Introduction
With few implementation requirements, Java is a high-level, class-based, object-oriented programming language. Because it is a general-purpose programming language, compiled Java code can run on any platform that supports Java without the need for recompilation. This is known as writing once and running anywhere (WORA).
Regardless of computer architecture, Java applications are often compiled to bytecode that is able to run on any Java virtual machine (JVM). Although Java's syntax is comparable to those of C and C++, neither language offers as many low-level features as Java.
This article will highlight and compare all of the available options.
Let's take a look at the most common methods for converting Float values to String and then we will discuss conversion of String to Float in java.
Also see about Iteration Statements in Java and Duck Number in Java.
String to Float
Let's look at the most typical methods for converting String to Float in java.
✨Float.parseFloat()
One of the most common approaches for converting string to float in java is to use the static method of Float: parseFloat (). The String argument is used to represent a primitive float value, which will be returned. Leading and trailing whitespaces are also ignored:
public class Main {
public static float convertingStringToFloat(String str)
{
return Float.parseFloat(str);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// The string value
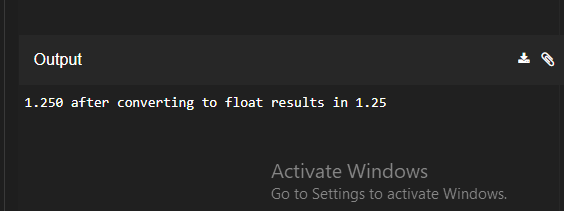
String mystringValue = "1.250";
float floatVal;
// Convert string to float
floatVal = convertingStringToFloat(mystringValue);
System.out.println(
mystringValue
+ " after converting to float results in "
+ floatVal);
}
}
💥If the String argument is null, we get a NullPointerException:
String givenStringvar = null;
assertThrows(NullPointerException.class, () -> Float.parseFloat(givenStringvar));💥If the String argument does not contain a parsable float, a NumberFormatException is thrown.
String givenStringvar = "3.23x";
assertThrows(NumberFormatException.class, () -> Float.parseFloat(givenStringvar));✨DecimalFormat
We can also use DecimalFormat to convert String to Float in java . One of the primary benefits is the ability to specify custom decimal point separators.
String givenStringvar = "3,250";
DecimalFormatSymbols mysymbols = new DecimalFormatSymbols();
mysymbols.setDecimalSeparator(',');
DecimalFormat mydecimalFormat = new DecimalFormat("#.000");
mydecimalFormat.setDecimalFormatSymbols(mysymbols);
Float res = decimalFormat.parse(givenStringvar).floatValue();
assertEquals(3.25f, res);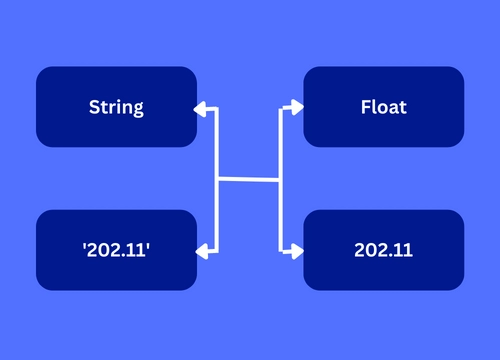
✨Float‘s Constructor
Finally, we can perform the string to float in java conversion directly using Float's function Object(). Internally, it will create the Float object by calling the static parseFloat() method of Float:
String givenStringvar = "3.25";
Float res = new Float(givenStringvar);
assertEquals(3.25f, res);This function Object() is no longer supported as of Java 9. Instead, we should think about using other static factory methods like parseFloat() or function valueOf(). Try this code by yourself on Online Java Compiler.
Must Read Conditional Statements in Java, Why is Java Platform Independent
See more, Solid Principles in java