Introduction
When we want to run a program on the terminal, we have to type a command in this window that takes the text. We can also put some more text after this command. Every word or thing that is separated by spaces after the command is called a command argument.
Command arguments are a way to supply additional information to a program when it is started. We generally use the command argument when we need to execute a program with some arguments. The Go program can receive every argument that is passed from the console, and it can be used as an input.
How to get Command Arguments in Go
There are two ways to get arguments from the command line in the Go programming language.
Flag Package
The first way to get Command Arguments is via flag package.
In Go language, we have a package named as flag to parse command arguments. Once we have declared our flags, we call flag.Parse() to execute the command-line parsing.
Example
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
)
func main(){
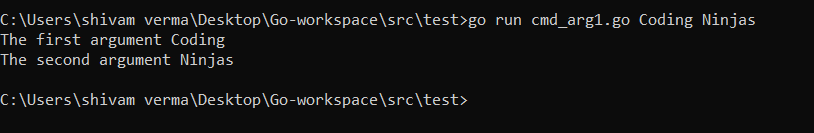
flag.Parse() // to get the command arguments
arg1 := flag.Arg(0) // returns first argument
arg2 := flag.Arg(1) // returns second argument
fmt.Println("The first argument " + arg1)
fmt.Println("The second argument " + arg2)
}Output:
OS Package
The second way to get Command Arguments is via the os package.
In Go language, we have a package named as os package containing an array called "Args". Args is an array of strings containing all the go command arguments passed.
The os.Args returns an array of command-line parameters. The first parameter of os.Args is the path of the program.
Example 1
package main
import (
"os"
"fmt"
)
func main(){
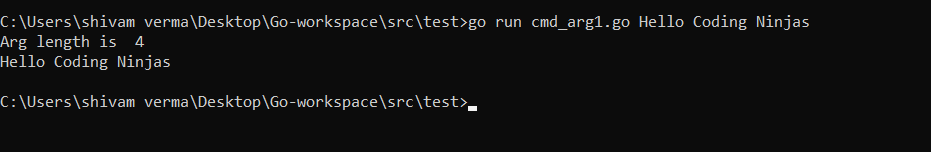
argLength:=len(os.Args)
fmt.Println("Arg length is ",argLength)
var str, arg string
for i:=1;i<argLength;i++{
str+=arg+os.Args[i]+" "
}
fmt.Println(str)
}Output:
Example 2
package main
import (
"os"
"fmt"
)
func main(){
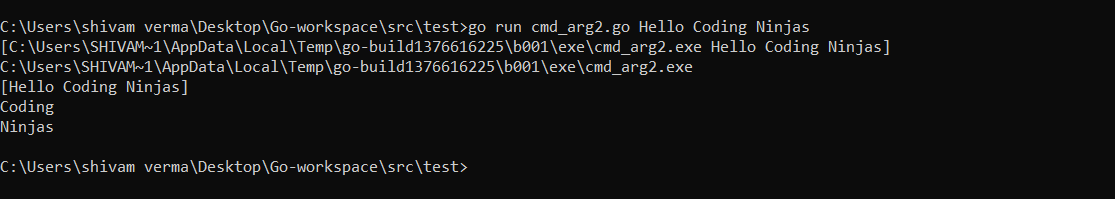
argWithpath:=os.Args //returns all arguments including path
programName:=os.Args[0]
argwithoutpath:=os.Args[1:] //returns all arguments after path
arg2:=os.Args[2] //returns second argument only
arg3:=os.Args[3] //returns third argument only
fmt.Println(argWithpath)
fmt.Println(programName)
fmt.Println(argwithoutpath)
fmt.Println(arg2)
fmt.Println(arg3)
}Output: