Introduction
Let’s discuss the Head and Layout of our HTML document, various elements that are a part of it, how to add images and links in our HTML file, and how to modify them by changing values of different associated attributes.
Using head and defining the proper layout of our web page helps in beautifying our website, hence enhancing the UI of our website. Let’s learn about them one by one.
Head Element in HTML
Head element is the container that stores the metadata (i.e. data about data) of our HTML document and it is placed between <html> and <body> tag.
It contains <title>, <style>, <meta>, <link>, <script> and <base> elements.
Let's learn about these elements one by one:
Various Elements in Head Tag
-
Title Element
It defines the title of our HTML document. It must be text-only and is shown in the browser’s title bar or the page’s tab.
The title element is a must to be mentioned in Head Tag.
It is also crucial for search engine optimization (SEO) as the search engine algorithms use the page title to decide the order when listing pages in search results. Moreover, it also provides a title for the page when it is added to favorites.
|
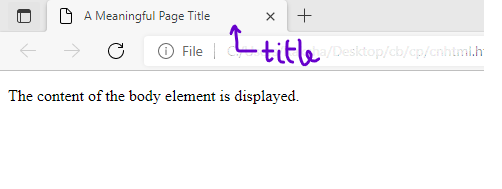
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>A Meaningful Page Title</title> </head> <body>
<p>The content of the body element is displayed.</p>
</body> </html> |
Output:
|
-
Style Element
It helps define the styling information for our HTML document.
So, we could add various CSS properties to different tags and elements of our HTML document.
Adding CSS via style element is known as using internal CSS for our document.
|
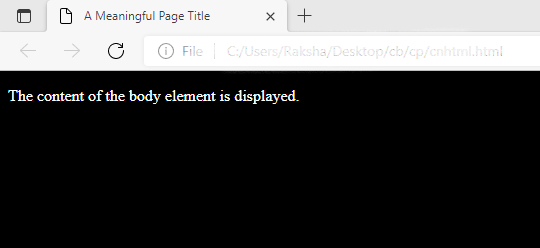
<<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>A Meaningful Page Title</title> <style> body { background-color: black; } p { color: white; } </style> </head> <body>
<p>The content of the body element is displayed.</p>
</body> </html> |
Output:
|
-
Link Element
It helps define the relationship between the current document and an external resource. It is often used to link external style sheets (or CSS files), allowing us to modularize and beautify our code.
So, we could add all the CSS properties to be used in a CSS document and then finally link it to our HTML document.

-
Script Element
It helps us link our HTML document with client-side JavaScript files.

-
Base Element
It specifies the base URL and the target for all relative URLs on a page.
It must have either an href/ target attribute and also, there could be only a single <base> element in an HTML document.
| <base href="https://www.codingninjas.com/" target="_blank"> |
Here, on clicking any relative path image/link, it redirects us to the links/images on the https://www.codingninjas.com/ page and displays it.
However, we can specify where to open the linked page via the target attribute.
It can have the following values:
-
_self: This is the default property, i.e., opens the linked page in the same tab/window where it was clicked.
-
_blank: It opens the linked page in a new window/tab.
-
_parent: It opens the linked page in the parent frame.|
- _top: It opens the linked page in the full body of the window.
Output:
|
Note: Coding Ninjas Website opens in a new tab.
-
Meta Element
It specifies the character set, page description, keywords, document's author, viewport settings, etc.
The metadata is not displayed on the web page but is used by browsers, search engines, and other web services.
Examples:
Define the character set used.
| <meta charset="UTF-8"> |
Define keywords for search engines
| <meta name="keywords" content="Head and Layout in HTML "> |
Define the author of a page
| <meta name="author" content="Head and Layout in HTML"> |