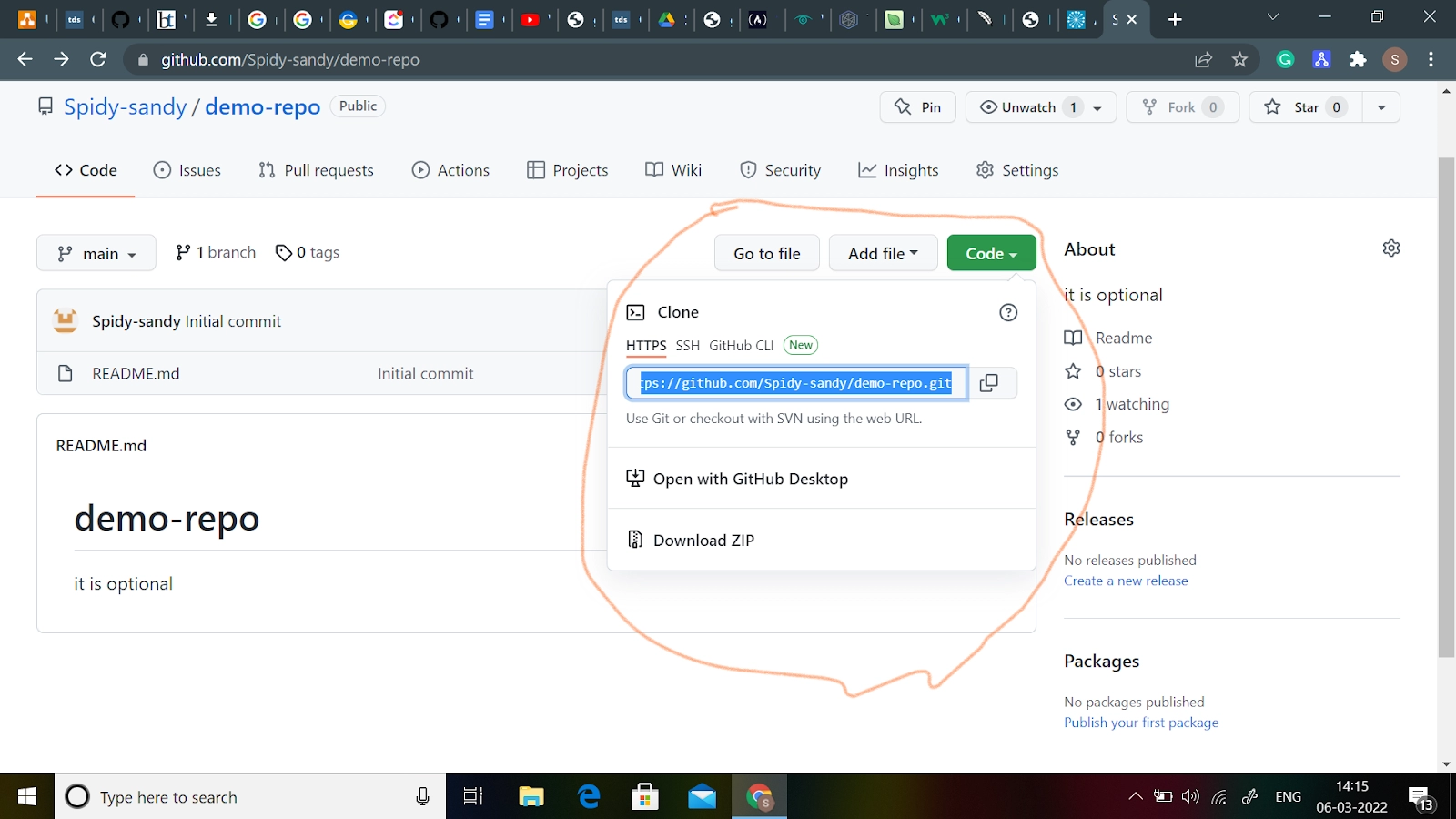
Copy the address and paste it into your terminal, then run the following command:
git clone "you just copied an HTTP-address"
Now your repository is on your system. You can enter it using the following command:
cd "path/to/cloned-repositry/repository-name"
Check out most important Git Interview Questions here.
FAQs
-
Is there a difference between Git and GitHub?
Yes, the primary distinction between Git and GitHub is that Git is a locally installed open-source tool for managing source code. GitHub is an online service to which Git users can connect and upload or download resources.
-
Is GitHub a free service?
With GitHub Free for user accounts, you can collaborate with an unlimited number of people on many public repositories with a full feature set and an unlimited number of private repositories with a limited feature set. Your GitHub Free user account includes features like GitHub Community Help.
-
Is GitHub secure?
GitHub is fairly safe and secure in and of itself, and you can entrust it with the repositories you host on it. If you have a private repository on GitHub, You wouldn't be concerned about GitHub being hacked and your data being leaked as a result.
Key Takeaways
In this article, we have discussed Git and GitHub, the difference between Git and GitHub, and we created and cloned a repository.
We hope that this blog has helped you enhance your knowledge regarding Git and GitHub and if you would like to learn more, check out the link. Do upvote our blog to help other ninjas grow.
Happy Coding!











